Learning Defects in Old Movies from Manually Assisted Restoration
Arthur Renaudeau,
Travis Seng,
Axel Carlier,
Jean-Denis Durou,
Fabien Pierre,
Francois Lauze,
Jean-François Aujol

Auto-TLDR; U-Net: Detecting Defects in Old Movies by Inpainting Techniques
Similar papers
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
A Lumen Segmentation Method in Ureteroscopy Images Based on a Deep Residual U-Net Architecture
Jorge Lazo, Marzullo Aldo, Sara Moccia, Michele Catellani, Benoit Rosa, Elena De Momi, Michel De Mathelin, Francesco Calimeri
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Ureteroscopy with Residual Units
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Comparison of Neural Network Approaches for Melanoma Classification
Maria Frasca, Michele Nappi, Michele Risi, Genoveffa Tortora, Alessia Auriemma Citarella
Auto-TLDR; Classification of Melanoma Using Deep Neural Network Methodologies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ground-truthing Large Human Behavior Monitoring Datasets
Tehreem Qasim, Robert Fisher, Naeem Bhatti

Auto-TLDR; Semi-automated Groundtruthing for Large Video Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota, Alexander Stone, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
Approach for Document Detection by Contours and Contrasts
Daniil Tropin, Sergey Ilyuhin, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov
Auto-TLDR; A countor-based method for arbitrary document detection on a mobile device
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Versatile Crack Inspection Portable System Based on Classifier Ensemble and Controlled Illumination
Milind Gajanan Padalkar, Carlos Beltran-Gonzalez, Matteo Bustreo, Alessio Del Bue, Vittorio Murino

Auto-TLDR; Lighting Conditions for Crack Detection in Ceramic Tile
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NephCNN: A Deep-Learning Framework for Vessel Segmentation in Nephrectomy Laparoscopic Videos
Alessandro Casella, Sara Moccia, Chiara Carlini, Emanuele Frontoni, Elena De Momi, Leonardo Mattos

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for kidney vessel segmentation from nephrectomy laparoscopic videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Benchmark Dataset for Segmenting Liver, Vasculature and Lesions from Large-Scale Computed Tomography Data
Bo Wang, Zhengqing Xu, Wei Xu, Qingsen Yan, Liang Zhang, Zheng You

Auto-TLDR; The Biggest Treatment-Oriented Liver Cancer Dataset for Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Training of a Two-Stage Neural Network for Defect Detection
Jakob Božič, Domen Tabernik, Danijel Skocaj
Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Training of Segmentation-based Neural Network for Surface Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human Segmentation with Dynamic LiDAR Data
Tao Zhong, Wonjik Kim, Masayuki Tanaka, Masatoshi Okutomi
Auto-TLDR; Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Human Segmentation with Dynamic Point Clouds
Learning to Segment Clustered Amoeboid Cells from Brightfield Microscopy Via Multi-Task Learning with Adaptive Weight Selection
Rituparna Sarkar, Suvadip Mukherjee, Elisabeth Labruyere, Jean-Christophe Olivo-Marin
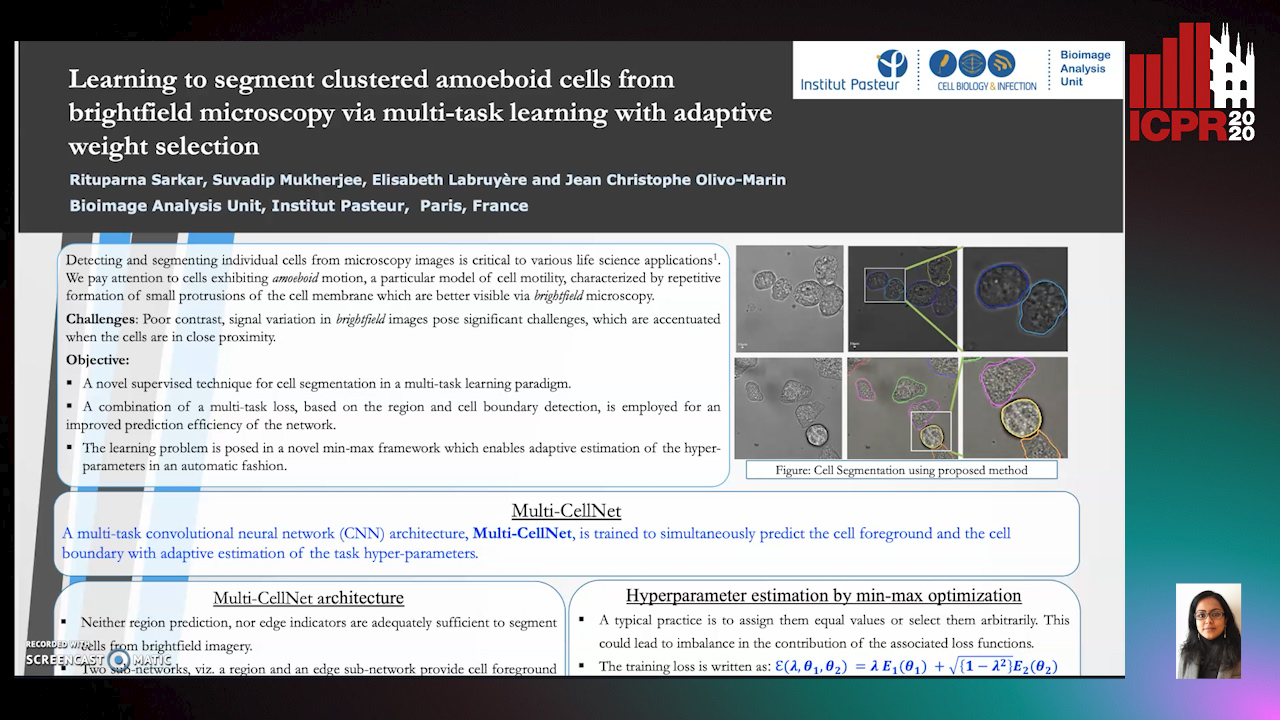
Auto-TLDR; Supervised Cell Segmentation from Microscopy Images using Multi-task Learning in a Multi-Task Learning Paradigm
Motion U-Net: Multi-Cue Encoder-Decoder Network for Motion Segmentation
Gani Rahmon, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan
Auto-TLDR; Motion U-Net: A Deep Learning Framework for Robust Moving Object Detection under Challenging Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation for Pedestrian Detection from Motion in Temporal Domain

Auto-TLDR; Motion Profile: Recognizing Pedestrians along with their Motion Directions in a Temporal Way
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved anomaly detection by training an autoencoder with skip connections on images corrupted with Stain-shaped noise
Anne-Sophie Collin, Christophe De Vleeschouwer
Auto-TLDR; Autoencoder with Skip Connections for Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A GAN-Based Blind Inpainting Method for Masonry Wall Images
Yahya Ibrahim, Balázs Nagy, Csaba Benedek

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Blind Inpainting Algorithm for Masonry Wall Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Semantic Segmentation of Structural Elements related to the Spinal Cord in the Lumbar Region by Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jhon Jairo Sáenz Gamboa, Maria De La Iglesia-Vaya, Jon Ander Gómez

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar Spine Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Moving Object Detection through Background Models for PTZ Camera
Kimin Yun, Hyung-Il Kim, Kangmin Bae, Jongyoul Park

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Moving Object Detection in a PTZ Camera through Two Background Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Realistic Novel View Generation for City-Scale Aerial Images
Koundinya Nouduri, Ke Gao, Joshua Fraser, Shizeng Yao, Hadi Aliakbarpour, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End 3D Voxel Renderer for Multi-View Stereo Data Generation and Evaluation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Coarse-To-Fine Foreground Segmentation Based on Co-Occurrence Pixel-Block and Spatio-Temporal Attention Model
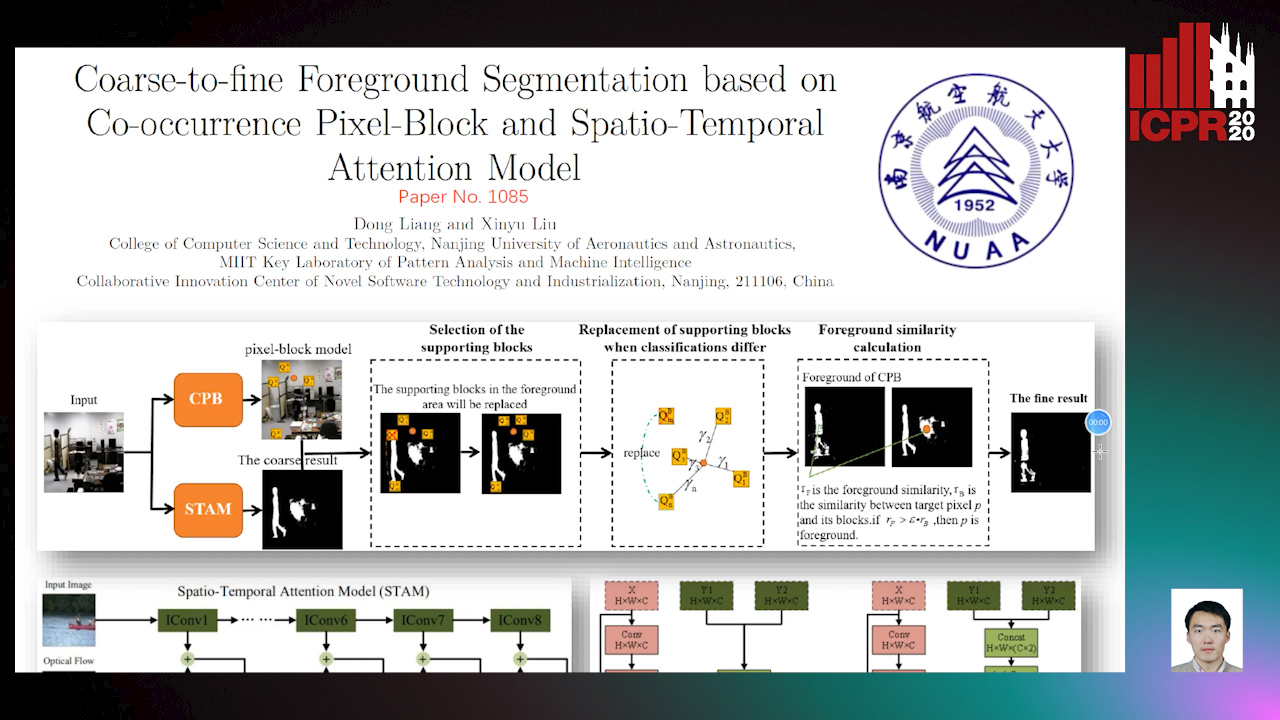
Auto-TLDR; Foreground Segmentation from coarse to Fine Using Co-occurrence Pixel-Block Model for Dynamic Scene
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GraphBGS: Background Subtraction Via Recovery of Graph Signals
Jhony Heriberto Giraldo Zuluaga, Thierry Bouwmans
Auto-TLDR; Graph BackGround Subtraction using Graph Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Anomalies from Video-Sequences: A Novel Descriptor
Giulia Orrù, Davide Ghiani, Maura Pintor, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Trit-based Measurement of Group Dynamics for Crowd Behavior Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Removing Raindrops from a Single Image Using Synthetic Data
Yoshihito Kokubo, Shusaku Asada, Hirotaka Maruyama, Masaru Koide, Kohei Yamamoto, Yoshihisa Suetsugu
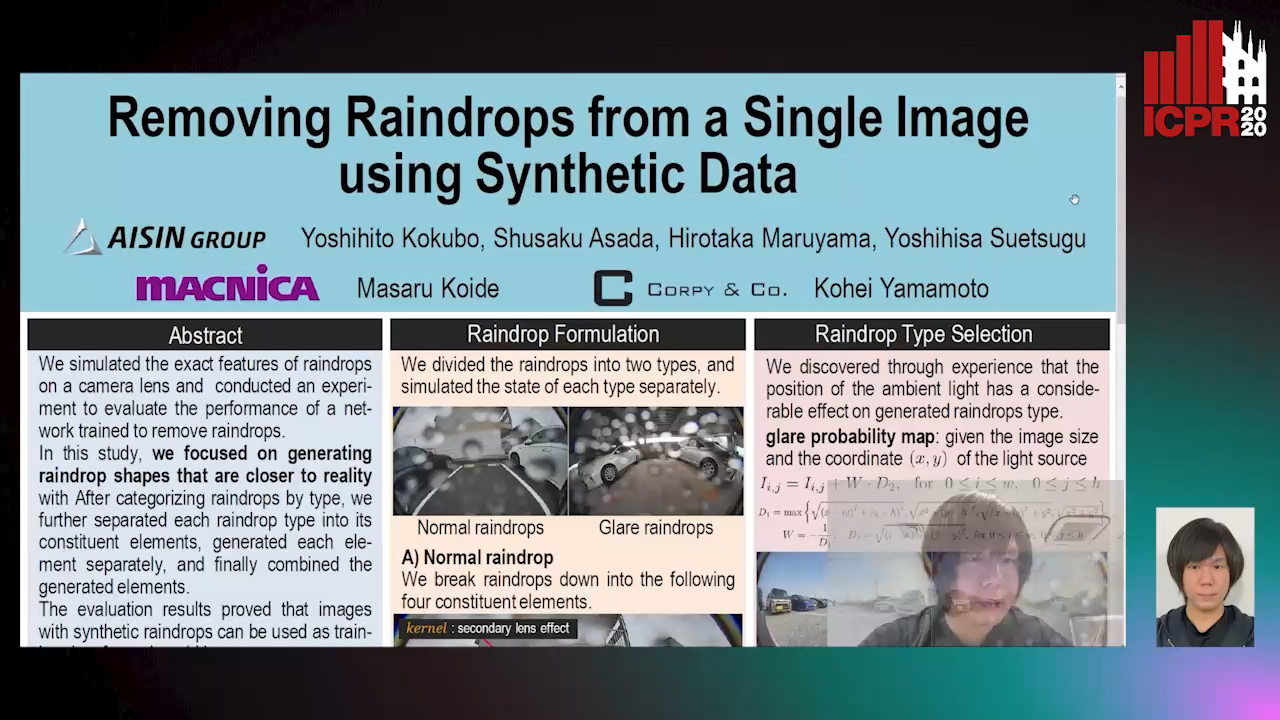
Auto-TLDR; Raindrop Removal Using Synthetic Raindrop Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Reconstruction by Spatio-Temporal Fusion of Blurred-Coded Image Pair
Anupama S, Prasan Shedligeri, Abhishek Pal, Kaushik Mitr

Auto-TLDR; Recovering Video from Motion-Blurred and Coded Exposure Images Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Complex-Object Visual Inspection: Empirical Studies on a Multiple Lighting Solution
Maya Aghaei, Matteo Bustreo, Pietro Morerio, Nicolò Carissimi, Alessio Del Bue, Vittorio Murino

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Illumination Setup for Automatic Visual Inspection of Complex Objects
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion and Region Aware Adversarial Learning for Fall Detection with Thermal Imaging
Vineet Mehta, Abhinav Dhall, Sujata Pal, Shehroz Khan

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Fall Detection with Adversarial Network using Thermal Imaging Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Machine-Learned Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation Masks
Stefano Zorzi, Ksenia Bittner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation masks using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Edge-Aware Monocular Dense Depth Estimation with Morphology
Zhi Li, Xiaoyang Zhu, Haitao Yu, Qi Zhang, Yongshi Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporally Smooth Dense Depth Maps Using Only a CPU
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Recurrent-Convolutional Model for AutomatedSegmentation of Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans
Francesca Murabito, Simone Palazzo, Federica Salanitri Proietto, Francesco Rundo, Ulas Bagci, Daniela Giordano, Rosalia Leonardi, Concetto Spampinato

Auto-TLDR; Automated Segmentation of Anatomical Structures in Craniomaxillofacial CT Scans using Fully Convolutional Deep Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TGCRBNW: A Dataset for Runner Bib Number Detection (and Recognition) in the Wild
Pablo Hernández-Carrascosa, Adrian Penate-Sanchez, Javier Lorenzo, David Freire Obregón, Modesto Castrillon

Auto-TLDR; Racing Bib Number Detection and Recognition in the Wild Using Faster R-CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FOANet: A Focus of Attention Network with Application to Myocardium Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud

Auto-TLDR; FOANet: A Hybrid Loss Function for Myocardium Segmentation of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vesselness Filters: A Survey with Benchmarks Applied to Liver Imaging
Jonas Lamy, Odyssée Merveille, Bertrand Kerautret, Nicolas Passat, Antoine Vacavant

Auto-TLDR; Comparison of Vessel Enhancement Filters for Liver Vascular Network Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DR2S: Deep Regression with Region Selection for Camera Quality Evaluation
Marcelin Tworski, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Salim Belkarfa, Attilio Fiandrotti, Marco Cagnazzo

Auto-TLDR; Texture Quality Estimation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Resource-Aware Corner Detection for Bio-Inspired Vision Sensors
Sherif Abdelmonem Sayed Mohamed, Jawad Yasin, Mohammad-Hashem Haghbayan, Antonio Miele, Jukka Veikko Heikkonen, Hannu Tenhunen, Juha Plosila

Auto-TLDR; Three Layer Filtering-Harris Algorithm for Event-based Cameras in Real-Time
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Human Embryo Cell Centroid Localization and Counting in Time-Lapse Sequences
Lisette Lockhart, Parvaneh Saeedi, Jason Au, Jon Havelock
Auto-TLDR; Automated Time-Lapse Estimation of Embryo Cell Stage in Time-lapse Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Edge-Guided CNN for Denoising Images from Portable Ultrasound Devices
Yingnan Ma, Fei Yang, Anup Basu

Auto-TLDR; Edge-Guided Convolutional Neural Network for Portable Ultrasound Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Walk the Lines: Object Contour Tracing CNN for Contour Completion of Ships

Auto-TLDR; Walk the Lines: A Convolutional Neural Network trained to follow object contours
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Story Comparison for Estimating Field of View Overlap in a Video Collection
Thierry Malon, Sylvie Chambon, Alain Crouzil, Vincent Charvillat

Auto-TLDR; Finding Videos with Overlapping Fields of View Using Video Data
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty Guided Recognition of Tiny Craters on the Moon
Thorsten Wilhelm, Christian Wöhler
Auto-TLDR; Accurately Detecting Tiny Craters in Remote Sensed Images Using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Residual Learning of Video Frame Interpolation Using Convolutional LSTM
Auto-TLDR; Video Frame Interpolation Using Residual Learning and Convolutional LSTMs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Adaptive Fusion Model Based on Kalman Filtering and LSTM for Fast Tracking of Road Signs
Chengliang Wang, Xin Xie, Chao Liao

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of ThunderNet and Region Growing Detector for Road Sign Detection and Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar