Quantified Facial Temporal-Expressiveness Dynamics for Affect Analysis
Md Taufeeq Uddin,
Shaun Canavan

Auto-TLDR; quantified facial Temporal-expressiveness Dynamics for quantified affect analysis
Similar papers
Automatic Estimation of Self-Reported Pain by Interpretable Representations of Motion Dynamics
Benjamin Szczapa, Mohammed Daoudi, Stefano Berretti, Pietro Pala, Zakia Hammal, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Pain Intensity Measurement from Facial Points Using Gram Matrices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Annotation of Corpora for Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions Analysis
Alex Mircoli, Claudia Diamantini, Domenico Potena, Emanuele Storti

Auto-TLDR; Automatic annotation of video subtitles on the basis of facial expressions using machine learning algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attribute-Based Quality Assessment for Demographic Estimation in Face Videos
Fabiola Becerra-Riera, Annette Morales-González, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Jean-Luc Dugelay
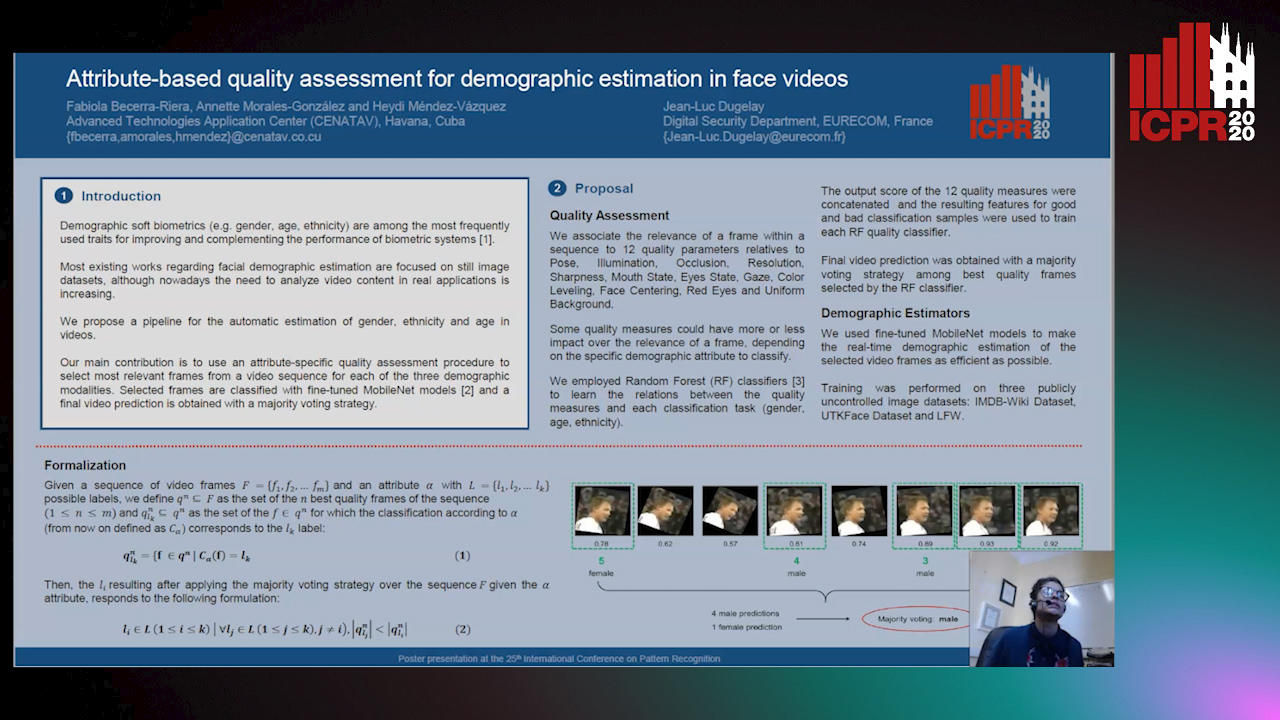
Auto-TLDR; Facial Demographic Estimation in Video Scenarios Using Quality Assessment
Interpretable Emotion Classification Using Temporal Convolutional Models
Manasi Bharat Gund, Abhiram Ravi Bharadwaj, Ifeoma Nwogu
Auto-TLDR; Understanding the Dynamics of Facial Emotion Expression with Spatiotemporal Representations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Learning of Dynamic Representations for Static Images
Siyang Song, Enrique Sanchez, Linlin Shen, Michel Valstar

Auto-TLDR; Facial Action Unit Intensity Estimation and Affect Estimation from Still Images with Multiple Temporal Scale
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Responsive Social Smile: A Machine-Learning Based Multimodal Behavior Assessment Framework towards Early Stage Autism Screening
Yueran Pan, Kunjing Cai, Ming Cheng, Xiaobing Zou, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Responsive Social Smile: A Machine Learningbased Assessment Framework for Early ASD Screening
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Emotional Blinded Face Representations
Alejandro Peña Almansa, Julian Fierrez, Agata Lapedriza, Aythami Morales

Auto-TLDR; Blind Face Representations for Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese-Structure Deep Neural Network Recognizing Changes in Facial Expression According to the Degree of Smiling
Kazuaki Kondo, Taichi Nakamura, Yuichi Nakamura, Shin'Ichi Satoh

Auto-TLDR; A Siamese-Structure Deep Neural Network for Happiness Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Nina Weng, Jiahao Wang, Annan Li, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; 2S-TCN: A Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MRP-Net: A Light Multiple Region Perception Neural Network for Multi-Label AU Detection
Yang Tang, Shuang Chen, Honggang Zhang, Gang Wang, Rui Yang

Auto-TLDR; MRP-Net: A Fast and Light Neural Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition Using Residual Masking Network
Luan Pham, Vu Huynh, Tuan Anh Tran

Auto-TLDR; Deep Residual Masking for Automatic Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition in Compressed Video
Xiaofeng Liu, Linghao Jin, Xu Han, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Facial Expression Representation in Compressed Video with Mutual Information Minimization
Learning Visual Voice Activity Detection with an Automatically Annotated Dataset
Stéphane Lathuiliere, Pablo Mesejo, Radu Horaud

Auto-TLDR; Deep Visual Voice Activity Detection with Optical Flow
Video-Based Facial Expression Recognition Using Graph Convolutional Networks
Daizong Liu, Hongting Zhang, Pan Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Network for Video-based Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sequential Non-Rigid Factorisation for Head Pose Estimation
Stefania Cristina, Kenneth Patrick Camilleri

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Shape-and-Motion Factorisation for Head Pose Estimation in Eye-Gaze Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Video Detection of the Active Speaker in Meetings
Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle, Lionel Pibre, Isabelle Ferrané

Auto-TLDR; Active Speaker Detection with Visual and Contextual Information from Meeting Context
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Action Units
Malaika Vijay, Nandagopal Netrakanti Vinayak, Maanvi Nunna, Subramanyam Natarajan

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Detection of Driver Drowsiness using Facial Action Units using Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial Bias in Vision-Based Voice Activity Detection
Kalin Stefanov, Mohammad Adiban, Giampiero Salvi
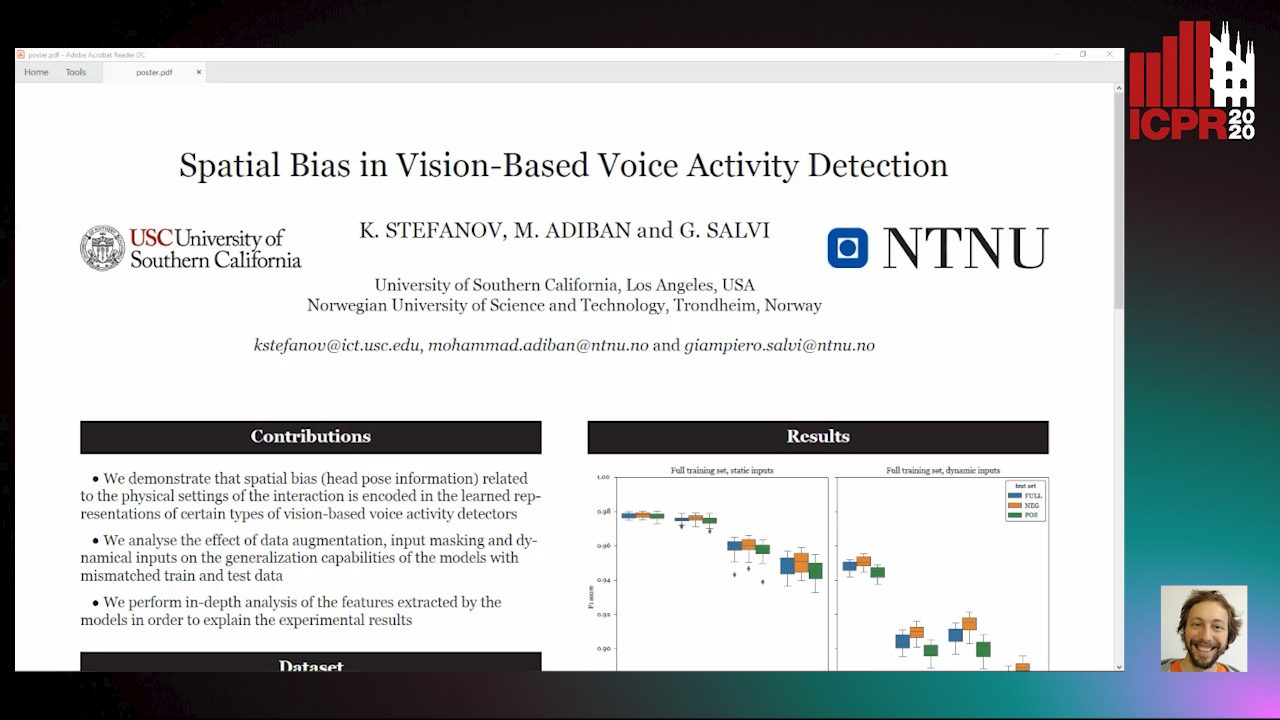
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Bias in Vision-based Voice Activity Detection in Multiparty Human-Human Interactions
A Quantitative Evaluation Framework of Video De-Identification Methods
Sathya Bursic, Alessandro D'Amelio, Marco Granato, Giuliano Grossi, Raffaella Lanzarotti

Auto-TLDR; Face de-identification using photo-reality and facial expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inner Eye Canthus Localization for Human Body Temperature Screening
Claudio Ferrari, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Localization of the Inner Eye Canthus in Thermal Face Images using 3D Morphable Face Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Anomalies from Video-Sequences: A Novel Descriptor
Giulia Orrù, Davide Ghiani, Maura Pintor, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Trit-based Measurement of Group Dynamics for Crowd Behavior Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General End-To-End Method for Characterizing Neuropsychiatric Disorders Using Free-Viewing Visual Scanning Tasks
Hong Yue Sean Liu, Jonathan Chung, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A general, data-driven, end-to-end framework that extracts relevant features of attentional bias from visual scanning behaviour and uses these features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Magnifying Spontaneous Facial Micro Expressions for Improved Recognition
Pratikshya Sharma, Sonya Coleman, Pratheepan Yogarajah, Laurence Taggart, Pradeepa Samarasinghe
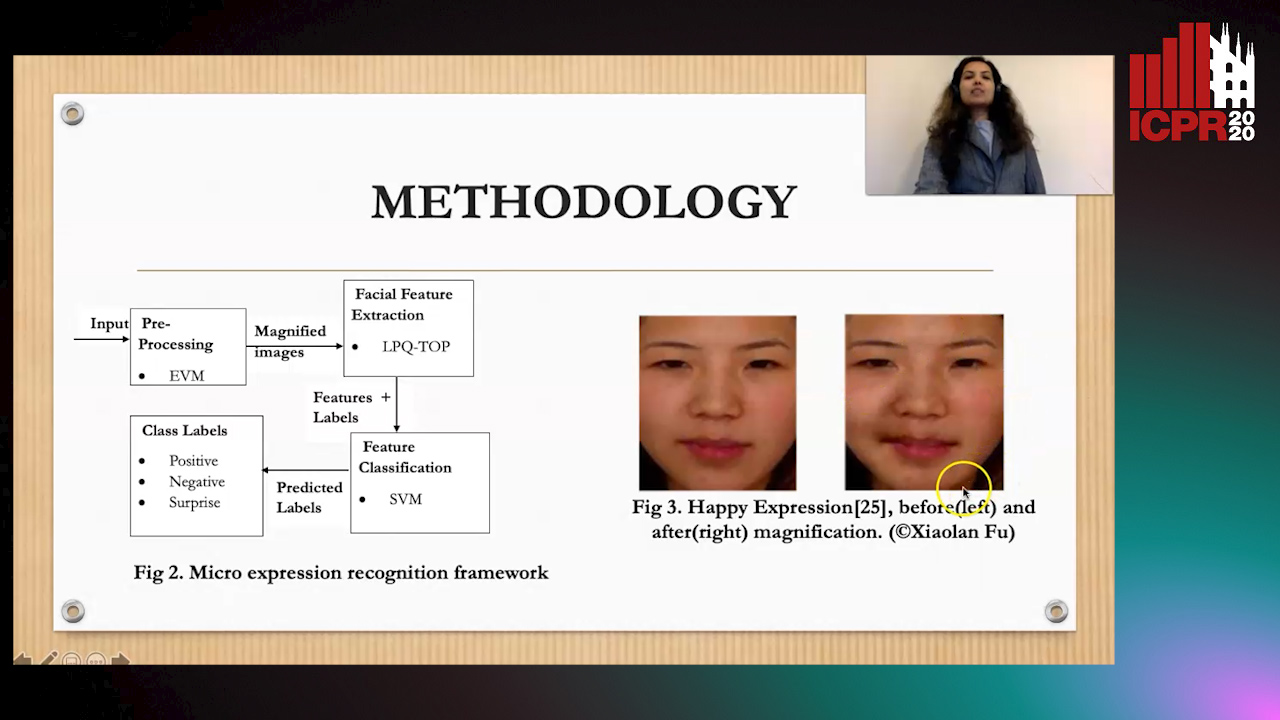
Auto-TLDR; Eulerian Video Magnification for Micro Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Multi-Task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis Based on Selective Feature Sharing
Rui Zhao, Tianshan Liu, Jun Xiao, P. K. Daniel Lun, Kin-Man Lam

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing American Sign Language Nonmanual Signal Grammar Errors in Continuous Videos
Elahe Vahdani, Longlong Jing, Ying-Li Tian, Matt Huenerfauth

Auto-TLDR; ASL-HW-RGBD: Recognizing Grammatical Errors in Continuous Sign Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AttendAffectNet: Self-Attention Based Networks for Predicting Affective Responses from Movies
Thi Phuong Thao Ha, Bt Balamurali, Herremans Dorien, Roig Gemma

Auto-TLDR; AttendAffectNet: A Self-Attention Based Network for Emotion Prediction from Movies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Using Meta Labels for the Training of Weighting Models in a Sample-Specific Late Fusion Classification Architecture
Peter Bellmann, Patrick Thiam, Friedhelm Schwenker
Auto-TLDR; A Late Fusion Architecture for Multiple Classifier Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Assessing the Severity of Health States Based on Social Media Posts
Shweta Yadav, Joy Prakash Sain, Amit Sheth, Asif Ekbal, Sriparna Saha, Pushpak Bhattacharyya

Auto-TLDR; A Multiview Learning Framework for Assessment of Health State in Online Health Communities
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unconstrained Facial Expression Recogniton Based on Cascade Decision and Gabor Filters
Yanhong Wu, Lijie Zhang, Guannan Chen, Pablo Navarrete Michelini

Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Neural Network for Facial Expression Recognition under unconstrained natural conditions
Exposing Deepfake Videos by Tracking Eye Movements
Meng Li, Beibei Liu, Yujiang Hu, Yufei Wang

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Approach to Detecting Deepfake Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Triplet Loss Based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Puneet Kumar, Sidharth Jain, Balasubramanian Raman, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Neural Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
Estimating Gaze Points from Facial Landmarks by a Remote Spherical Camera

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation from a Spherical Image from Facial Landmarks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Analytics Gait Trend Measurement for Fall Prevention and Health Monitoring
Lawrence O'Gorman, Xinyi Liu, Md Imran Sarker, Mariofanna Milanova

Auto-TLDR; Towards Health Monitoring of Gait with Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
XGBoost to Interpret the Opioid Patients’ StateBased on Cognitive and Physiological Measures
Arash Shokouhmand, Omid Dehzangi, Jad Ramadan, Victor Finomore, Nasser M. Nasarabadi, Ali Rezai
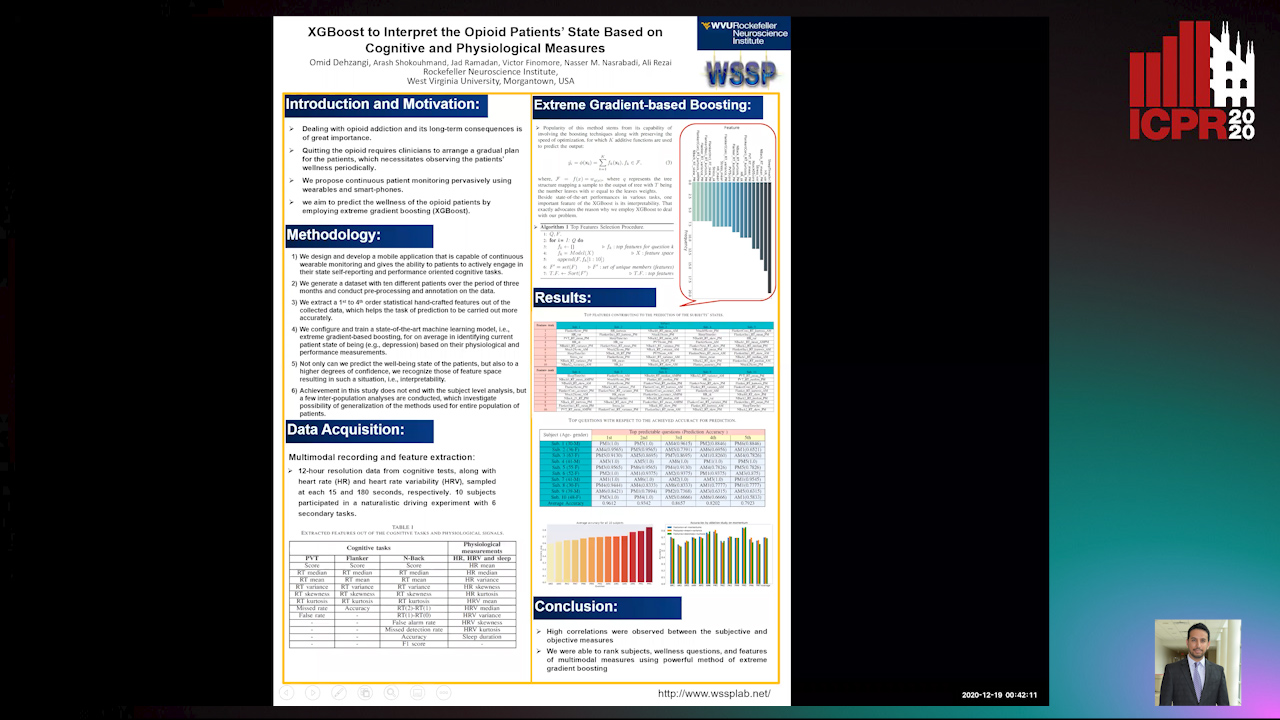
Auto-TLDR; Predicting the Wellness of Opioid Addictions Using Multi-modal Sensor Data
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inferring Functional Properties from Fluid Dynamics Features
Andrea Schillaci, Maurizio Quadrio, Carlotta Pipolo, Marcello Restelli, Giacomo Boracchi

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Convective Properties of Computational Fluid Dynamics for Medical Diagnosis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition by Using a Disentangled Identity-Invariant Expression Representation
Auto-TLDR; Transfer-based Expression Recognition Generative Adversarial Network (TER-GAN)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks