Deep Next-Best-View Planner for Cross-Season Visual Route Classification

Auto-TLDR; Active Visual Place Recognition using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Similar papers
Object-Oriented Map Exploration and Construction Based on Auxiliary Task Aided DRL
Junzhe Xu, Jianhua Zhang, Shengyong Chen, Honghai Liu

Auto-TLDR; Auxiliary Task Aided Deep Reinforcement Learning for Environment Exploration by Autonomous Robots
Towards life-long mapping of dynamic environments using temporal persistence modeling
Georgios Tsamis, Ioannis Kostavelis, Dimitrios Giakoumis, Dimitrios Tzovaras

Auto-TLDR; Lifelong Mapping for Mobile Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Bayesian Approach to Reinforcement Learning of Vision-Based Vehicular Control
Zahra Gharaee, Karl Holmquist, Linbo He, Michael Felsberg

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Map-Based Temporally Consistent Geolocalization through Learning Motion Trajectories

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Motion Trajectories for Geolocalization of Object on Topological Map using Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Embodied Visual Navigation in Real Environments through Habitat
Marco Rosano, Antonino Furnari, Luigi Gulino, Giovanni Maria Farinella
Auto-TLDR; Learning Navigation Policies on Real World Observations using Real World Images and Sensor and Actuation Noise
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RISEdb: A Novel Indoor Localization Dataset
Carlos Sanchez Belenguer, Erik Wolfart, Álvaro Casado Coscollá, Vitor Sequeira

Auto-TLDR; Indoor Localization Using LiDAR SLAM and Smartphones: A Benchmarking Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Low Dimensional State Representation Learning with Reward-Shaped Priors
Nicolò Botteghi, Ruben Obbink, Daan Geijs, Mannes Poel, Beril Sirmacek, Christoph Brune, Abeje Mersha, Stefano Stramigioli

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning in Robotics
Do We Really Need Scene-Specific Pose Encoders?

Auto-TLDR; Pose Regression Using Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Similarity
Loop-closure detection by LiDAR scan re-identification
Jukka Peltomäki, Xingyang Ni, Jussi Puura, Joni-Kristian Kamarainen, Heikki Juhani Huttunen

Auto-TLDR; Loop-Closing Detection from LiDAR Scans Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Benchmarking Cameras for OpenVSLAM Indoors
Kevin Chappellet, Guillaume Caron, Fumio Kanehiro, Ken Sakurada, Abderrahmane Kheddar

Auto-TLDR; OpenVSLAM: Benchmarking Camera Types for Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Future Prediction Leveraging Synthetic Trajectories
Lorenzo Berlincioni, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Trajectory Prediction using Markov Chains
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Localization for Autonomous Driving: Mapping the Accurate Location in the City Maze
Dongfang Liu, Yiming Cui, Xiaolei Guo, Wei Ding, Baijian Yang, Yingjie Chen

Auto-TLDR; Feature Voting for Robust Visual Localization in Urban Settings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
Real-Time End-To-End Lane ID Estimation Using Recurrent Networks
Ibrahim Halfaoui, Fahd Bouzaraa, Onay Urfalioglu

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time, Vision-Only Lane Identification Using Monocular Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explore and Explain: Self-Supervised Navigation and Recounting
Roberto Bigazzi, Federico Landi, Marcella Cornia, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Exploring a Photorealistic Environment for Explanation and Navigation
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trajectory Representation Learning for Multi-Task NMRDP Planning
Firas Jarboui, Vianney Perchet

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Non Markovian Reward Decision Processes for Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vacant Parking Space Detection Based on Task Consistency and Reinforcement Learning
Manh Hung Nguyen, Tzu-Yin Chao, Ching-Chun Huang
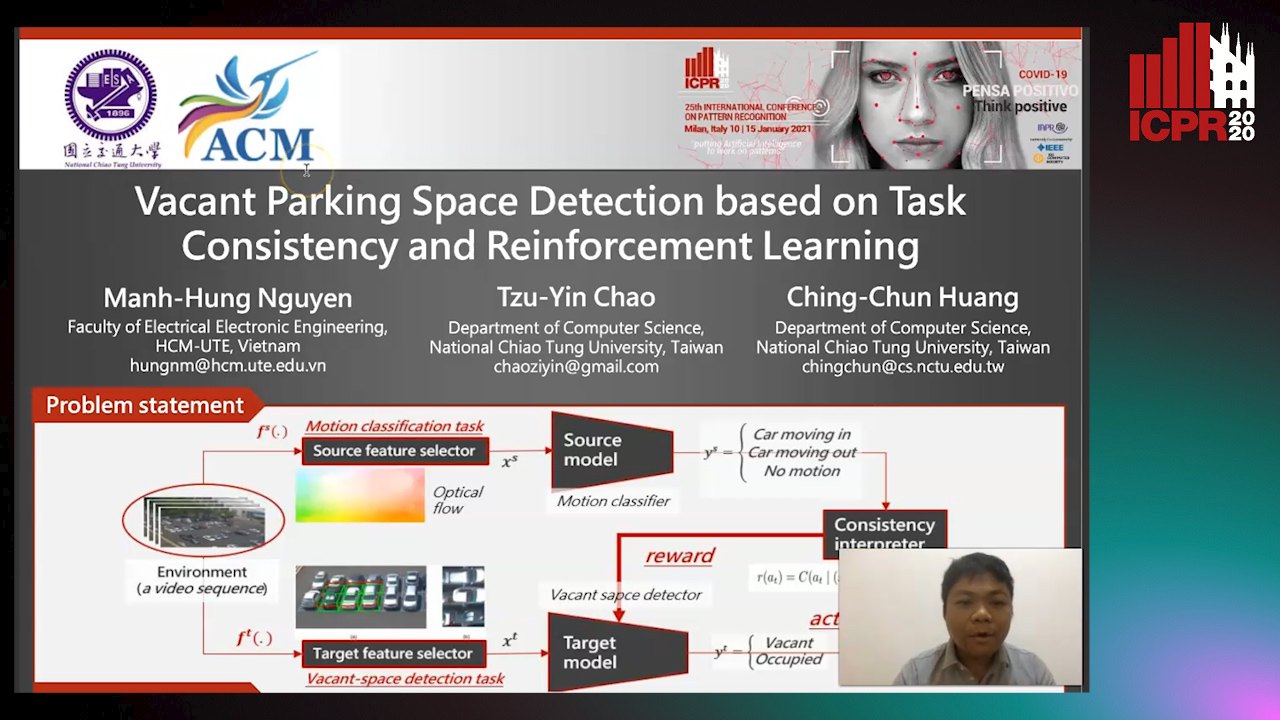
Auto-TLDR; Vacant Space Detection via Semantic Consistency Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Reinforcement Learning on a Budget: 3D Control and Reasoning without a Supercomputer
Edward Beeching, Jilles Steeve Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin, Christian Wolf

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning in Mobile Robots Using 3D Environment Scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving by Transferring Visual Features
Hongli Zhou, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving by Transferring Visual Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Shape Consistent 2D Keypoint Estimation under Domain Shift
Levi Vasconcelos, Massimiliano Mancini, Davide Boscaini, Barbara Caputo, Elisa Ricci

Auto-TLDR; Deep Adaptation for Keypoint Prediction under Domain Shift
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Fine-Grained Dataset and Its Efficient Semantic Segmentation for Unstructured Driving Scenarios
Kai Andreas Metzger, Peter Mortimer, Hans J "Joe" Wuensche

Auto-TLDR; TAS500: A Semantic Segmentation Dataset for Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2D: A Self-Supervised Method for Depth Estimation from Polarimetry
Marc Blanchon, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Daniel Braun, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Regularization for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vehicle Lane Merge Visual Benchmark
Auto-TLDR; A Benchmark for Automated Cooperative Maneuvering Using Multi-view Video Streams and Ground Truth Vehicle Description
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Robotic Grasping on Monocular Images Via Multi-Task Learning and Positional Loss
William Prew, Toby Breckon, Magnus Bordewich, Ulrik Beierholm
Auto-TLDR; Improving grasping performance from monocularcolour images in an end-to-end CNN architecture with multi-task learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Graph Embedding
Lukas Hedegaard, Omar Ali Sheikh-Omar, Alexandros Iosifidis
Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation from the Perspective of Multi-view Graph Embedding and Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Localization of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Corridor Environments Using Deep Learning
Ram Padhy, Shahzad Ahmad, Sachin Verma, Sambit Bakshi, Pankaj Kumar Sa
Auto-TLDR; A monocular vision assisted localization algorithm for indoor corridor environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can You Trust Your Pose? Confidence Estimation in Visual Localization
Luca Ferranti, Xiaotian Li, Jani Boutellier, Juho Kannala

Auto-TLDR; Pose Confidence Estimation in Large-Scale Environments: A Light-weight Approach to Improving Pose Estimation Pipeline
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Segment Dynamic Objects Using SLAM Outliers
Dupont Romain, Mohamed Tamaazousti, Hervé Le Borgne
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Segmentation of Dynamic Objects Using SLAM Outliers Using Consensus Inversion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Surface Material Dataset for Robotics Applications (SMDRA): A Dataset with Friction Coefficient and RGB-D for Surface Segmentation
Donghun Noh, Hyunwoo Nam, Min Sung Ahn, Hosik Chae, Sangjoon Lee, Kyle Gillespie, Dennis Hong
Auto-TLDR; A Surface Material Dataset for Robotics Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ActionSpotter: Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Temporal Action Spotting in Videos
Guillaume Vaudaux-Ruth, Adrien Chan-Hon-Tong, Catherine Achard

Auto-TLDR; ActionSpotter: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Action Spotting in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Segmentation Tracking from Generic Video Cues
Amirhossein Kardoost, Sabine Müller, Joachim Weickert, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; A Light-Weight Variational Framework for Video Object Segmentation in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Networks for Trajectory Forecasting
Francesco Giuliari, Hasan Irtiza, Marco Cristani, Fabio Galasso

Auto-TLDR; TransformerNetworks for Trajectory Prediction of People Interactions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stage Adaptive Object Scene Flow Using Hybrid CNN-CRF Model
Congcong Li, Haoyu Ma, Qingmin Liao

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive object scene flow estimation using a hybrid CNN-CRF model and adaptive iteration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Effective Deployment of CNNs for 3DoF Pose Estimation and Grasping in Industrial Settings
Daniele De Gregorio, Riccardo Zanella, Gianluca Palli, Luigi Di Stefano
Auto-TLDR; Automated Deep Learning for Robotic Grasping Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AV-SLAM: Autonomous Vehicle SLAM with Gravity Direction Initialization
Kaan Yilmaz, Baris Suslu, Sohini Roychowdhury, L. Srikar Muppirisetty

Auto-TLDR; VI-SLAM with AGI: A combination of three SLAM algorithms for autonomous vehicles
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Effect of Multi-Step Methods on Overestimation in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Lingheng Meng, Rob Gorbet, Dana Kulić

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Step DDPG for Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Reinforcement Learning Lead to Healthy Life?: Simulation Study Based on User Activity Logs
Masami Takahashi, Masahiro Kohjima, Takeshi Kurashima, Hiroyuki Toda

Auto-TLDR; Reinforcement Learning for Healthy Daily Life
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AerialMPTNet: Multi-Pedestrian Tracking in Aerial Imagery Using Temporal and Graphical Features
Maximilian Kraus, Seyed Majid Azimi, Emec Ercelik, Reza Bahmanyar, Peter Reinartz, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; AerialMPTNet: A novel approach for multi-pedestrian tracking in geo-referenced aerial imagery by fusing appearance features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Simple Domain Shifting Network for Generating Low Quality Images
Guruprasad Hegde, Avinash Nittur Ramesh, Kanchana Vaishnavi Gandikota, Michael Möller, Roman Obermaisser
Auto-TLDR; Robotic Image Classification Using Quality degrading networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar