Learning from Learners: Adapting Reinforcement Learning Agents to Be Competitive in a Card Game
Pablo Vinicius Alves De Barros,
Ana Tanevska,
Alessandra Sciutti

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Reinforcement Learning for Competitive Card Games
Similar papers
Self-Play or Group Practice: Learning to Play Alternating Markov Game in Multi-Agent System
Chin-Wing Leung, Shuyue Hu, Ho-Fung Leung

Auto-TLDR; Group Practice for Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AVD-Net: Attention Value Decomposition Network for Deep Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Zhang Yuanxin, Huimin Ma, Yu Wang
Auto-TLDR; Attention Value Decomposition Network for Cooperative Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Bayesian Approach to Reinforcement Learning of Vision-Based Vehicular Control
Zahra Gharaee, Karl Holmquist, Linbo He, Michael Felsberg

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Reinforcement Learning on a Budget: 3D Control and Reasoning without a Supercomputer
Edward Beeching, Jilles Steeve Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin, Christian Wolf

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning in Mobile Robots Using 3D Environment Scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Effect of Multi-Step Methods on Overestimation in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Lingheng Meng, Rob Gorbet, Dana Kulić

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Step DDPG for Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object-Oriented Map Exploration and Construction Based on Auxiliary Task Aided DRL
Junzhe Xu, Jianhua Zhang, Shengyong Chen, Honghai Liu

Auto-TLDR; Auxiliary Task Aided Deep Reinforcement Learning for Environment Exploration by Autonomous Robots
Low Dimensional State Representation Learning with Reward-Shaped Priors
Nicolò Botteghi, Ruben Obbink, Daan Geijs, Mannes Poel, Beril Sirmacek, Christoph Brune, Abeje Mersha, Stefano Stramigioli

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning in Robotics
Detecting and Adapting to Crisis Pattern with Context Based Deep Reinforcement Learning
Eric Benhamou, David Saltiel Saltiel, Jean-Jacques Ohana Ohana, Jamal Atif Atif

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning for Financial Crisis Detection and Dis-Investment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Meta Learning Via Learned Loss
Sarah Bechtle, Artem Molchanov, Yevgen Chebotar, Edward Thomas Grefenstette, Ludovic Righetti, Gaurav Sukhatme, Franziska Meier

Auto-TLDR; meta-learning for learning parametric loss functions that generalize across different tasks and model architectures
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving by Transferring Visual Features
Hongli Zhou, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving by Transferring Visual Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explore and Explain: Self-Supervised Navigation and Recounting
Roberto Bigazzi, Federico Landi, Marcella Cornia, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Exploring a Photorealistic Environment for Explanation and Navigation
ActionSpotter: Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Temporal Action Spotting in Videos
Guillaume Vaudaux-Ruth, Adrien Chan-Hon-Tong, Catherine Achard

Auto-TLDR; ActionSpotter: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Action Spotting in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trajectory Representation Learning for Multi-Task NMRDP Planning
Firas Jarboui, Vianney Perchet

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Non Markovian Reward Decision Processes for Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Embodied Visual Navigation in Real Environments through Habitat
Marco Rosano, Antonino Furnari, Luigi Gulino, Giovanni Maria Farinella
Auto-TLDR; Learning Navigation Policies on Real World Observations using Real World Images and Sensor and Actuation Noise
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAG-Net: Double Attentive Graph Neural Network for Trajectory Forecasting
Alessio Monti, Alessia Bertugli, Simone Calderara, Rita Cucchiara
Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Generative Model for Multi-modal Human Motion Behaviour in Urban Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vacant Parking Space Detection Based on Task Consistency and Reinforcement Learning
Manh Hung Nguyen, Tzu-Yin Chao, Ching-Chun Huang
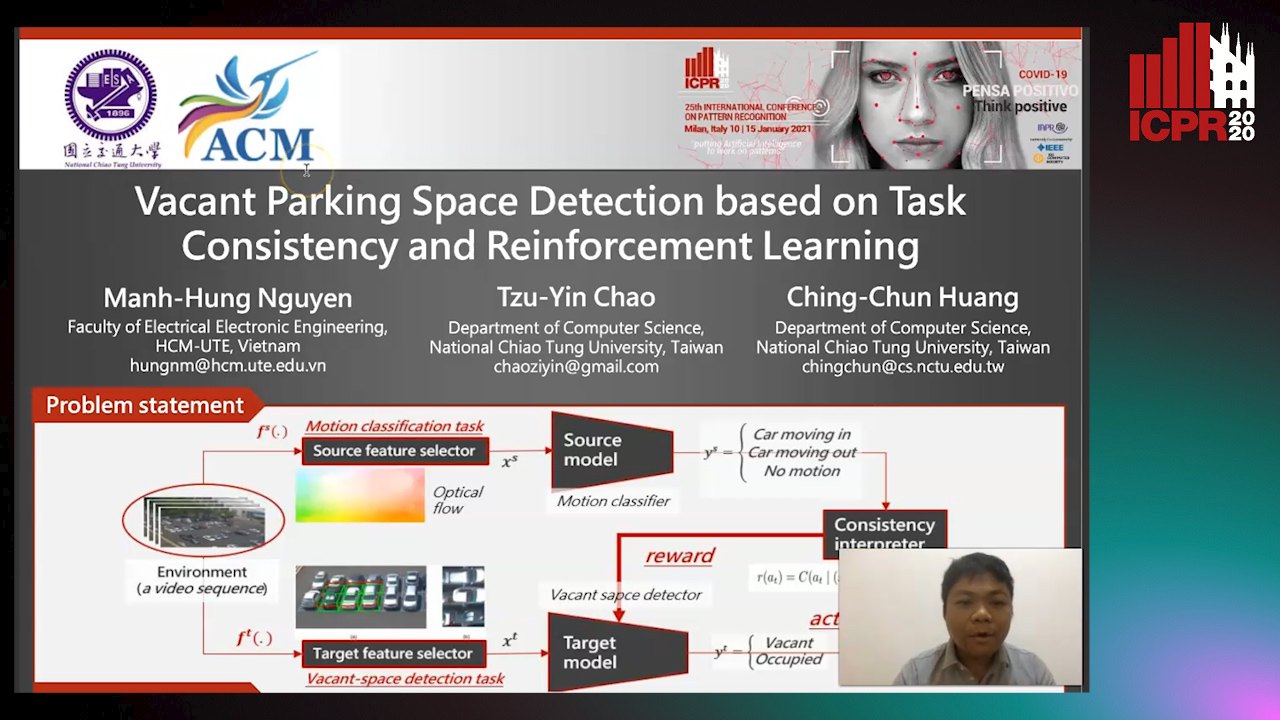
Auto-TLDR; Vacant Space Detection via Semantic Consistency Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Reinforcement Learning Lead to Healthy Life?: Simulation Study Based on User Activity Logs
Masami Takahashi, Masahiro Kohjima, Takeshi Kurashima, Hiroyuki Toda

Auto-TLDR; Reinforcement Learning for Healthy Daily Life
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Actor Dual-Critic Model for Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Ruchika Chavhan, Biplab Banerjee, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Subhasis Chaudhuri
Auto-TLDR; Actor Dual-Critic Training for Remote Sensing Image Captioning Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Remote Sensing Image Attribute Learning for Active Object Detection
Nuo Xu, Chunlei Huo, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Attribute Learning for Active Object Detection
SAILenv: Learning in Virtual Visual Environments Made Simple
Enrico Meloni, Luca Pasqualini, Matteo Tiezzi, Marco Gori, Stefano Melacci

Auto-TLDR; SAILenv: A Simple and Customized Platform for Visual Recognition in Virtual 3D Environment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Object Tracking in Drone Images with Deep Reinforcement Learning

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Reinforcement Learning based Single Object Tracker for Drone Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AOAM: Automatic Optimization of Adjacency Matrix for Graph Convolutional Network
Yuhang Zhang, Hongshuai Ren, Jiexia Ye, Xitong Gao, Yang Wang, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu

Auto-TLDR; Adjacency Matrix for Graph Convolutional Network in Non-Euclidean Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RLST: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Scene Text Detection Refinement
Xuan Peng, Zheng Huang, Kai Chen, Jie Guo, Weidong Qiu
Auto-TLDR; Saccadic Eye Movements and Peripheral Vision for Scene Text Detection using Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Intransitivity Model for Matchup and Pairwise Comparison
Yan Gu, Jiuding Duan, Hisashi Kashima

Auto-TLDR; Blade-Chest: A Low-Rank Matrix Approach for Probabilistic Ranking of Players
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Visual Question Answering Using Active Perception on Static Images
Theodoros Bozinis, Nikolaos Passalis, Anastasios Tefas

Auto-TLDR; Fine-Grained Visual Question Answering with Reinforcement Learning-based Active Perception
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning with Delayed Feedback
Pranavan Theivendiram, Terence Sim

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Machine Learning with Delayed Feedback
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ILS-SUMM: Iterated Local Search for Unsupervised Video Summarization
Yair Shemer, Daniel Rotman, Nahum Shimkin

Auto-TLDR; ILS-SUMM: Iterated Local Search for Video Summarization
Visual Prediction of Driver Behavior in Shared Road Areas
Peter Gawronski, Darius Burschka
Auto-TLDR; Predicting Vehicle Behavior in Shared Road Segment Intersections Using Topological Knowledge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multilinear Sampling Algorithm to Estimate Shapley Values
Auto-TLDR; A sampling method for Shapley values for multilayer Perceptrons
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Future Prediction Leveraging Synthetic Trajectories
Lorenzo Berlincioni, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Trajectory Prediction using Markov Chains
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Robotic Grasping on Monocular Images Via Multi-Task Learning and Positional Loss
William Prew, Toby Breckon, Magnus Bordewich, Ulrik Beierholm
Auto-TLDR; Improving grasping performance from monocularcolour images in an end-to-end CNN architecture with multi-task learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Experience Replay: A Bag of Tricks for Continual Learning
Pietro Buzzega, Matteo Boschini, Angelo Porrello, Simone Calderara

Auto-TLDR; Experience Replay for Continual Learning: A Practical Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Networks for Trajectory Forecasting
Francesco Giuliari, Hasan Irtiza, Marco Cristani, Fabio Galasso

Auto-TLDR; TransformerNetworks for Trajectory Prediction of People Interactions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Next-Best-View Planner for Cross-Season Visual Route Classification

Auto-TLDR; Active Visual Place Recognition using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Switching Dynamical Systems with Deep Neural Networks
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev, Ramses J. Sanchez

Auto-TLDR; Variational RNN for Switching Dynamics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards life-long mapping of dynamic environments using temporal persistence modeling
Georgios Tsamis, Ioannis Kostavelis, Dimitrios Giakoumis, Dimitrios Tzovaras

Auto-TLDR; Lifelong Mapping for Mobile Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Sequential Pattern Information for Active Learning from Sequential Data
Raul Fidalgo-Merino, Lorenzo Gabrielli, Enrico Checchi

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Pattern Information for Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Class-Incremental Learning with Pre-Allocated Fixed Classifiers
Federico Pernici, Matteo Bruni, Claudio Baecchi, Francesco Turchini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Class-Incremental Learning with Pre-allocated Output Nodes for Fixed Classifier
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Algorithm Recommendation for Data Streams
Jáder Martins Camboim De Sá, Andre Luis Debiaso Rossi, Gustavo Enrique De Almeida Prado Alves Batista, Luís Paulo Faina Garcia

Auto-TLDR; Meta-Learning for Algorithm Selection in Time-Changing Data Streams
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AG-GAN: An Attentive Group-Aware GAN for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Yue Song, Niccolò Bisagno, Syed Zohaib Hassan, Nicola Conci
Auto-TLDR; An attentive group-aware GAN for motion prediction in crowded scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real Time Fencing Move Classification and Detection at Touch Time During a Fencing Match
Cem Ekin Sunal, Chris G. Willcocks, Boguslaw Obara

Auto-TLDR; Fencing Body Move Classification and Detection Using Deep Learning
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Domain Generalization Baselines
Francesco Cappio Borlino, Antonio D'Innocente, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Style Transfer Data Augmentation for Domain Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Composer: A Hash-Based Duplicative Neural Network for Generating Multi-Instrument Songs
Jacob Galajda, Brandon Royal, Kien Hua

Auto-TLDR; Deep Composer for Intelligence Duplication
Multi-Attribute Learning with Highly Imbalanced Data
Lady Viviana Beltran Beltran, Mickaël Coustaty, Nicholas Journet, Juan C. Caicedo, Antoine Doucet
Auto-TLDR; Data Imbalance in Multi-Attribute Deep Learning Models: Adaptation to face each one of the problems derived from imbalance
Abstract Slides Poster Similar