Improving Explainability of Integrated Gradients with Guided Non-Linearity
Hyuk Jin Kwon,
Hyung Il Koo,
Nam Ik Cho

Auto-TLDR; Guided Non-linearity for Attribution in Convolutional Neural Networks
Similar papers
Understanding Integrated Gradients with SmoothTaylor for Deep Neural Network Attribution
Gary Shing Wee Goh, Sebastian Lapuschkin, Leander Weber, Wojciech Samek, Alexander Binder
Auto-TLDR; SmoothGrad: bridging Integrated Gradients and SmoothGrad from the Taylor's theorem perspective
Zoom-CAM: Generating Fine-Grained Pixel Annotations from Image Labels
Xiangwei Shi, Seyran Khademi, Yunqiang Li, Jan Van Gemert
Auto-TLDR; Zoom-CAM for Weakly Supervised Object Localization and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFPP: Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid for Black-Box Model Explanations
Qing Yang, Xia Zhu, Jong-Kae Fwu, Yun Ye, Ganmei You, Yuan Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid for Explainable Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Generalizable Saliency Map-Based Interpretation of Model Outcome
Shailja Thakur, Sebastian Fischmeister
Auto-TLDR; Interpretability of Deep Neural Networks Using Salient Input and Output
Combining Similarity and Adversarial Learning to Generate Visual Explanation: Application to Medical Image Classification
Martin Charachon, Roberto Roberto Ardon, Celine Hudelot, Paul-Henry Cournède, Camille Ruppli

Auto-TLDR; Explaining Black-Box Machine Learning Models with Visual Explanation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Color, Edge, and Pixel-Wise Explanation of Predictions Based onInterpretable Neural Network Model

Auto-TLDR; Explainable Deep Neural Network with Edge Detecting Filters
Explainable Feature Embedding Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Pathological Image Analysis
Kazuki Uehara, Masahiro Murakawa, Hirokazu Nosato, Hidenori Sakanashi
Auto-TLDR; Explainable Diagnosis Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Pathological Image Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Early Biological Models to CNNs: Do They Look Where Humans Look?
Marinella Iole Cadoni, Andrea Lagorio, Enrico Grosso, Jia Huei Tan, Chee Seng Chan

Auto-TLDR; Comparing Neural Networks to Human Fixations for Semantic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Auto Encoding Explanatory Examples with Stochastic Paths
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Ramses J. Sanchez, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Stochastic Path: Explaining a Classifier's Decision Making Process using latent codes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Does DCNN Make Decisions?
Yi Lin, Namin Wang, Xiaoqing Ma, Ziwei Li, Gang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Deep Convolutional Neural Network's Decision-Making Interpretability
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock Module for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Junhui Yin, Siqing Zhang, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Jun Guo
Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Guided Dropblock for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CQNN: Convolutional Quadratic Neural Networks

Auto-TLDR; Quadratic Neural Network for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Neuron-Based Network Pruning Based on Majority Voting
Ali Alqahtani, Xianghua Xie, Ehab Essa, Mark W. Jones

Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Neural Network Pruning using Majority Voting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Localization of Retinal Lesions Via Weakly-Supervised Learning

Auto-TLDR; Weakly Learning of Lesions in Fundus Images Using Multi-level Feature Maps and Classification Score
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explanation-Guided Training for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Classification
Jiamei Sun, Sebastian Lapuschkin, Wojciech Samek, Yunqing Zhao, Ngai-Man Cheung, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Explaination-Guided Training for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Kernel-Based LIME with Feature Dependency Sampling
Sheng Shi, Yangzhou Du, Fan Wei

Auto-TLDR; Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation with Feature Dependency Sampling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CCA: Exploring the Possibility of Contextual Camouflage Attack on Object Detection
Shengnan Hu, Yang Zhang, Sumit Laha, Ankit Sharma, Hassan Foroosh

Auto-TLDR; Contextual camouflage attack for object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction for Deep Neural Networks
Pak Lun Kevin Ding, Martin Sarah, Baoxin Li
Auto-TLDR; Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probability Guided Maxout
Claudio Ferrari, Stefano Berretti, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Probability Guided Maxout for CNN Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Attention and Global Representation Collaborating for Fine-Grained Classification
He Zhang, Yunming Bai, Hui Zhang, Jing Liu, Xingguang Li, Zhaofeng He

Auto-TLDR; Weighted Region Network for Cosmetic Contact Lenses Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Multiple Instance Learning with Spatial Attention for ROP Case Classification, Instance Selection and Abnormality Localization
Xirong Li, Wencui Wan, Yang Zhou, Jianchun Zhao, Qijie Wei, Junbo Rong, Pengyi Zhou, Limin Xu, Lijuan Lang, Yuying Liu, Chengzhi Niu, Dayong Ding, Xuemin Jin

Auto-TLDR; MIL-SA: Deep Multiple Instance Learning for Automated Screening of Retinopathy of Prematurity
Unsupervised Sound Source Localization From Audio-Image Pairs Using Input Gradient Map
Tomohiro Tanaka, Takahiro Shinozaki
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Sound Localization Using Gradient Method
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ResNet-Like Architecture with Low Hardware Requirements
Elena Limonova, Daniil Alfonso, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov

Auto-TLDR; BM-ResNet: Bipolar Morphological ResNet for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attack-Agnostic Adversarial Detection on Medical Data Using Explainable Machine Learning
Matthew Watson, Noura Al Moubayed

Auto-TLDR; Explainability-based Detection of Adversarial Samples on EHR and Chest X-Ray Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Information of Feature Maps and Pruning of Deep Neural Networks
Mohammadreza Soltani, Suya Wu, Jie Ding, Robert Ravier, Vahid Tarokh

Auto-TLDR; Compressing Deep Neural Models Using Mutual Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Noise Injection for Training Stochastic Student Networks from Deterministic Teachers
Yi Xiang Marcus Tan, Yuval Elovici, Alexander Binder

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Stochastic Networks for Adversarial Attacks
Improved Residual Networks for Image and Video Recognition
Ionut Cosmin Duta, Li Liu, Fan Zhu, Ling Shao
Auto-TLDR; Residual Networks for Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Order Feature Statistical Model for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Qingtao Wang, Ke Zhang, Shaoli Huang, Lianbo Zhang, Jin Fan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Order Feature Statistical Method for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention As Activation
Yimian Dai, Stefan Oehmcke, Fabian Gieseke, Yiquan Wu, Kobus Barnard

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Activation Units for Convolutional Networks
Feature-Dependent Cross-Connections in Multi-Path Neural Networks
Dumindu Tissera, Kasun Vithanage, Rukshan Wijesinghe, Kumara Kahatapitiya, Subha Fernando, Ranga Rodrigo
Auto-TLDR; Multi-path Networks for Adaptive Feature Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HFP: Hardware-Aware Filter Pruning for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Acceleration
Fang Yu, Chuanqi Han, Pengcheng Wang, Ruoran Huang, Xi Huang, Li Cui

Auto-TLDR; Hardware-Aware Filter Pruning for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Verifying the Causes of Adversarial Examples
Honglin Li, Yifei Fan, Frieder Ganz, Tony Yezzi, Payam Barnaghi

Auto-TLDR; Exploring the Causes of Adversarial Examples in Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Collaborative Human Machine Attention Module for Character Recognition
Chetan Ralekar, Tapan Gandhi, Santanu Chaudhury

Auto-TLDR; A Collaborative Human-Machine Attention Module for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
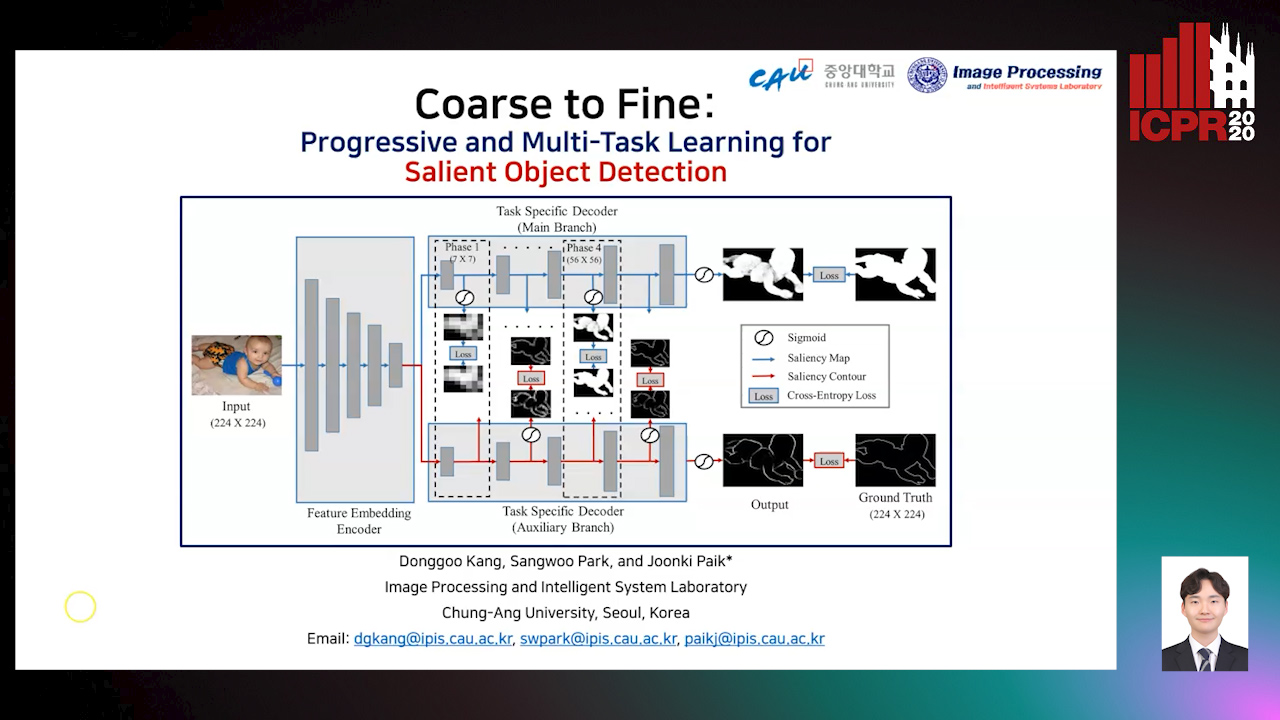
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Training for Audio Classifiers
Raymel Alfonso Sallo, Mohammad Esmaeilpour, Patrick Cardinal

Auto-TLDR; Adversarially Training for Robust Neural Networks against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EM-Net: Deep Learning for Electron Microscopy Image Segmentation
Afshin Khadangi, Thomas Boudier, Vijay Rajagopal

Auto-TLDR; EM-net: Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Electron Microscopy Image Segmentation
Dynamic Multi-Path Neural Network
Yingcheng Su, Yichao Wu, Ken Chen, Ding Liang, Xiaolin Hu

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Multi-path Neural Network
Single Image Super-Resolution with Dynamic Residual Connection
Karam Park, Jae Woong Soh, Nam Ik Cho

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Residual Attention Network for Lightweight Single Image Super-Residual Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Polynomial Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Person Re-Identification
Wenjie Ding, Xing Wei, Rongrong Ji, Xiaopeng Hong, Yihong Gong

Auto-TLDR; Polynomial Universal Adversarial Perturbation for Re-identification Methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity