Learning to Segment Dynamic Objects Using SLAM Outliers
Dupont Romain,
Mohamed Tamaazousti,
Hervé Le Borgne
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Segmentation of Dynamic Objects Using SLAM Outliers Using Consensus Inversion
Similar papers
Benchmarking Cameras for OpenVSLAM Indoors
Kevin Chappellet, Guillaume Caron, Fumio Kanehiro, Ken Sakurada, Abderrahmane Kheddar

Auto-TLDR; OpenVSLAM: Benchmarking Camera Types for Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Segmentation Tracking from Generic Video Cues
Amirhossein Kardoost, Sabine Müller, Joachim Weickert, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; A Light-Weight Variational Framework for Video Object Segmentation in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RISEdb: A Novel Indoor Localization Dataset
Carlos Sanchez Belenguer, Erik Wolfart, Álvaro Casado Coscollá, Vitor Sequeira

Auto-TLDR; Indoor Localization Using LiDAR SLAM and Smartphones: A Benchmarking Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AV-SLAM: Autonomous Vehicle SLAM with Gravity Direction Initialization
Kaan Yilmaz, Baris Suslu, Sohini Roychowdhury, L. Srikar Muppirisetty

Auto-TLDR; VI-SLAM with AGI: A combination of three SLAM algorithms for autonomous vehicles
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
Edge-Aware Monocular Dense Depth Estimation with Morphology
Zhi Li, Xiaoyang Zhu, Haitao Yu, Qi Zhang, Yongshi Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporally Smooth Dense Depth Maps Using Only a CPU
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2D: A Self-Supervised Method for Depth Estimation from Polarimetry
Marc Blanchon, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Daniel Braun, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Regularization for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Segmentation with Pairwise Matches and Unknown Number of Motions
Federica Arrigoni, Tomas Pajdla, Luca Magri

Auto-TLDR; Motion Segmentation using Multi-Modelfitting andpermutation synchronization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards life-long mapping of dynamic environments using temporal persistence modeling
Georgios Tsamis, Ioannis Kostavelis, Dimitrios Giakoumis, Dimitrios Tzovaras

Auto-TLDR; Lifelong Mapping for Mobile Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stage Adaptive Object Scene Flow Using Hybrid CNN-CRF Model
Congcong Li, Haoyu Ma, Qingmin Liao

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive object scene flow estimation using a hybrid CNN-CRF model and adaptive iteration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vehicle Lane Merge Visual Benchmark
Auto-TLDR; A Benchmark for Automated Cooperative Maneuvering Using Multi-view Video Streams and Ground Truth Vehicle Description
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Resource-Aware Corner Detection for Bio-Inspired Vision Sensors
Sherif Abdelmonem Sayed Mohamed, Jawad Yasin, Mohammad-Hashem Haghbayan, Antonio Miele, Jukka Veikko Heikkonen, Hannu Tenhunen, Juha Plosila

Auto-TLDR; Three Layer Filtering-Harris Algorithm for Event-based Cameras in Real-Time
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Can You Trust Your Pose? Confidence Estimation in Visual Localization
Luca Ferranti, Xiaotian Li, Jani Boutellier, Juho Kannala

Auto-TLDR; Pose Confidence Estimation in Large-Scale Environments: A Light-weight Approach to Improving Pose Estimation Pipeline
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
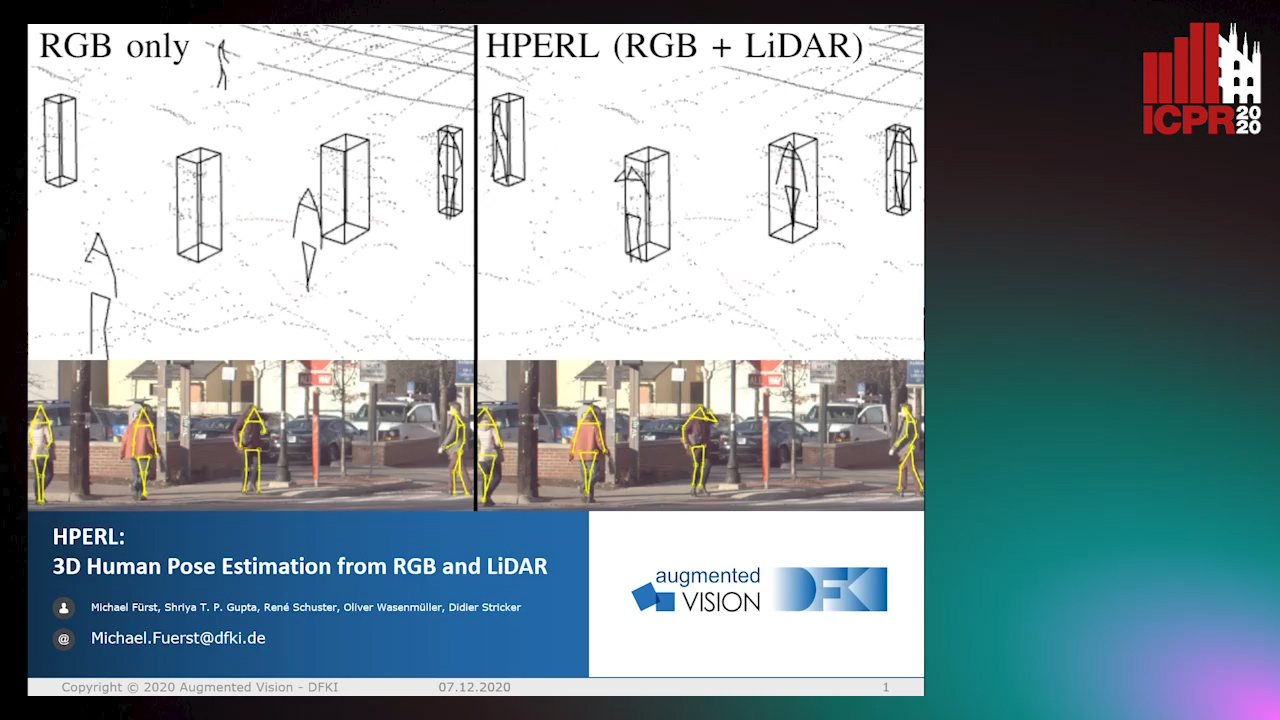
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Map-Based Temporally Consistent Geolocalization through Learning Motion Trajectories

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Motion Trajectories for Geolocalization of Object on Topological Map using Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Future Prediction Leveraging Synthetic Trajectories
Lorenzo Berlincioni, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Trajectory Prediction using Markov Chains
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partially Supervised Multi-Task Network for Single-View Dietary Assessment
Ya Lu, Thomai Stathopoulou, Stavroula Mougiakakou
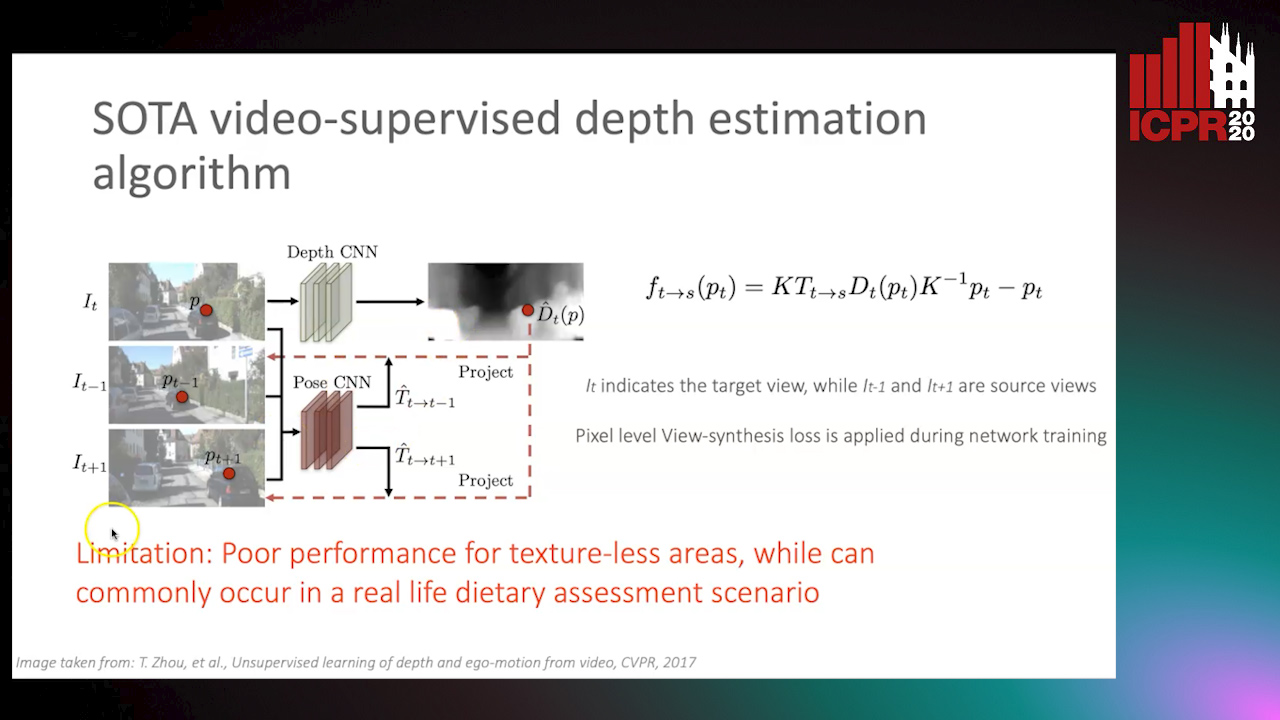
Auto-TLDR; Food Volume Estimation from a Single Food Image via Geometric Understanding and Semantic Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SECI-GAN: Semantic and Edge Completion for Dynamic Objects Removal
Francesco Pinto, Andrea Romanoni, Matteo Matteucci, Phil Torr

Auto-TLDR; SECI-GAN: Semantic and Edge Conditioned Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Severe Occlusion: Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation with Gated Convolution
Renshu Gu, Gaoang Wang, Jenq-Neng Hwang

Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation for Multi-Human Videos with Occlusion
Object-Oriented Map Exploration and Construction Based on Auxiliary Task Aided DRL
Junzhe Xu, Jianhua Zhang, Shengyong Chen, Honghai Liu

Auto-TLDR; Auxiliary Task Aided Deep Reinforcement Learning for Environment Exploration by Autonomous Robots
Total Estimation from RGB Video: On-Line Camera Self-Calibration, Non-Rigid Shape and Motion

Auto-TLDR; Joint Auto-Calibration, Pose and 3D Reconstruction of a Non-rigid Object from an uncalibrated RGB Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPT: A Dataset for Identity Preserved Tracking in Closed Domains
Thomas Heitzinger, Martin Kampel
Auto-TLDR; Identity Preserved Tracking Using Depth Data for Privacy and Privacy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation Network for Fast Video Object Segmentation
Dexiang Hong, Guorong Li, Kai Xu, Li Su, Qingming Huang

Auto-TLDR; Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Augmented Reality: Fast, Precise, and Smooth Planar Object Tracking
Dmitrii Matveichev, Daw-Tung Lin
Auto-TLDR; Planar Object Tracking with Sparse Optical Flow Tracking and Descriptor Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Future Urban Scenes Generation through Vehicles Synthesis
Alessandro Simoni, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Simone Calderara, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Predicting the Future of an Urban Scene with a Novel View Synthesis Paradigm
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAILenv: Learning in Virtual Visual Environments Made Simple
Enrico Meloni, Luca Pasqualini, Matteo Tiezzi, Marco Gori, Stefano Melacci

Auto-TLDR; SAILenv: A Simple and Customized Platform for Visual Recognition in Virtual 3D Environment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human Segmentation with Dynamic LiDAR Data
Tao Zhong, Wonjik Kim, Masayuki Tanaka, Masatoshi Okutomi
Auto-TLDR; Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Human Segmentation with Dynamic Point Clouds
Leveraging a Weakly Adversarial Paradigm for Joint Learning of Disparity and Confidence Estimation
Matteo Poggi, Fabio Tosi, Filippo Aleotti, Stefano Mattoccia

Auto-TLDR; Joint Training of Deep-Networks for Outlier Detection from Stereo Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Movement-Induced Priors for Deep Stereo
Yuxin Hou, Muhammad Kamran Janjua, Juho Kannala, Arno Solin

Auto-TLDR; Fusing Stereo Disparity Estimation with Movement-induced Prior Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Holistic Grid Fusion Based Stop Line Estimation
Runsheng Xu, Faezeh Tafazzoli, Li Zhang, Timo Rehfeld, Gunther Krehl, Arunava Seal

Auto-TLDR; Fused Multi-Sensory Data for Stop Lines Detection in Intersection Scenarios
NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu, Amnir Hadachi, Damien Vivet, Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Step Approach to Lidar-Camera Calibration
Yingna Su, Yaqing Ding, Jian Yang, Hui Kong

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Lidar-camera System for Ego-motion Estimation and Scene Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Next-Best-View Planner for Cross-Season Visual Route Classification

Auto-TLDR; Active Visual Place Recognition using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Derivation of Geometrically and Semantically Annotated UAV Datasets at Large Scales from 3D City Models
Sidi Wu, Lukas Liebel, Marco Körner
Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Dataset of Synthetic UAV Imagery for Geometric and Semantic Annotation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Localization of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Corridor Environments Using Deep Learning
Ram Padhy, Shahzad Ahmad, Sachin Verma, Sambit Bakshi, Pankaj Kumar Sa
Auto-TLDR; A monocular vision assisted localization algorithm for indoor corridor environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Street-Map Based Validation of Semantic Segmentation in Autonomous Driving
Laura Von Rueden, Tim Wirtz, Fabian Hueger, Jan David Schneider, Nico Piatkowski, Christian Bauckhage

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation Mask Validation Using A-priori Knowledge from Street Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Find Good Correspondences of Multiple Objects
Youye Xie, Yingheng Tang, Gongguo Tang, William Hoff

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Object Inliers and Outliers for Perspective-n-Point and Object Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Deep Learning Methods for Automated Damage Detection in Extreme Events at Various Scales
Yongsheng Bai, Alper Yilmaz, Halil Sezen

Auto-TLDR; Robust Mask R-CNN for Crack Detection in Extreme Events
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ID Documents Matching and Localization with Multi-Hypothesis Constraints
Guillaume Chiron, Nabil Ghanmi, Ahmad Montaser Awal

Auto-TLDR; Identity Document Localization in the Wild Using Multi-hypothesis Exploration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar