MFPP: Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid for Black-Box Model Explanations
Qing Yang,
Xia Zhu,
Jong-Kae Fwu,
Yun Ye,
Ganmei You,
Yuan Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid for Explainable Deep Neural Network
Similar papers
Zoom-CAM: Generating Fine-Grained Pixel Annotations from Image Labels
Xiangwei Shi, Seyran Khademi, Yunqiang Li, Jan Van Gemert
Auto-TLDR; Zoom-CAM for Weakly Supervised Object Localization and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Generalizable Saliency Map-Based Interpretation of Model Outcome
Shailja Thakur, Sebastian Fischmeister
Auto-TLDR; Interpretability of Deep Neural Networks Using Salient Input and Output
Understanding Integrated Gradients with SmoothTaylor for Deep Neural Network Attribution
Gary Shing Wee Goh, Sebastian Lapuschkin, Leander Weber, Wojciech Samek, Alexander Binder
Auto-TLDR; SmoothGrad: bridging Integrated Gradients and SmoothGrad from the Taylor's theorem perspective
Improving Explainability of Integrated Gradients with Guided Non-Linearity
Hyuk Jin Kwon, Hyung Il Koo, Nam Ik Cho

Auto-TLDR; Guided Non-linearity for Attribution in Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Color, Edge, and Pixel-Wise Explanation of Predictions Based onInterpretable Neural Network Model

Auto-TLDR; Explainable Deep Neural Network with Edge Detecting Filters
Superpixel-Based Refinement for Object Proposal Generation
Christian Wilms, Simone Frintrop

Auto-TLDR; Superpixel-based Refinement of AttentionMask for Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CCA: Exploring the Possibility of Contextual Camouflage Attack on Object Detection
Shengnan Hu, Yang Zhang, Sumit Laha, Ankit Sharma, Hassan Foroosh

Auto-TLDR; Contextual camouflage attack for object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Head Design for Object Detectors
Shivang Agarwal, Frederic Jurie
Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical Anchor for SSD Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Does DCNN Make Decisions?
Yi Lin, Namin Wang, Xiaoqing Ma, Ziwei Li, Gang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Deep Convolutional Neural Network's Decision-Making Interpretability
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation Refinement Using Entropy and Boundary-guided Monte Carlo Sampling and Directed Regional Search
Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Ruojing Wang, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Directed Region Search and Refinement for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combining Similarity and Adversarial Learning to Generate Visual Explanation: Application to Medical Image Classification
Martin Charachon, Roberto Roberto Ardon, Celine Hudelot, Paul-Henry Cournède, Camille Ruppli

Auto-TLDR; Explaining Black-Box Machine Learning Models with Visual Explanation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Cascade Point Search Network for High Precision Bar Chart Component Detection
Junyu Luo, Jinpeng Wang, Chin-Yew Lin
Auto-TLDR; Object Detection of Chart Components in Chart Images Using Point-based and Region-Based Object Detection Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ScarfNet: Multi-Scale Features with Deeply Fused and Redistributed Semantics for Enhanced Object Detection
Jin Hyeok Yoo, Dongsuk Kum, Jun Won Choi
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Fusion of Multi-scale Feature Maps for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Kernel-Based LIME with Feature Dependency Sampling
Sheng Shi, Yangzhou Du, Fan Wei

Auto-TLDR; Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation with Feature Dependency Sampling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Early Biological Models to CNNs: Do They Look Where Humans Look?
Marinella Iole Cadoni, Andrea Lagorio, Enrico Grosso, Jia Huei Tan, Chee Seng Chan

Auto-TLDR; Comparing Neural Networks to Human Fixations for Semantic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Utilising Visual Attention Cues for Vehicle Detection and Tracking
Feiyan Hu, Venkatesh Gurram Munirathnam, Noel E O'Connor, Alan Smeaton, Suzanne Little
Auto-TLDR; Visual Attention for Object Detection and Tracking in Driver-Assistance Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explainable Feature Embedding Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Pathological Image Analysis
Kazuki Uehara, Masahiro Murakawa, Hirokazu Nosato, Hidenori Sakanashi
Auto-TLDR; Explainable Diagnosis Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Pathological Image Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection Leveraging on Simultaneous Super-Resolution
Hong Ji, Zhi Gao, Xiaodong Liu, Tiancan Mei

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution via Generative Adversarial Network for Small Object Detection
FastSal: A Computationally Efficient Network for Visual Saliency Prediction

Auto-TLDR; MobileNetV2: A Convolutional Neural Network for Saliency Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection Based on Improved Faster R-CNN
Tao Wang, Can Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Foreground-Focused Domain Adaption for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Unsupervised Object Detection
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
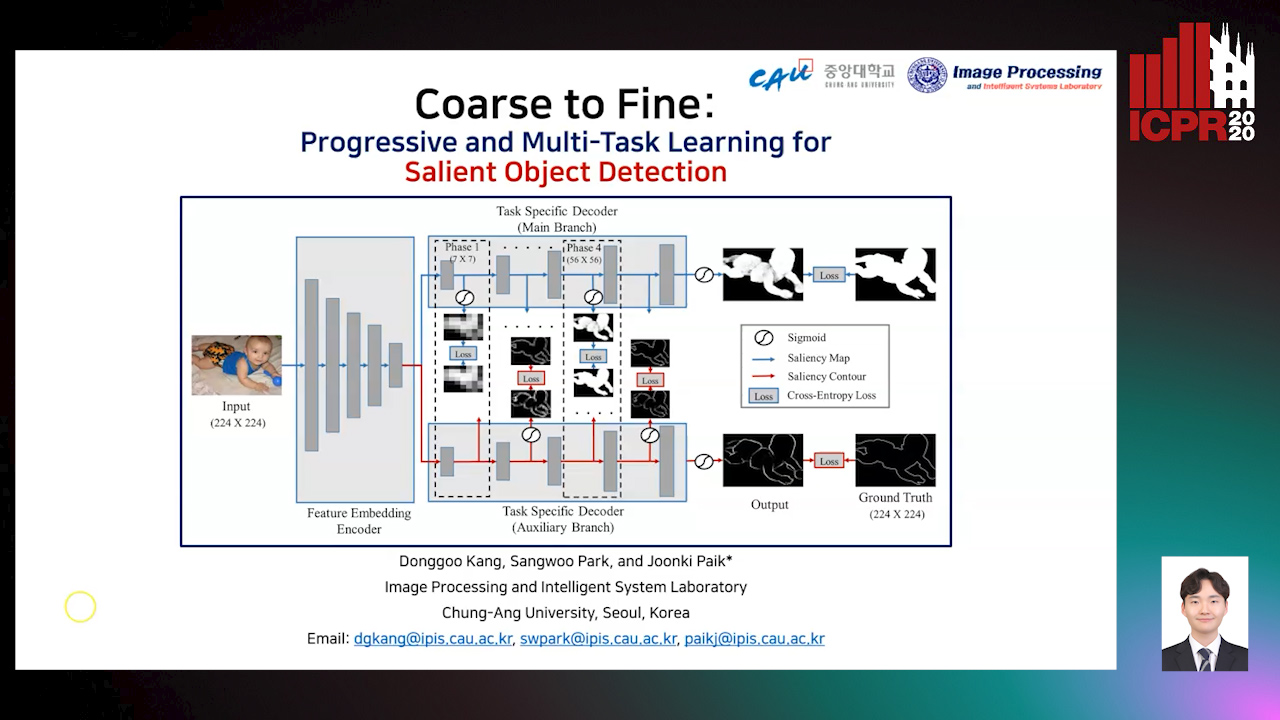
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Localization of Retinal Lesions Via Weakly-Supervised Learning

Auto-TLDR; Weakly Learning of Lesions in Fundus Images Using Multi-level Feature Maps and Classification Score
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Auto Encoding Explanatory Examples with Stochastic Paths
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Ramses J. Sanchez, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Stochastic Path: Explaining a Classifier's Decision Making Process using latent codes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiscale Attention-Based Prototypical Network for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Yifei Zhang, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Semantic Segmentation with Multiscale Feature Attention
StrongPose: Bottom-up and Strong Keypoint Heat Map Based Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; StrongPose: A bottom-up box-free approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
Vision-Based Layout Detection from Scientific Literature Using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Scientific Literature Layout Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Convolutional STN for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Akhil Meethal, Marco Pedersoli, Soufiane Belharbi, Eric Granger

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Localization for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar