Detecting Anomalies from Video-Sequences: A Novel Descriptor
Giulia Orrù,
Davide Ghiani,
Maura Pintor,
Gian Luca Marcialis,
Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Trit-based Measurement of Group Dynamics for Crowd Behavior Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Similar papers
Anomaly Detection, Localization and Classification for Railway Inspection
Riccardo Gasparini, Andrea D'Eusanio, Guido Borghi, Stefano Pini, Giuseppe Scaglione, Simone Calderara, Eugenio Fedeli, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Anomaly Detection and Localization using thermal images in the lowlight environment
Ground-truthing Large Human Behavior Monitoring Datasets
Tehreem Qasim, Robert Fisher, Naeem Bhatti

Auto-TLDR; Semi-automated Groundtruthing for Large Video Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Video Anomaly Detection by Estimating Likelihood of Representations

Auto-TLDR; Video Anomaly Detection in the latent feature space using a deep probabilistic model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion and Region Aware Adversarial Learning for Fall Detection with Thermal Imaging
Vineet Mehta, Abhinav Dhall, Sujata Pal, Shehroz Khan

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Fall Detection with Adversarial Network using Thermal Imaging Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-Mode Iterative Denoiser: Tackling the Weak Label for Anomaly Detection

Auto-TLDR; A Dual-Mode Iterative Denoiser for Crowd Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Analytics Gait Trend Measurement for Fall Prevention and Health Monitoring
Lawrence O'Gorman, Xinyi Liu, Md Imran Sarker, Mariofanna Milanova

Auto-TLDR; Towards Health Monitoring of Gait with Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PIF: Anomaly detection via preference embedding
Filippo Leveni, Luca Magri, Giacomo Boracchi, Cesare Alippi

Auto-TLDR; PIF: Anomaly Detection with Preference Embedding for Structured Patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Open-World Group Retrieval with Ambiguity Removal: A Benchmark
Ling Mei, Jian-Huang Lai, Zhanxiang Feng, Xiaohua Xie

Auto-TLDR; P2GSM-AR: Re-identifying changing groups of people under the open-world and group-ambiguity scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Story Comparison for Estimating Field of View Overlap in a Video Collection
Thierry Malon, Sylvie Chambon, Alain Crouzil, Vincent Charvillat

Auto-TLDR; Finding Videos with Overlapping Fields of View Using Video Data
Automatic Annotation of Corpora for Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions Analysis
Alex Mircoli, Claudia Diamantini, Domenico Potena, Emanuele Storti

Auto-TLDR; Automatic annotation of video subtitles on the basis of facial expressions using machine learning algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attribute-Based Quality Assessment for Demographic Estimation in Face Videos
Fabiola Becerra-Riera, Annette Morales-González, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Jean-Luc Dugelay
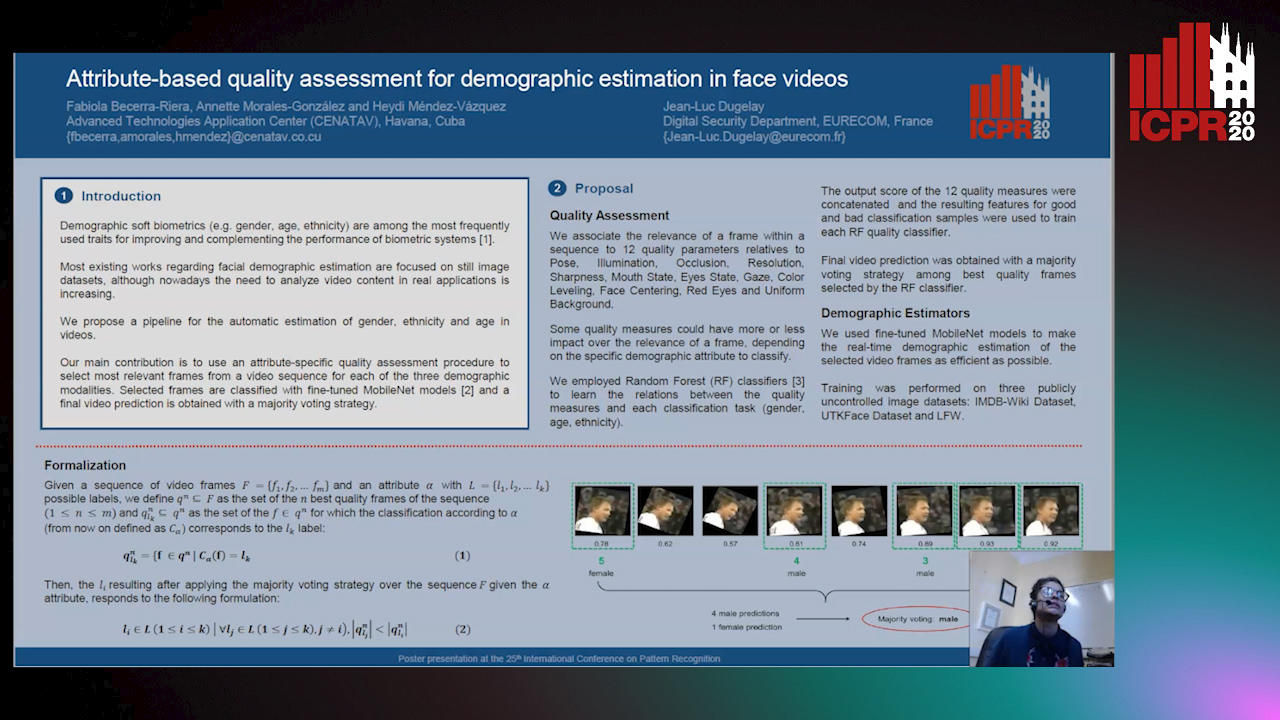
Auto-TLDR; Facial Demographic Estimation in Video Scenarios Using Quality Assessment
Fall Detection by Human Pose Estimation and Kinematic Theory
Vincenzo Dentamaro, Donato Impedovo, Giuseppe Pirlo

Auto-TLDR; A Decision Support System for Automatic Fall Detection on Le2i and URFD Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
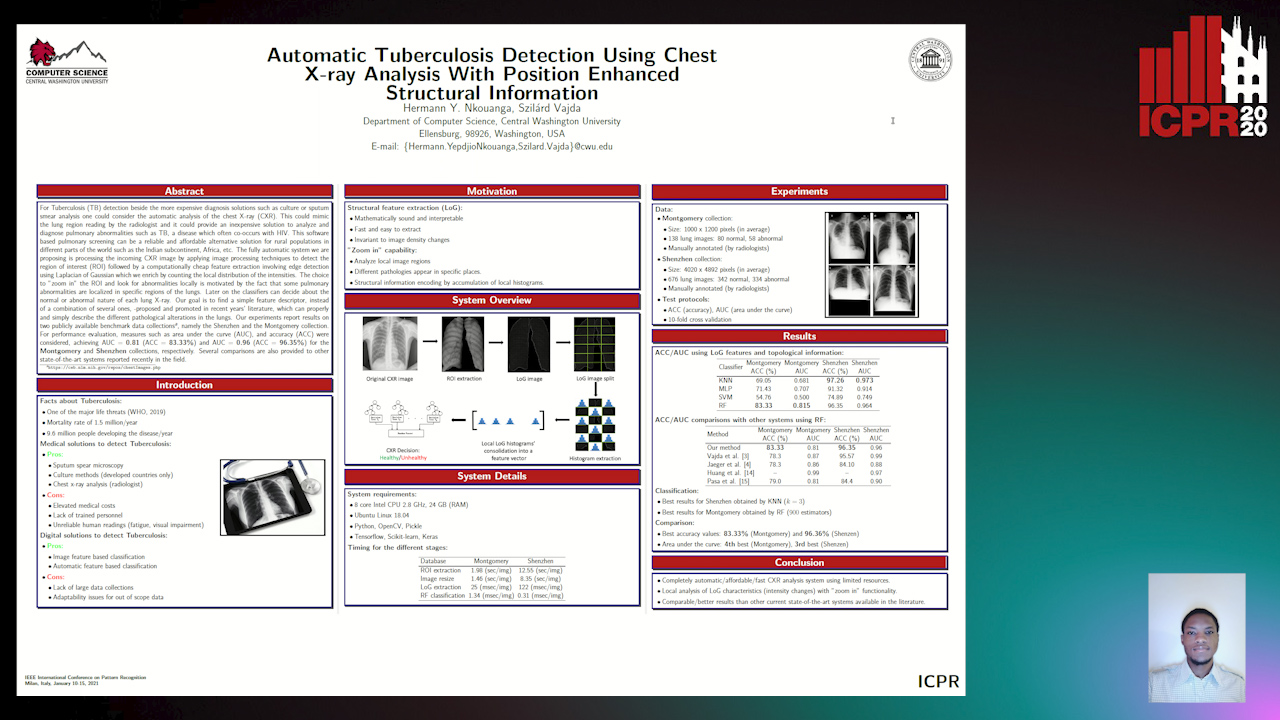
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Resource-Aware Corner Detection for Bio-Inspired Vision Sensors
Sherif Abdelmonem Sayed Mohamed, Jawad Yasin, Mohammad-Hashem Haghbayan, Antonio Miele, Jukka Veikko Heikkonen, Hannu Tenhunen, Juha Plosila

Auto-TLDR; Three Layer Filtering-Harris Algorithm for Event-based Cameras in Real-Time
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Merged 1D-2D Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Nerve Detection in Ultrasound Images
Mohammad Alkhatib, Adel Hafiane, Pierre Vieyres

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Deep Neural Networks to Detect Median Nerve in Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Evaluation of Anomaly Detection Algorithms for the Real-World Applications
Marija Ivanovska, Domen Tabernik, Danijel Skocaj, Janez Pers

Auto-TLDR; Evaluating Anomaly Detection Algorithms for Practical Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Crowdsourced Verification for Operating Calving Surveillance Systems at an Early Stage
Yusuke Okimoto, Soshi Kawata, Susumu Saito, Nakano Teppei, Tetsuji Ogawa

Auto-TLDR; Crowdsourcing for Data-Driven Video Surveillance
Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota, Alexander Stone, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Visual Voice Activity Detection with an Automatically Annotated Dataset
Stéphane Lathuiliere, Pablo Mesejo, Radu Horaud

Auto-TLDR; Deep Visual Voice Activity Detection with Optical Flow
PHNet: Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Shiqiao Meng, Jiajie Li, Weiwei Guo, Jinfeng Jiang, Lai Ye

Auto-TLDR; PHNet: A Parasite-Host Network for Video Crowd Counting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantified Facial Temporal-Expressiveness Dynamics for Affect Analysis
Md Taufeeq Uddin, Shaun Canavan

Auto-TLDR; quantified facial Temporal-expressiveness Dynamics for quantified affect analysis
IPT: A Dataset for Identity Preserved Tracking in Closed Domains
Thomas Heitzinger, Martin Kampel
Auto-TLDR; Identity Preserved Tracking Using Depth Data for Privacy and Privacy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Toward Building a Data-Driven System ForDetecting Mounting Actions of Black Beef Cattle
Yuriko Kawano, Susumu Saito, Nakano Teppei, Ikumi Kondo, Ryota Yamazaki, Hiromi Kusaka, Minoru Sakaguchi, Tetsuji Ogawa

Auto-TLDR; Cattle Mounting Action Detection Using Crowdsourcing and Pattern Recognition
Uncertainty Guided Recognition of Tiny Craters on the Moon
Thorsten Wilhelm, Christian Wöhler
Auto-TLDR; Accurately Detecting Tiny Craters in Remote Sensed Images Using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Defects in Old Movies from Manually Assisted Restoration
Arthur Renaudeau, Travis Seng, Axel Carlier, Jean-Denis Durou, Fabien Pierre, Francois Lauze, Jean-François Aujol

Auto-TLDR; U-Net: Detecting Defects in Old Movies by Inpainting Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Action Units
Malaika Vijay, Nandagopal Netrakanti Vinayak, Maanvi Nunna, Subramanyam Natarajan

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Detection of Driver Drowsiness using Facial Action Units using Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
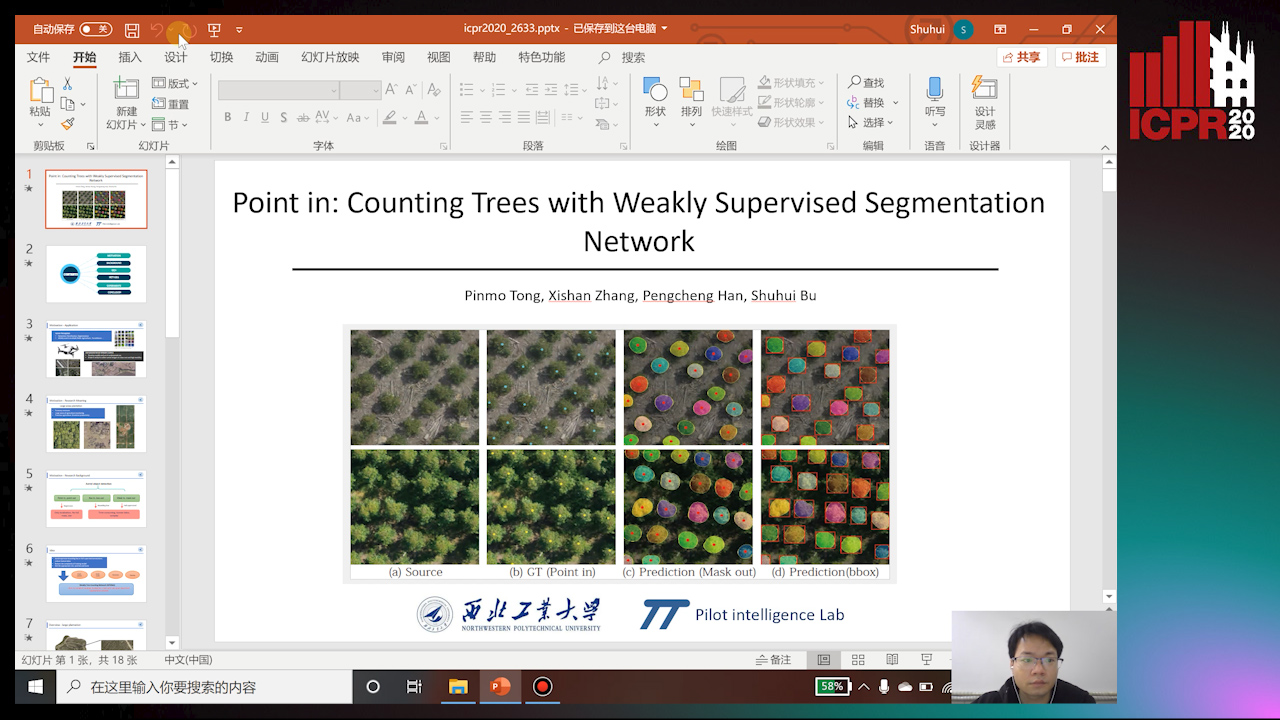
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse-To-Fine Foreground Segmentation Based on Co-Occurrence Pixel-Block and Spatio-Temporal Attention Model
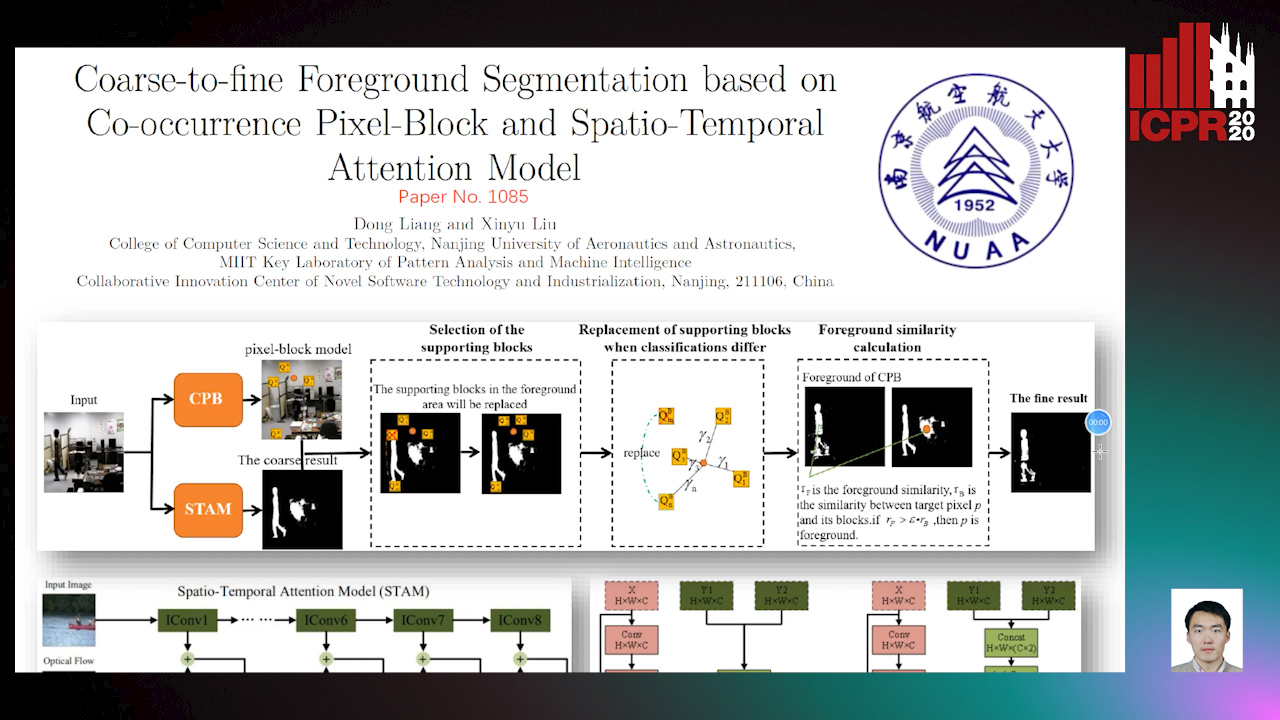
Auto-TLDR; Foreground Segmentation from coarse to Fine Using Co-occurrence Pixel-Block Model for Dynamic Scene
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Which are the factors affecting the performance of audio surveillance systems?
Antonio Greco, Antonio Roberto, Alessia Saggese, Mario Vento

Auto-TLDR; Sound Event Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Visual Representations on MIVIA Audio Events
Magnifying Spontaneous Facial Micro Expressions for Improved Recognition
Pratikshya Sharma, Sonya Coleman, Pratheepan Yogarajah, Laurence Taggart, Pradeepa Samarasinghe
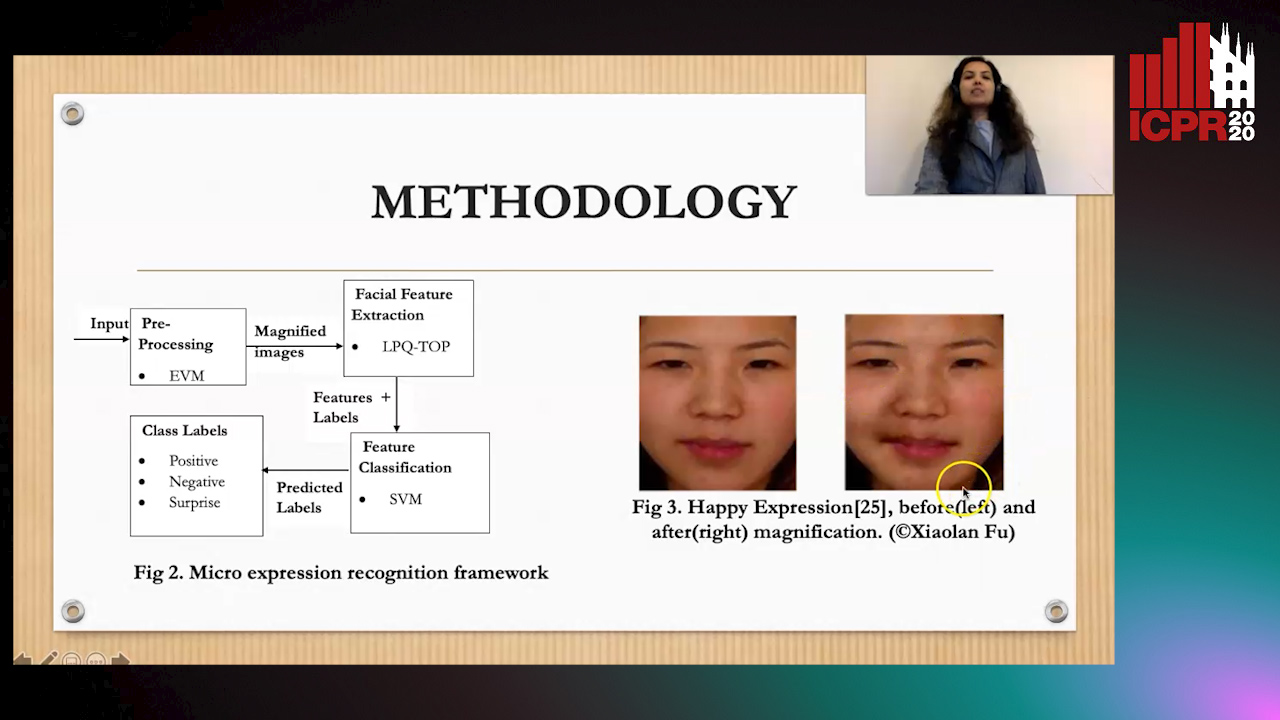
Auto-TLDR; Eulerian Video Magnification for Micro Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AerialMPTNet: Multi-Pedestrian Tracking in Aerial Imagery Using Temporal and Graphical Features
Maximilian Kraus, Seyed Majid Azimi, Emec Ercelik, Reza Bahmanyar, Peter Reinartz, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; AerialMPTNet: A novel approach for multi-pedestrian tracking in geo-referenced aerial imagery by fusing appearance features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar