A Dual-Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion

Auto-TLDR; Image Fusion Using Autoencoder for Deep Learning
Similar papers
CSpA-DN: Channel and Spatial Attention Dense Network for Fusing PET and MRI Images
Bicao Li, Zhoufeng Liu, Shan Gao, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Jun Sun, Zongmin Wang

Auto-TLDR; CSpA-DN: Unsupervised Fusion of PET and MR Images with Channel and Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Fusion of RGB and NIR Paired Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks

Auto-TLDR; Deep Fusion of RGB and NIR paired images in low light condition using convolutional neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Near-Infrared Depth-Independent Image Dehazing using Haar Wavelets
Sumit Laha, Ankit Sharma, Shengnan Hu, Hassan Foroosh
Auto-TLDR; A fusion algorithm for haze removal using Haar wavelets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-focus Image Fusion for Confocal Microscopy Using U-Net Regression Map
Md Maruf Hossain Shuvo, Yasmin M. Kassim, Filiz Bunyak, Olga V. Glinskii, Leike Xie, Vladislav V Glinsky, Virginia H. Huxley, Kannappan Palaniappan

Auto-TLDR; Independent Single Channel U-Net Fusion for Multi-focus Microscopy Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatical Enhancement and Denoising of Extremely Low-Light Images
Yuda Song, Yunfang Zhu, Xin Du

Auto-TLDR; INSNet: Illumination and Noise Separation Network for Low-Light Image Restoring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Fractal Network for Single Image Super Resolution by Widening and Deepening
Jiahang Gu, Zhaowei Qu, Xiaoru Wang, Jiawang Dan, Junwei Sun
Auto-TLDR; Residual fractal convolutional network for single image super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Focus Image Fusion Method Based on Fractal Dimension and Guided Filtering
Nikoo Dehghani, Ehsanollah Kabir
Auto-TLDR; Fractal Dimension-based Multi-focus Image Fusion with Guide Filtering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RSAN: Residual Subtraction and Attention Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Shuo Wei, Xin Sun, Haoran Zhao, Junyu Dong

Auto-TLDR; RSAN: Residual subtraction and attention network for super-resolution
Neural Architecture Search for Image Super-Resolution Using Densely Connected Search Space: DeCoNAS

Auto-TLDR; DeCoNASNet: Automated Neural Architecture Search for Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SIDGAN: Single Image Dehazing without Paired Supervision
Pan Wei, Xin Wang, Lei Wang, Ji Xiang, Zihan Wang

Auto-TLDR; DehazeGAN: An End-to-End Generative Adversarial Network for Image Dehazing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Splitting and Upscaling Structure for Super-Resolution

Auto-TLDR; PSUS: Progressive and Upscaling Layer for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Low-Light Image Enhancement for Object Detection Via End-To-End Training
Haifeng Guo, Yirui Wu, Tong Lu

Auto-TLDR; Object Detection using Low-Light Image Enhancement for End-to-End Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail-Revealing Deep Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Xinchen Ye, Yuyao Xu, Rui Xu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; A Dual-branch Aggregation Network for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LiNet: A Lightweight Network for Image Super Resolution
Armin Mehri, Parichehr Behjati Ardakani, Angel D. Sappa

Auto-TLDR; LiNet: A Compact Dense Network for Lightweight Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Super-Resolution Network with Incremental Enhancement of Facial Parsing Information
Shuang Liu, Chengyi Xiong, Zhirong Gao

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Face Super-Resolution with Incremental Boosting Facial Parsing Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A NoGAN Approach for Image and Video Restoration and Compression Artifact Removal
Mameli Filippo, Marco Bertini, Leonardo Galteri, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Image and Video Compression Artifact Removal and Restoration
Single Image Deblurring Using Bi-Attention Network

Auto-TLDR; Bi-Attention Neural Network for Single Image Deblurring
CT-UNet: An Improved Neural Network Based on U-Net for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Huanran Ye, Sheng Liu, Kun Jin, Haohao Cheng
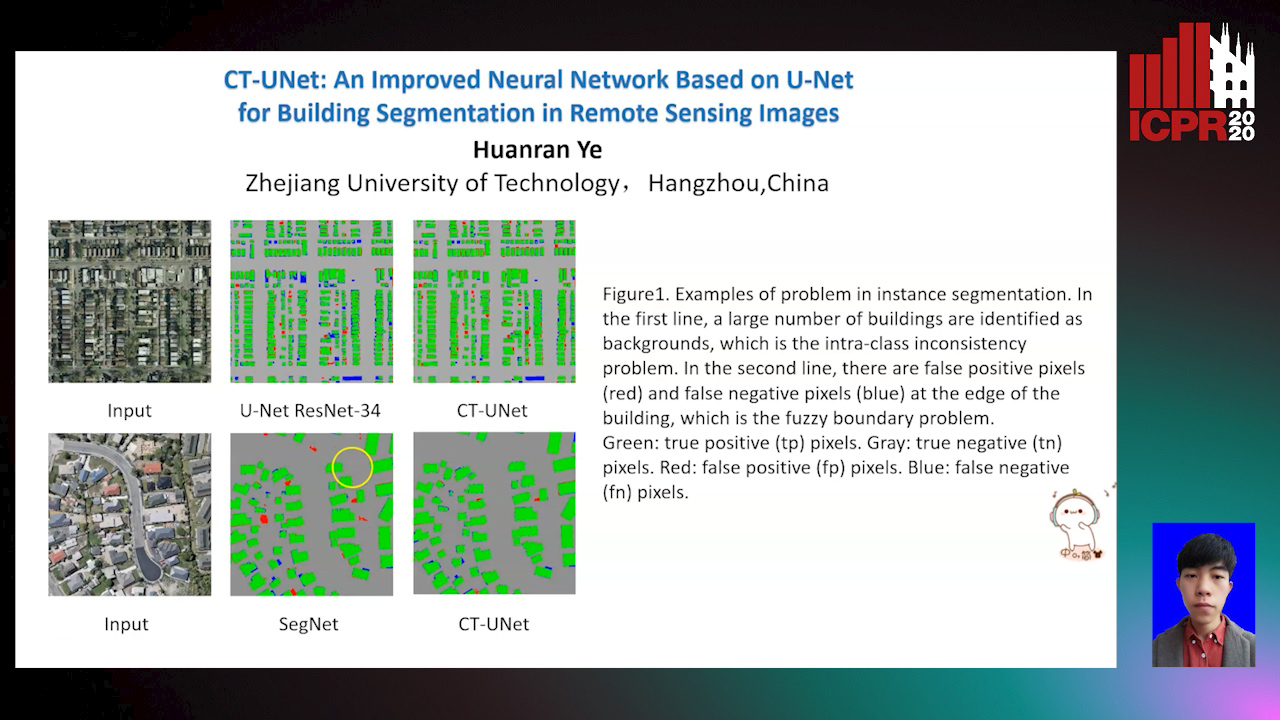
Auto-TLDR; Context-Transfer-UNet: A UNet-based Network for Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wavelet Attention Embedding Networks for Video Super-Resolution
Young-Ju Choi, Young-Woon Lee, Byung-Gyu Kim

Auto-TLDR; Wavelet Attention Embedding Network for Video Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
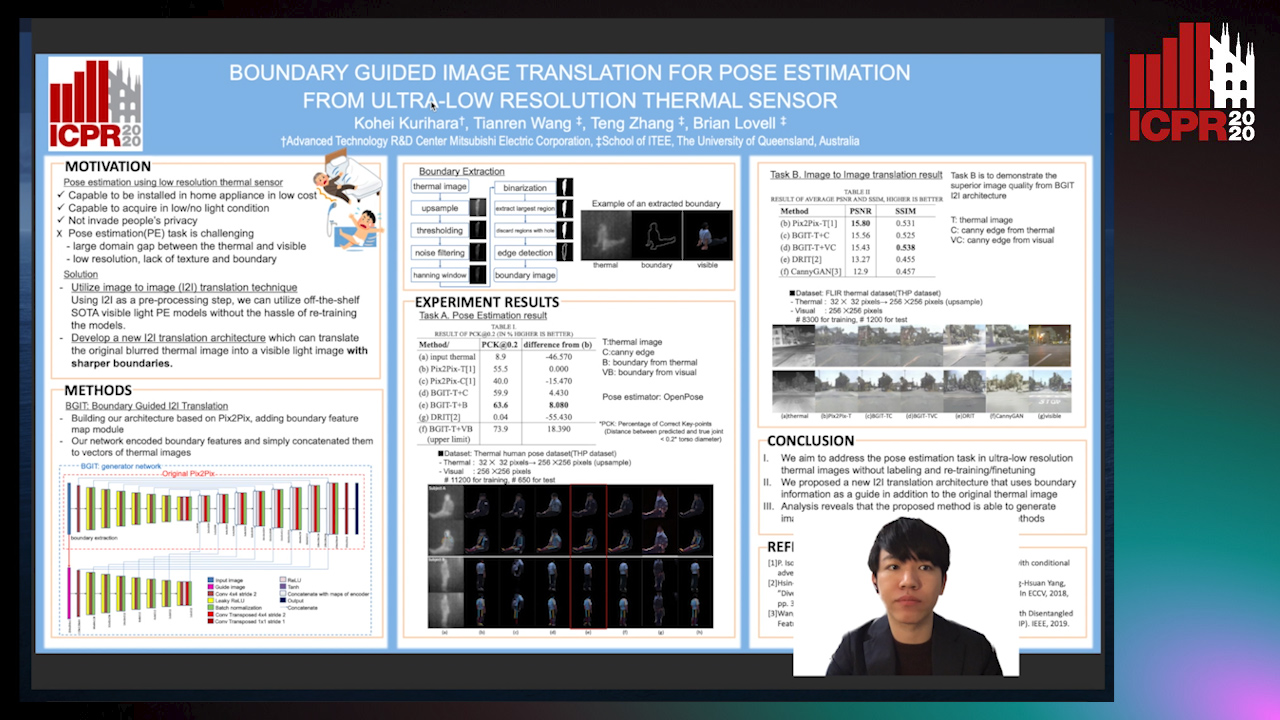
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
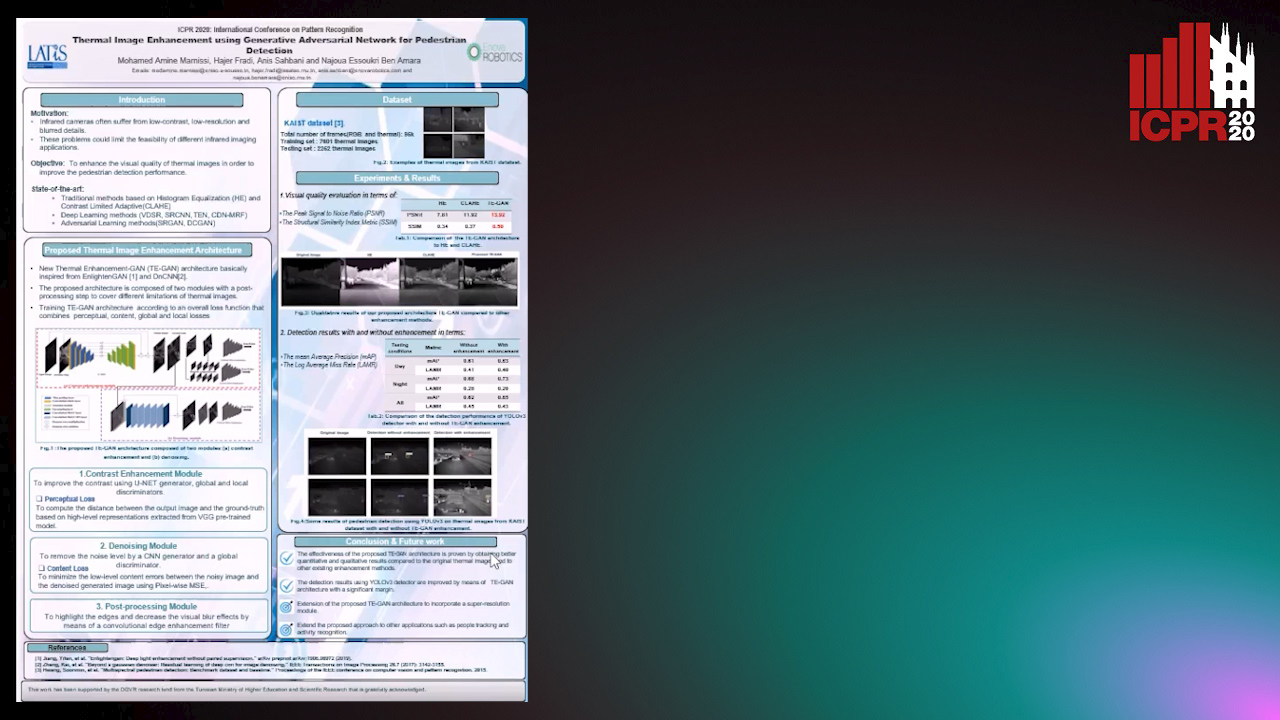
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single Image Super-Resolution with Dynamic Residual Connection
Karam Park, Jae Woong Soh, Nam Ik Cho

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Residual Attention Network for Lightweight Single Image Super-Residual Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Lightening with Dedicated CNN Architecture
Li-Wen Wang, Wan-Chi Siu, Zhi-Song Liu, Chu-Tak Li, P. K. Daniel Lun

Auto-TLDR; VLN: Video Lightening Network for Driving Assistant Systems in Dark Environment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Compressive Autoencoders for Full-Image-To-Image Hiding
Xiyao Liu, Ziping Ma, Xingbei Guo, Jialu Hou, Lei Wang, Gerald Schaefer, Hui Fang

Auto-TLDR; J-CAE: Joint Compressive Autoencoder for Image Hiding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MBD-GAN: Model-Based Image Deblurring with a Generative Adversarial Network

Auto-TLDR; Model-Based Deblurring GAN for Inverse Imaging
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Mucong Ye, Ouyang Jinpeng, Ge Chen, Jing Zhang, Xiaogang Yu
Auto-TLDR; EFPN: Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Learning of Face Attribute Synthesis
Ning Xin, Shaohui Xu, Fangzhe Nan, Xiaoli Dong, Weijun Li, Yuanzhou Yao

Auto-TLDR; Continuous Learning for Face Attribute Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Reconstruction by Spatio-Temporal Fusion of Blurred-Coded Image Pair
Anupama S, Prasan Shedligeri, Abhishek Pal, Kaushik Mitr

Auto-TLDR; Recovering Video from Motion-Blurred and Coded Exposure Images Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
CURL: Neural Curve Layers for Global Image Enhancement
Sean Moran, Steven Mcdonagh, Greg Slabaugh

Auto-TLDR; CURL: Neural CURve Layers for Image Enhancement
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explorable Tone Mapping Operators
Su Chien-Chuan, Yu-Lun Liu, Hung Jin Lin, Ren Wang, Chia-Ping Chen, Yu-Lin Chang, Soo-Chang Pei

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based multimodal tone-mapping from HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Iterative Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Rao Muhammad Umer, Gian Luca Foresti, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; ISRResCNet: Deep Iterative Super-Resolution Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-resolution
Selective Kernel and Motion-Emphasized Loss Based Attention-Guided Network for HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scenes
Yipeng Deng, Qin Liu, Takeshi Ikenaga

Auto-TLDR; SK-AHDRNet: A Deep Network with attention module and motion-emphasized loss function to produce ghost-free HDR images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Layer Information Refining Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Hongyi Zhang, Wen Lu, Xiaopeng Sun

Auto-TLDR; Interlaced Spatial Attention Block for Single Image Super-Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Realistic Novel View Generation for City-Scale Aerial Images
Koundinya Nouduri, Ke Gao, Joshua Fraser, Shizeng Yao, Hadi Aliakbarpour, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End 3D Voxel Renderer for Multi-View Stereo Data Generation and Evaluation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MANet: Multimodal Attention Network Based Point-View Fusion for 3D Shape Recognition
Yaxin Zhao, Jichao Jiao, Ning Li
Auto-TLDR; Fusion Network for 3D Shape Recognition based on Multimodal Attention Mechanism
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
UHRSNet: A Semantic Segmentation Network Specifically for Ultra-High-Resolution Images

Auto-TLDR; Ultra-High-Resolution Segmentation with Local and Global Feature Fusion
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Super Resolution by Recursive Aggregation
Zhengxiong Luo Zhengxiong Luo, Yan Huang, Shang Li, Liang Wang, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Recursive Aggregation Network for Efficient Deep Super Resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Imagery Using Synthesized Images
My Kieu, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Leonardo Galteri, Marco Bertini, Andrew Bagdanov, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Improving Pedestrian Detection in the thermal domain using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail Fusion GAN: High-Quality Translation for Unpaired Images with GAN-Based Data Augmentation
Ling Li, Yaochen Li, Chuan Wu, Hang Dong, Peilin Jiang, Fei Wang

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation with GAN-based Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deeply-Fused Attentive Network for Stereo Matching
Zuliu Yang, Xindong Ai, Weida Yang, Yong Zhao, Qifei Dai, Fuchi Li

Auto-TLDR; DF-Net: Deep Learning-based Network for Stereo Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast and Accurate Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Dilated Asymmetric Convolutions
Leonel Rosas-Arias, Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai
Auto-TLDR; FASSD-Net: Dilated Asymmetric Pyramidal Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DA-RefineNet: Dual-Inputs Attention RefineNet for Whole Slide Image Segmentation
Ziqiang Li, Rentuo Tao, Qianrun Wu, Bin Li

Auto-TLDR; DA-RefineNet: A dual-inputs attention network for whole slide image segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar