An Empirical Bayes Approach to Topic Modeling
Auto-TLDR; An Empirical Bayes Based Framework for Topic Modeling in Documents
Similar papers
Deep Topic Modeling by Multilayer Bootstrap Network and Lasso
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Deep Topic Modeling with Multilayer Bootstrap Network and Lasso
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Assortative-Constrained Stochastic Block Models
Daniel Gribel, Thibaut Vidal, Michel Gendreau

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Stochastic Block Models for Assortative Communities in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Episode Boundary Detection with Joint Episode-Topic Model
Shunyao Wang, Ye Tian, Ruidong Wang, Yang Du, Han Yan, Ruilin Yang, Jian Ma
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Video Episode Boundary Detection for Bullet Screen Comment Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Dependent Gaussian Experts in Local Approximation

Auto-TLDR; A novel approach for aggregating the Gaussian experts by detecting strong violations of conditional independence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cluster-Size Constrained Network Partitioning
Maksim Mironov, Konstantin Avrachenkov
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Graph Clustering with Stochastic Block Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Learning Random Forests for Random Forest Clustering
Manuele Bicego, Francisco Escolano

Auto-TLDR; Learning Random Forests for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probabilistic Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering with Bayesian Inference
Jiansheng Fang, Xiaoqing Zhang, Yan Hu, Yanwu Xu, Ming Yang, Jiang Liu

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering
Uniform and Non-Uniform Sampling Methods for Sub-Linear Time K-Means Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Sub-linear Time Clustering with Constant Approximation Ratio for K-Means Problem
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sketch-Based Community Detection Via Representative Node Sampling
Mahlagha Sedghi, Andre Beckus, George Atia
Auto-TLDR; Sketch-based Clustering of Community Detection Using a Small Sketch
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Epitomic Variational Graph Autoencoder
Rayyan Ahmad Khan, Muhammad Umer Anwaar, Martin Kleinsteuber
Auto-TLDR; EVGAE: A Generative Variational Autoencoder for Graph Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatically Mining Relevant Variable Interactions Via Sparse Bayesian Learning
Ryoichiro Yafune, Daisuke Sakuma, Yasuo Tabei, Noritaka Saito, Hiroto Saigo

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Bayes for Interpretable Non-linear Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General Model for Learning Node and Graph Representations Jointly
Auto-TLDR; Joint Community Detection/Dynamic Routing for Graph Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmenting Messy Text: Detecting Boundaries in Text Derived from Historical Newspaper Images

Auto-TLDR; Text Segmentation of Marriage Announcements Using Deep Learning-based Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Pattern Detection in Time-Varying Graphical Models
Federico Tomasi, Veronica Tozzo, Annalisa Barla

Auto-TLDR; A dynamical network inference model that leverages on kernels to consider general temporal patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Switching Dynamical Systems with Deep Neural Networks
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev, Ramses J. Sanchez

Auto-TLDR; Variational RNN for Switching Dynamics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Aware Unsupervised Learning with Joint Variational Attention and Automatic Clustering
Wang Ru, Lin Li, Peipei Wang, Liu Peiyu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Variational Attention Encoder-Decoder for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Label Incorporated Graph Neural Networks for Text Classification
Yuan Xin, Linli Xu, Junliang Guo, Jiquan Li, Xin Sheng, Yuanyuan Zhou
Auto-TLDR; Graph Neural Networks for Semi-supervised Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Deep-Neural-Network Mixture Modeling with Semi-Supervised MinMax+EM Learning
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Deep Neural Networks for Generative Mixture Modeling and Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Active Sampling for Pairwise Comparisons via Approximate Message Passing and Information Gain Maximization
Aliaksei Mikhailiuk, Clifford Wilmot, Maria Perez-Ortiz, Dingcheng Yue, Rafal Mantiuk

Auto-TLDR; ASAP: An Active Sampling Algorithm for Pairwise Comparison Data
Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu, Shichong Yang, Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Zero-Shot Text Classification with Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network
Tengfei Liu, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network for Zero-shot Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JECL: Joint Embedding and Cluster Learning for Image-Text Pairs
Sean Yang, Kuan-Hao Huang, Bill Howe
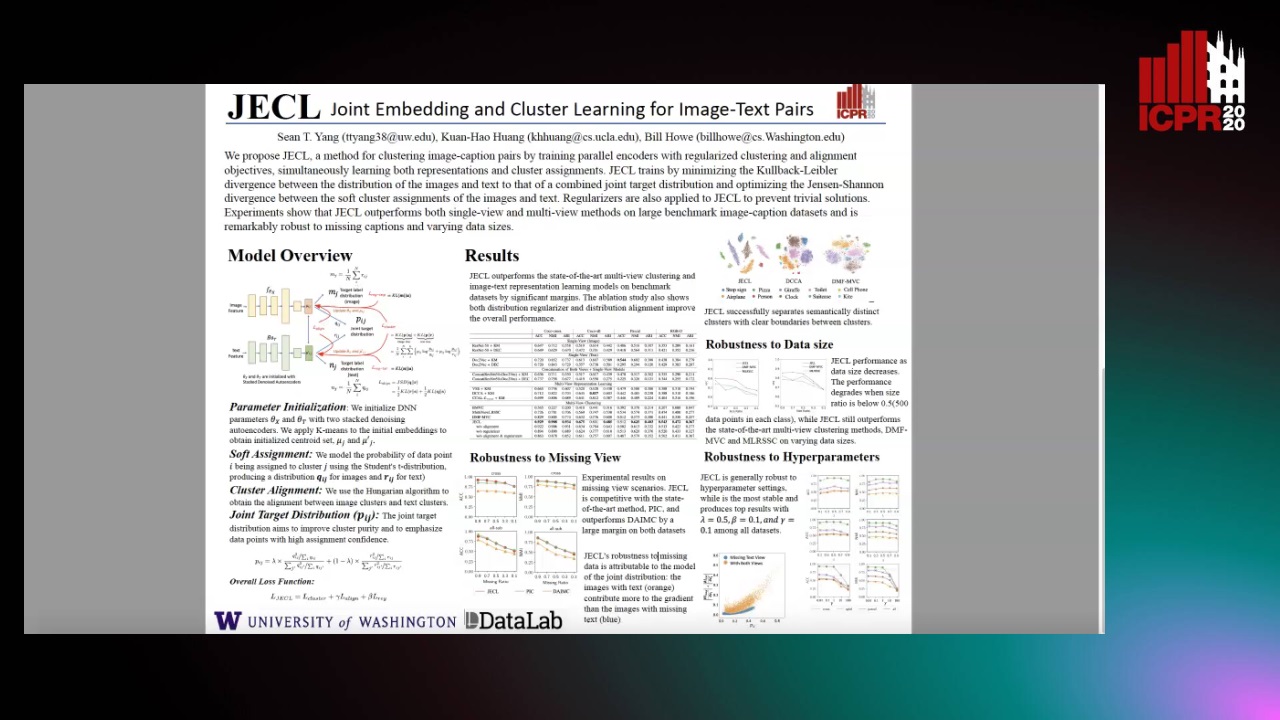
Auto-TLDR; JECL: Clustering Image-Caption Pairs with Parallel Encoders and Regularized Clusters
Scalable Direction-Search-Based Approach to Subspace Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Fast Direction-Search-Based Subspace Clustering
Textual-Content Based Classification of Bundles of Untranscribed of Manuscript Images
José Ramón Prieto Fontcuberta, Enrique Vidal, Vicente Bosch, Carlos Alonso, Carmen Orcero, Lourdes Márquez

Auto-TLDR; Probabilistic Indexing for Text-based Classification of Manuscripts
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Characterisation of Unweighted and Weighted Networks
Jianjia Wang, Hui Wu, Edwin Hancock
Auto-TLDR; Thermodynamic Characterisation of Networks as Particles of the Thermal System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Watermelon: A Novel Feature Selection Method Based on Bayes Error Rate Estimation and a New Interpretation of Feature Relevance and Redundancy
Auto-TLDR; Feature Selection Using Bayes Error Rate Estimation for Dynamic Feature Selection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Neural Textual Representations for Citation Recommendation
Thanh Binh Kieu, Inigo Jauregi Unanue, Son Bao Pham, Xuan-Hieu Phan, M. Piccardi

Auto-TLDR; Sentence-BERT cascaded with Siamese and triplet networks for citation recommendation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VOWEL: A Local Online Learning Rule for Recurrent Networks of Probabilistic Spiking Winner-Take-All Circuits
Hyeryung Jang, Nicolas Skatchkovsky, Osvaldo Simeone

Auto-TLDR; VOWEL: A Variational Online Local Training Rule for Winner-Take-All Spiking Neural Networks
Equation Attention Relationship Network (EARN) : A Geometric Deep Metric Framework for Learning Similar Math Expression Embedding
Saleem Ahmed, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; Representational Learning for Similarity Based Retrieval of Mathematical Expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Spectral Feature Learning for Mixed Data of Categorical and Numerical Type
Saswata Sahoo, Souradip Chakraborty

Auto-TLDR; Feature Learning in Mixed Type of Variable by an undirected graph
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hcore-Init: Neural Network Initialization Based on Graph Degeneracy
Stratis Limnios, George Dasoulas, Dimitrios Thilikos, Michalis Vazirgiannis
Auto-TLDR; K-hypercore: Graph Mining for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts
Wenbo Zhao, Yang Gao, Shahan Ali Memon, Bhiksha Raj, Rita Singh

Auto-TLDR; A Binary Tree-structured Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts for Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Global Self-attention Mechanism for Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Global Self-Attention Mechanism for Graph Convolutional Networks
3CS Algorithm for Efficient Gaussian Process Model Retrieval
Fabian Berns, Kjeld Schmidt, Ingolf Bracht, Christian Beecks

Auto-TLDR; Efficient retrieval of Gaussian Process Models for large-scale data using divide-&-conquer-based approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sign-Constrained Support Vector Machines
Kenya Tajima, Kouhei Tsuchida, Esmeraldo Ronnie Rey Zara, Naoya Ohta, Tsuyoshi Kato
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Sign Constraints for Learning Linear Support Vector Machine
An Invariance-Guided Stability Criterion for Time Series Clustering Validation
Florent Forest, Alex Mourer, Mustapha Lebbah, Hanane Azzag, Jérôme Lacaille

Auto-TLDR; An invariance-guided method for clustering model selection in time series data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bayesian Active Learning for Maximal Information Gain on Model Parameters
Kasra Arnavaz, Aasa Feragen, Oswin Krause, Marco Loog

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian assumptions for Bayesian classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpolation in Auto Encoders with Bridge Processes
Carl Ringqvist, Henrik Hult, Judith Butepage, Hedvig Kjellstrom
Auto-TLDR; Stochastic interpolations from auto encoders trained on flattened sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Region and Relations Based Multi Attention Network for Graph Classification
Manasvi Aggarwal, M. Narasimha Murty
Auto-TLDR; R2POOL: A Graph Pooling Layer for Non-euclidean Structures
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Segmentation with Pairwise Matches and Unknown Number of Motions
Federica Arrigoni, Tomas Pajdla, Luca Magri

Auto-TLDR; Motion Segmentation using Multi-Modelfitting andpermutation synchronization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generation of Hypergraphs from the N-Best Parsing of 2D-Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Noya Ernesto, Joan Andreu Sánchez, Jose Miguel Benedi

Auto-TLDR; Hypergraphs: A Compact Representation of the N-best parse trees from 2D-PCFGs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Multi-View Based Multi-Objective Clustering Algorithm

Auto-TLDR; MTMV-MO: Multi-task multi-view multi-objective optimization for multi-task clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Double Manifolds Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization for Data Representation
Jipeng Guo, Shuai Yin, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu

Auto-TLDR; Double Manifolds Regularized Non-negative Matrix Factorization for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Discovery for Visual Test Generation
Neil Hallonquist, Laurent Younes, Donald Geman

Auto-TLDR; Visual Question Answering over Graphs: A Probabilistic Framework for VQA
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar