Active Sampling for Pairwise Comparisons via Approximate Message Passing and Information Gain Maximization
Aliaksei Mikhailiuk,
Clifford Wilmot,
Maria Perez-Ortiz,
Dingcheng Yue,
Rafal Mantiuk

Auto-TLDR; ASAP: An Active Sampling Algorithm for Pairwise Comparison Data
Similar papers
Factor Screening Using Bayesian Active Learning and Gaussian Process Meta-Modelling
Cheng Li, Santu Rana, Andrew William Gill, Dang Nguyen, Sunil Kumar Gupta, Svetha Venkatesh

Auto-TLDR; Data-Efficient Bayesian Active Learning for Factor Screening in Combat Simulations
Sketch-Based Community Detection Via Representative Node Sampling
Mahlagha Sedghi, Andre Beckus, George Atia
Auto-TLDR; Sketch-based Clustering of Community Detection Using a Small Sketch
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probabilistic Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering with Bayesian Inference
Jiansheng Fang, Xiaoqing Zhang, Yan Hu, Yanwu Xu, Ming Yang, Jiang Liu

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering
Multi-annotator Probabilistic Active Learning
Marek Herde, Daniel Kottke, Denis Huseljic, Bernhard Sick

Auto-TLDR; MaPAL: Multi-annotator Probabilistic Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Dependent Gaussian Experts in Local Approximation

Auto-TLDR; A novel approach for aggregating the Gaussian experts by detecting strong violations of conditional independence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bayesian Active Learning for Maximal Information Gain on Model Parameters
Kasra Arnavaz, Aasa Feragen, Oswin Krause, Marco Loog

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian assumptions for Bayesian classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Budgeted Batch Mode Active Learning with Generalized Cost and Utility Functions
Arvind Agarwal, Shashank Mujumdar, Nitin Gupta, Sameep Mehta

Auto-TLDR; Active Learning Based on Utility and Cost Functions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3CS Algorithm for Efficient Gaussian Process Model Retrieval
Fabian Berns, Kjeld Schmidt, Ingolf Bracht, Christian Beecks

Auto-TLDR; Efficient retrieval of Gaussian Process Models for large-scale data using divide-&-conquer-based approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Sampling of Pareto Frontiers with Binary Constraints Using Regression and Classification

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Optimization for Black-Box Multi-Objective Optimizing Problems with Binary Constraints
DR2S: Deep Regression with Region Selection for Camera Quality Evaluation
Marcelin Tworski, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Salim Belkarfa, Attilio Fiandrotti, Marco Cagnazzo

Auto-TLDR; Texture Quality Estimation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Parameter Distributions to Detect Concept Drift in Data Streams
Johannes Haug, Gjergji Kasneci

Auto-TLDR; A novel framework for the detection of concept drift in streaming environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rank-Based Ordinal Classification

Auto-TLDR; Ordinal Classification with Order
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Pattern Detection in Time-Varying Graphical Models
Federico Tomasi, Veronica Tozzo, Annalisa Barla

Auto-TLDR; A dynamical network inference model that leverages on kernels to consider general temporal patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The eXPose Approach to Crosslier Detection
Antonio Barata, Frank Takes, Hendrik Van Den Herik, Cor Veenman

Auto-TLDR; EXPose: Crosslier Detection Based on Supervised Category Modeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatically Mining Relevant Variable Interactions Via Sparse Bayesian Learning
Ryoichiro Yafune, Daisuke Sakuma, Yasuo Tabei, Noritaka Saito, Hiroto Saigo

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Bayes for Interpretable Non-linear Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Intransitivity Model for Matchup and Pairwise Comparison
Yan Gu, Jiuding Duan, Hisashi Kashima

Auto-TLDR; Blade-Chest: A Low-Rank Matrix Approach for Probabilistic Ranking of Players
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Assortative-Constrained Stochastic Block Models
Daniel Gribel, Thibaut Vidal, Michel Gendreau

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Stochastic Block Models for Assortative Communities in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantifying Model Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Via Bayesian Deep Gradient Descent
Riccardo Barbano, Chen Zhang, Simon Arridge, Bangti Jin

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Neural Networks for Inverse Reconstruction via Bayesian Knowledge-Aided Computation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Rank for Active Learning: A Listwise Approach
Minghan Li, Xialei Liu, Joost Van De Weijer, Bogdan Raducanu

Auto-TLDR; Learning Loss for Active Learning
GPSRL: Learning Semi-Parametric Bayesian Survival Rule Lists from Heterogeneous Patient Data
Ameer Hamza Shakur, Xiaoning Qian, Zhangyang Wang, Bobak Mortazavi, Shuai Huang

Auto-TLDR; Semi-parametric Bayesian Survival Rule List Model for Heterogeneous Survival Data
Graph Discovery for Visual Test Generation
Neil Hallonquist, Laurent Younes, Donald Geman

Auto-TLDR; Visual Question Answering over Graphs: A Probabilistic Framework for VQA
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multilinear Sampling Algorithm to Estimate Shapley Values
Auto-TLDR; A sampling method for Shapley values for multilayer Perceptrons
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Watermelon: A Novel Feature Selection Method Based on Bayes Error Rate Estimation and a New Interpretation of Feature Relevance and Redundancy
Auto-TLDR; Feature Selection Using Bayes Error Rate Estimation for Dynamic Feature Selection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Equation Attention Relationship Network (EARN) : A Geometric Deep Metric Framework for Learning Similar Math Expression Embedding
Saleem Ahmed, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; Representational Learning for Similarity Based Retrieval of Mathematical Expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Heuristic-Based Decision Tree for Connected Components Labeling of 3D Volumes
Maximilian Söchting, Stefano Allegretti, Federico Bolelli, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; Entropy Partitioning Decision Tree for Connected Components Labeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MINT: Deep Network Compression Via Mutual Information-Based Neuron Trimming
Madan Ravi Ganesh, Jason Corso, Salimeh Yasaei Sekeh
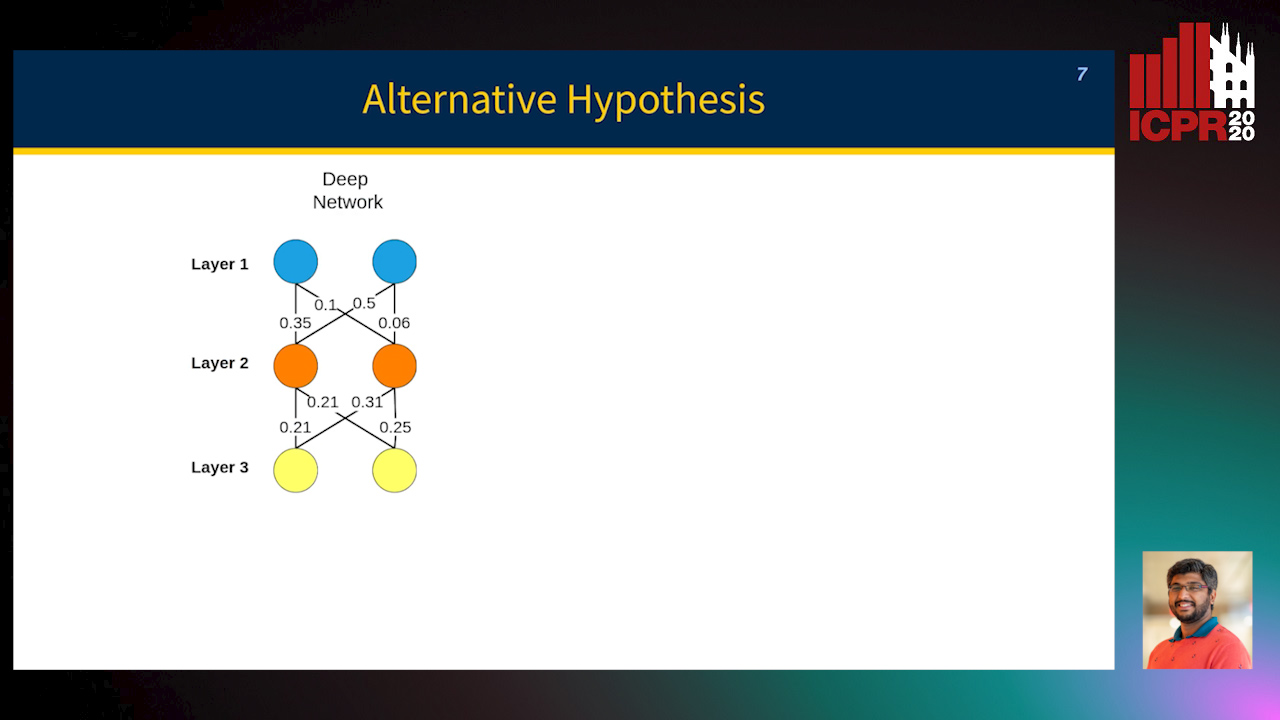
Auto-TLDR; Mutual Information-based Neuron Trimming for Deep Compression via Pruning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Sequential Pattern Information for Active Learning from Sequential Data
Raul Fidalgo-Merino, Lorenzo Gabrielli, Enrico Checchi

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Pattern Information for Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts
Wenbo Zhao, Yang Gao, Shahan Ali Memon, Bhiksha Raj, Rita Singh

Auto-TLDR; A Binary Tree-structured Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts for Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Learning Random Forests for Random Forest Clustering
Manuele Bicego, Francisco Escolano

Auto-TLDR; Learning Random Forests for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Naturally Constrained Online Expectation Maximization
Daniela Pamplona, Antoine Manzanera
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Online Expectation-Maximization for Probabilistic Principal Components Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Adaptive Minority Oversampling Technique for Improved Classification in Data Imbalanced Scenarios
Ayush Tripathi, Rupayan Chakraborty, Sunil Kumar Kopparapu

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Minority OverSampling Technique for Imbalanced Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Algorithm Recommendation for Data Streams
Jáder Martins Camboim De Sá, Andre Luis Debiaso Rossi, Gustavo Enrique De Almeida Prado Alves Batista, Luís Paulo Faina Garcia

Auto-TLDR; Meta-Learning for Algorithm Selection in Time-Changing Data Streams
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph-Based Image Decoding for Multiplexed in Situ RNA Detection
Gabriele Partel, Carolina Wahlby
Auto-TLDR; A Graph-based Decoding Approach for Multiplexed In situ RNA Detection
Quantifying the Use of Domain Randomization
Mohammad Ani, Hector Basevi, Ales Leonardis

Auto-TLDR; Evaluating Domain Randomization for Synthetic Image Generation by directly measuring the difference between realistic and synthetic data distributions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Minority Class Oriented Active Learning for Imbalanced Datasets
Umang Aggarwal, Adrian Popescu, Celine Hudelot

Auto-TLDR; Active Learning for Imbalanced Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Reinforcement Learning Lead to Healthy Life?: Simulation Study Based on User Activity Logs
Masami Takahashi, Masahiro Kohjima, Takeshi Kurashima, Hiroyuki Toda

Auto-TLDR; Reinforcement Learning for Healthy Daily Life
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Low-Cost Lipschitz-Independent Adaptive Importance Sampling of Stochastic Gradients
Huikang Liu, Xiaolu Wang, Jiajin Li, Man-Cho Anthony So

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Importance Sampling for Stochastic Gradient Descent
Unveiling Groups of Related Tasks in Multi-Task Learning
Jordan Frecon, Saverio Salzo, Massimiliano Pontil

Auto-TLDR; Continuous Bilevel Optimization for Multi-Task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explainable Online Validation of Machine Learning Models for Practical Applications
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Thomas Motz, Michael Scheidt, Andreas Markus Hartel, Andreas Koch, Enkelejda Kasneci

Auto-TLDR; A Reformulation of Regression and Classification for Machine Learning Algorithm Validation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uniform and Non-Uniform Sampling Methods for Sub-Linear Time K-Means Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Sub-linear Time Clustering with Constant Approximation Ratio for K-Means Problem
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering
Shuai Yang, Wenqi Zhu, Yuesheng Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering with Piecewise Correlation Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Categorizing the Feature Space for Two-Class Imbalance Learning
Rosa Sicilia, Ermanno Cordelli, Paolo Soda
Auto-TLDR; Efficient Ensemble of Classifiers for Minority Class Inference
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Matching of Kernel Means
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Matching of Kernel Means for Knowledge Discovery and Feature Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classification and Feature Selection Using a Primal-Dual Method and Projections on Structured Constraints
Michel Barlaud, Antonin Chambolle, Jean_Baptiste Caillau

Auto-TLDR; A Constrained Primal-dual Method for Structured Feature Selection on High Dimensional Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scalable Direction-Search-Based Approach to Subspace Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Fast Direction-Search-Based Subspace Clustering
Motion Segmentation with Pairwise Matches and Unknown Number of Motions
Federica Arrigoni, Tomas Pajdla, Luca Magri

Auto-TLDR; Motion Segmentation using Multi-Modelfitting andpermutation synchronization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Quadratic Spherical Mutual Information Hashing for Fast Image Retrieval
Nikolaos Passalis, Anastasios Tefas

Auto-TLDR; Quadratic Mutual Information for Large-Scale Hashing and Information Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar