ActionSpotter: Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Temporal Action Spotting in Videos
Guillaume Vaudaux-Ruth,
Adrien Chan-Hon-Tong,
Catherine Achard

Auto-TLDR; ActionSpotter: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Action Spotting in Video
Similar papers
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Pyramid Hierarchies for Multi-Scale Temporal Action Detection
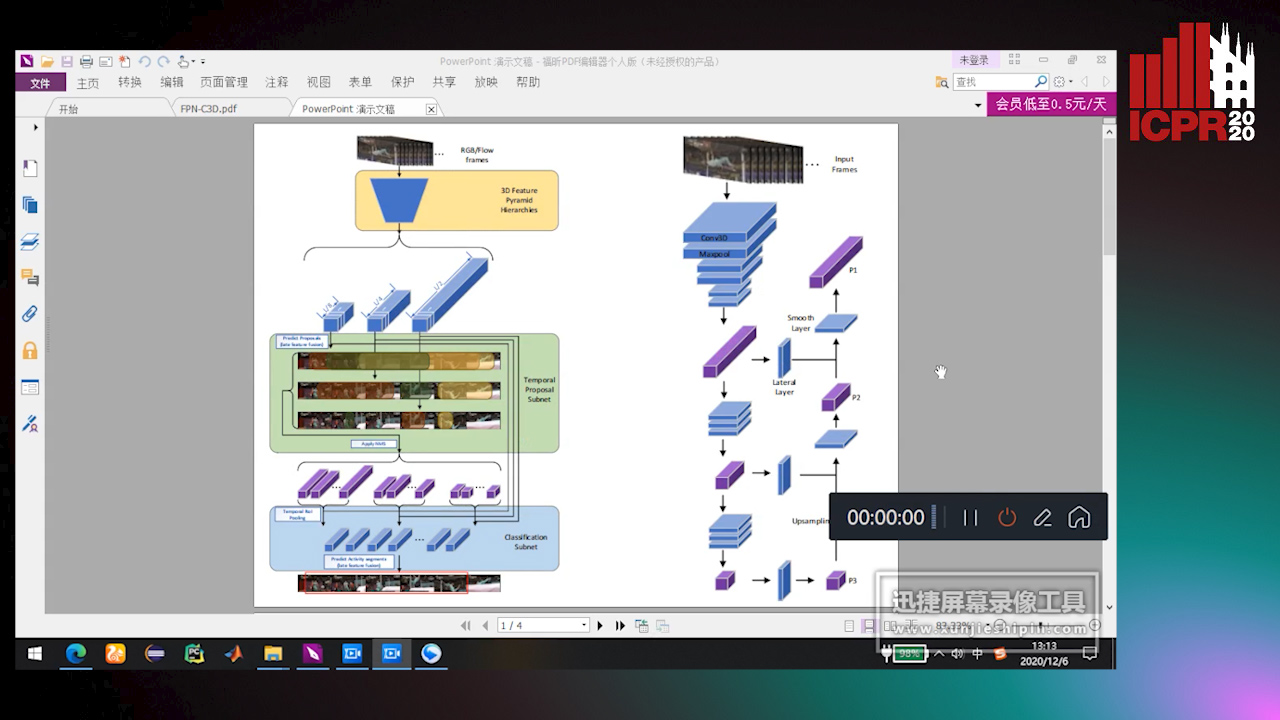
Auto-TLDR; Temporal Action Detection using Pyramid Hierarchies and Multi-scale Feature Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Precise Temporal Action Localization with Quantified Temporal Structure of Actions
Chongkai Lu, Ruimin Li, Hong Fu, Bin Fu, Yihao Wang, Wai Lun Lo, Zheru Chi

Auto-TLDR; Action progression networks for temporal action detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
You Ought to Look Around: Precise, Large Span Action Detection
Ge Pan, Zhang Han, Fan Yu, Yonghong Song, Yuanlin Zhang, Han Yuan

Auto-TLDR; YOLA: Local Feature Extraction for Action Localization with Variable receptive field
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Bayesian Approach to Reinforcement Learning of Vision-Based Vehicular Control
Zahra Gharaee, Karl Holmquist, Linbo He, Michael Felsberg

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object-Oriented Map Exploration and Construction Based on Auxiliary Task Aided DRL
Junzhe Xu, Jianhua Zhang, Shengyong Chen, Honghai Liu

Auto-TLDR; Auxiliary Task Aided Deep Reinforcement Learning for Environment Exploration by Autonomous Robots
Multi-Scale 2D Representation Learning for Weakly-Supervised Moment Retrieval
Ding Li, Rui Wu, Zhizhong Zhang, Yongqiang Tang, Wensheng Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale 2D Representation Learning for Weakly Supervised Video Moment Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Object Tracking in Drone Images with Deep Reinforcement Learning

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Reinforcement Learning based Single Object Tracker for Drone Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning from Learners: Adapting Reinforcement Learning Agents to Be Competitive in a Card Game
Pablo Vinicius Alves De Barros, Ana Tanevska, Alessandra Sciutti

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Reinforcement Learning for Competitive Card Games
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty-Sensitive Activity Recognition: A Reliability Benchmark and the CARING Models
Alina Roitberg, Monica Haurilet, Manuel Martinez, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; CARING: Calibrated Action Recognition with Input Guidance
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Relevance Detection in Cataract Surgery Videos by Spatio-Temporal Action Localization
Negin Ghamsarian, Mario Taschwer, Doris Putzgruber, Stephanie. Sarny, Klaus Schoeffmann

Auto-TLDR; relevance-based retrieval in cataract surgery videos
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Actor Dual-Critic Model for Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Ruchika Chavhan, Biplab Banerjee, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Subhasis Chaudhuri
Auto-TLDR; Actor Dual-Critic Training for Remote Sensing Image Captioning Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Reinforcement Learning on a Budget: 3D Control and Reasoning without a Supercomputer
Edward Beeching, Jilles Steeve Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin, Christian Wolf

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning in Mobile Robots Using 3D Environment Scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Group Activities from Skeletons without Individual Action Labels
Fabio Zappardino, Tiberio Uricchio, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Lean Pose Only for Group Activity Recognition
RLST: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Scene Text Detection Refinement
Xuan Peng, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen, Jie Guo, Weidong Qiu
Auto-TLDR; Saccadic Eye Movements and Peripheral Vision for Scene Text Detection using Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D Deep Video Capsule Network with Temporal Shift for Action Recognition
Théo Voillemin, Hazem Wannous, Jean-Philippe Vandeborre

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Shift Module over Capsule Network for Action Recognition in Continuous Videos
Text Synopsis Generation for Egocentric Videos
Aidean Sharghi, Niels Lobo, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Egocentric Video Summarization Using Multi-task Learning for End-to-End Learning
Vacant Parking Space Detection Based on Task Consistency and Reinforcement Learning
Manh Hung Nguyen, Tzu-Yin Chao, Ching-Chun Huang
Auto-TLDR; Vacant Space Detection via Semantic Consistency Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Object Deformation and Motion Adaption for Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
Xiaoyang Zheng, Xin Tan, Jianming Guo, Lizhuang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation with Mask-propagation-based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation for Action Anticipation Via Label Smoothing
Guglielmo Camporese, Pasquale Coscia, Antonino Furnari, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Modal Framework for Action Anticipation using Long Short-Term Memory Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota, Alexander Stone, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
ILS-SUMM: Iterated Local Search for Unsupervised Video Summarization
Yair Shemer, Daniel Rotman, Nahum Shimkin

Auto-TLDR; ILS-SUMM: Iterated Local Search for Video Summarization
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Spatiotemporal Fine-Tuning
Kenessary Koishybay, Medet Mukushev, Anara Sandygulova

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Gloss Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Summarization with a Dual Attention Capsule Network
Hao Fu, Hongxing Wang, Jianyu Yang

Auto-TLDR; Dual Self-Attention Capsule Network for Video Summarization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Light3DPose: Real-Time Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation from Multiple Views
Alessio Elmi, Davide Mazzini, Pietro Tortella

Auto-TLDR; 3D Pose Estimation of Multiple People from a Few calibrated Camera Views using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explore and Explain: Self-Supervised Navigation and Recounting
Roberto Bigazzi, Federico Landi, Marcella Cornia, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Exploring a Photorealistic Environment for Explanation and Navigation
Meta Learning Via Learned Loss
Sarah Bechtle, Artem Molchanov, Yevgen Chebotar, Edward Thomas Grefenstette, Ludovic Righetti, Gaurav Sukhatme, Franziska Meier

Auto-TLDR; meta-learning for learning parametric loss functions that generalize across different tasks and model architectures
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar