Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota,
Alexander Stone,
Kenny Davila,
Srirangaraj Setlur,
Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
Similar papers
Feature Embedding Based Text Instance Grouping for Largely Spaced and Occluded Text Detection
Pan Gao, Qi Wan, Renwu Gao, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; Text Instance Embedding Based Feature Embeddings for Multiple Text Instance Grouping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Accurate Threshold Insensitive Kernel Detector for Arbitrary Shaped Text
Xijun Qian, Yifan Liu, Yu-Bin Yang

Auto-TLDR; TIKD: threshold insensitive kernel detector for arbitrary shaped text
Vision-Based Layout Detection from Scientific Literature Using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Scientific Literature Layout Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Approximate Modelling of the Next Combination Result for Stopping the Text Recognition in a Video
Konstantin Bulatov, Nadezhda Fedotova, Vladimir V. Arlazarov

Auto-TLDR; Stopping Video Stream Recognition of a Text Field Using Optimized Computation Scheme
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Not 3D Re-ID: Simple Single Stream 2D Convolution for Robust Video Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; ResNet50-IBN for Video-based Person Re-Identification using Single Stream 2D Convolution Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Text Baseline Recognition Using a Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network
Matthias Wödlinger, Robert Sablatnig

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Baseline Detection of Handwritten Text Using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised deep learning for text line segmentation
Berat Kurar Barakat, Ahmad Droby, Reem Alaasam, Borak Madi, Irina Rabaev, Raed Shammes, Jihad El-Sana
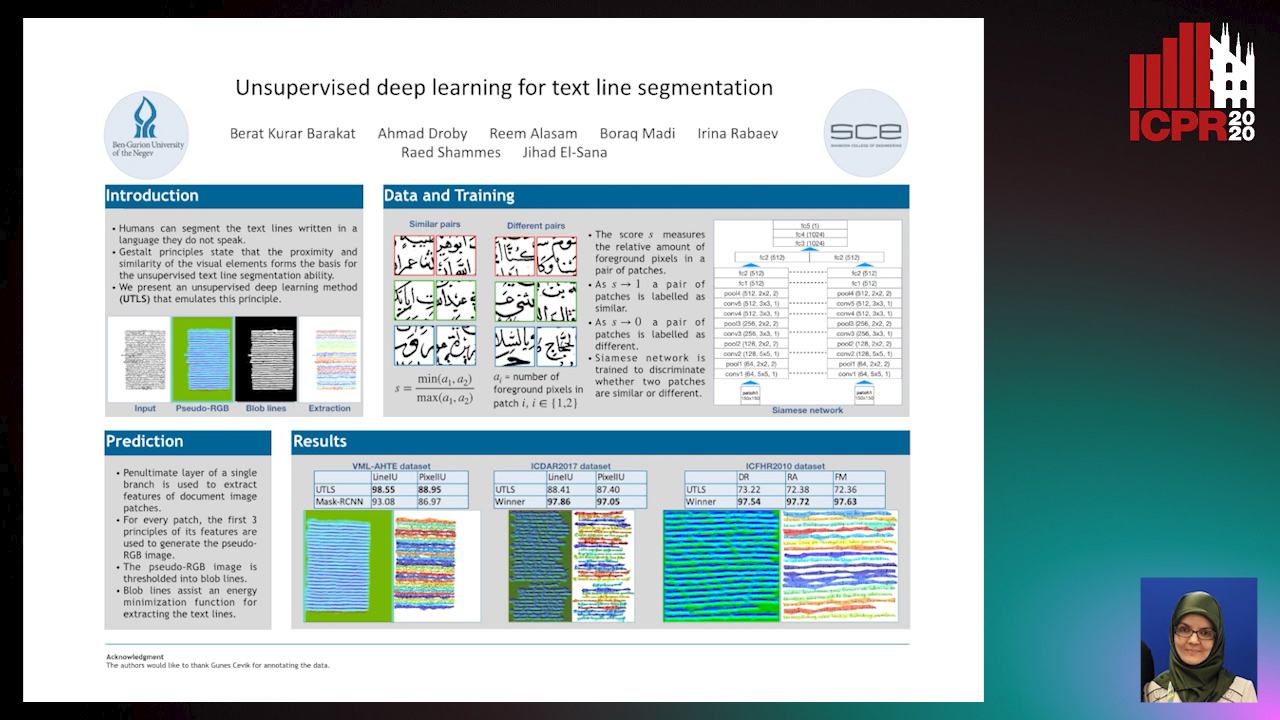
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Deep Learning for Handwritten Text Line Segmentation without Annotation
Text Recognition - Real World Data and Where to Find Them
Klára Janoušková, Lluis Gomez, Dimosthenis Karatzas, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Weakly Annotated Images for Text Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Integrated Approach of Deep Learning and Symbolic Analysis for Digital PDF Table Extraction
Mengshi Zhang, Daniel Perelman, Vu Le, Sumit Gulwani
Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning and Symbolic Reasoning for Unstructured PDF Table Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutually Guided Dual-Task Network for Scene Text Detection
Mengbiao Zhao, Wei Feng, Fei Yin, Xu-Yao Zhang, Cheng-Lin Liu

Auto-TLDR; A dual-task network for word-level and line-level text detection
Self-Training for Domain Adaptive Scene Text Detection
Yudi Chen, Wei Wang, Yu Zhou, Fei Yang, Dongbao Yang, Weiping Wang

Auto-TLDR; A self-training framework for image-based scene text detection
Recursive Recognition of Offline Handwritten Mathematical Expressions
Marco Cotogni, Claudio Cusano, Antonino Nocera

Auto-TLDR; Online Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition with Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Approach for Document Detection by Contours and Contrasts
Daniil Tropin, Sergey Ilyuhin, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov
Auto-TLDR; A countor-based method for arbitrary document detection on a mobile device
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Synopsis Generation for Egocentric Videos
Aidean Sharghi, Niels Lobo, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Egocentric Video Summarization Using Multi-task Learning for End-to-End Learning
RLST: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Scene Text Detection Refinement
Xuan Peng, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen, Jie Guo, Weidong Qiu
Auto-TLDR; Saccadic Eye Movements and Peripheral Vision for Scene Text Detection using Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Few-Shot Learning Approach for Historical Ciphered Manuscript Recognition
Mohamed Ali Souibgui, Alicia Fornés, Yousri Kessentini, Crina Tudor

Auto-TLDR; Handwritten Ciphers Recognition Using Few-Shot Object Detection
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Stratified Multi-Task Learning for Robust Spotting of Scene Texts
Kinjal Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; Feature Representation Block for Multi-task Learning of Scene Text
Learning Object Deformation and Motion Adaption for Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
Xiaoyang Zheng, Xin Tan, Jianming Guo, Lizhuang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation with Mask-propagation-based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
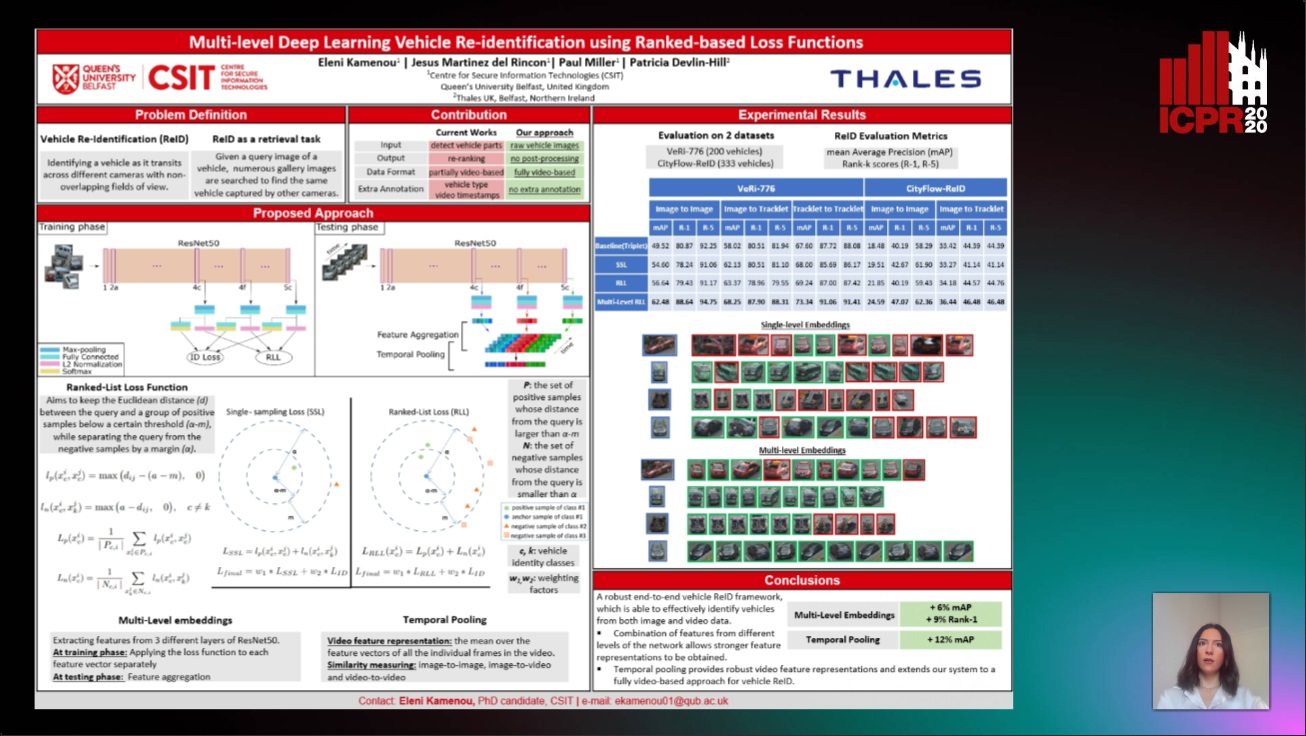
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The HisClima Database: Historical Weather Logs for Automatic Transcription and Information Extraction
Verónica Romero, Joan Andreu Sánchez

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Handwritten Text Recognition and Information Extraction from Historical Weather Logs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Story Comparison for Estimating Field of View Overlap in a Video Collection
Thierry Malon, Sylvie Chambon, Alain Crouzil, Vincent Charvillat

Auto-TLDR; Finding Videos with Overlapping Fields of View Using Video Data
Writer Identification Using Deep Neural Networks: Impact of Patch Size and Number of Patches
Akshay Punjabi, José Ramón Prieto Fontcuberta, Enrique Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Writer Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SynDHN: Multi-Object Fish Tracker Trained on Synthetic Underwater Videos
Mygel Andrei Martija, Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Underwater Multi-Object Tracking in the Wild with Deep Hungarian Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PICK: Processing Key Information Extraction from Documents Using Improved Graph Learning-Convolutional Networks
Wenwen Yu, Ning Lu, Xianbiao Qi, Ping Gong, Rong Xiao

Auto-TLDR; PICK: A Graph Learning Framework for Key Information Extraction from Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Equation Attention Relationship Network (EARN) : A Geometric Deep Metric Framework for Learning Similar Math Expression Embedding
Saleem Ahmed, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; Representational Learning for Similarity Based Retrieval of Mathematical Expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ActionSpotter: Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Temporal Action Spotting in Videos
Guillaume Vaudaux-Ruth, Adrien Chan-Hon-Tong, Catherine Achard

Auto-TLDR; ActionSpotter: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Action Spotting in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression by Learning Feature Embeddings

Auto-TLDR; FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression for Multiple Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Defects in Old Movies from Manually Assisted Restoration
Arthur Renaudeau, Travis Seng, Axel Carlier, Jean-Denis Durou, Fabien Pierre, Francois Lauze, Jean-François Aujol

Auto-TLDR; U-Net: Detecting Defects in Old Movies by Inpainting Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Relevance Detection in Cataract Surgery Videos by Spatio-Temporal Action Localization
Negin Ghamsarian, Mario Taschwer, Doris Putzgruber, Stephanie. Sarny, Klaus Schoeffmann

Auto-TLDR; relevance-based retrieval in cataract surgery videos
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Word Recognition Using Multiple Hypotheses and Deep Embeddings
Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; EmbedNet: fuse recognition-based and recognition-free approaches for word recognition using learning-based methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The DeepScoresV2 Dataset and Benchmark for Music Object Detection
Lukas Tuggener, Yvan Putra Satyawan, Alexander Pacha, Jürgen Schmidhuber, Thilo Stadelmann

Auto-TLDR; DeepScoresV2: an extended version of the DeepScores dataset for optical music recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Based Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval with Audio Similarity Learning
Pavlos Avgoustinakis, Giorgos Kordopatis-Zilos, Symeon Papadopoulos, Andreas L. Symeonidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; AuSiL: Audio Similarity Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Carlos Roig Mari, David Varas, Issey Masuda, Juan Carlos Riveiro, Elisenda Bou-Balust

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ConvMath : A Convolutional Sequence Network for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Zuoyu Yan, Xiaode Zhang, Liangcai Gao, Ke Yuan, Zhi Tang
Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Sequence Modeling for Mathematical Expressions Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TCATD: Text Contour Attention for Scene Text Detection
Ziling Hu, Wu Xingjiao, Jing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Text Contour Attention Text Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Precise Temporal Action Localization with Quantified Temporal Structure of Actions
Chongkai Lu, Ruimin Li, Hong Fu, Bin Fu, Yihao Wang, Wai Lun Lo, Zheru Chi

Auto-TLDR; Action progression networks for temporal action detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Hierarchical Framework for Leaf Instance Segmentation: Application to Plant Phenotyping
Swati Bhugra, Kanish Garg, Santanu Chaudhury, Brejesh Lall

Auto-TLDR; Under-segmentation of plant image using a graph based formulation to extract leaf shape knowledge for the task of leaf instance segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Pyramid Hierarchies for Multi-Scale Temporal Action Detection
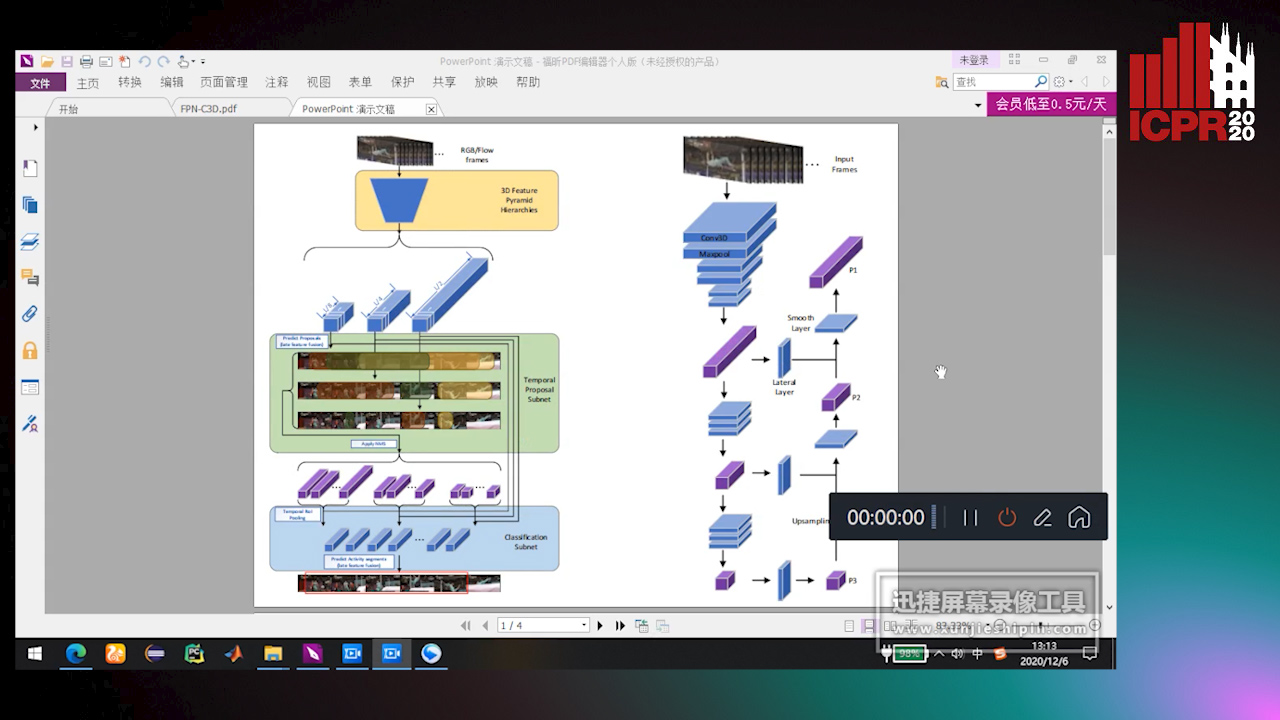
Auto-TLDR; Temporal Action Detection using Pyramid Hierarchies and Multi-scale Feature Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar