Estimating Gaze Points from Facial Landmarks by a Remote Spherical Camera

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation from a Spherical Image from Facial Landmarks
Similar papers
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
User-Independent Gaze Estimation by Extracting Pupil Parameter and Its Mapping to the Gaze Angle

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation using Pupil Shape for Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sequential Non-Rigid Factorisation for Head Pose Estimation
Stefania Cristina, Kenneth Patrick Camilleri

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Shape-and-Motion Factorisation for Head Pose Estimation in Eye-Gaze Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection and Correspondence Matching of Corneal Reflections for Eye Tracking Using Deep Learning
Soumil Chugh, Braiden Brousseau, Jonathan Rose, Moshe Eizenman

Auto-TLDR; A Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Corneal Reflection Detection and Matching in Extended Reality Eye Tracking Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exposing Deepfake Videos by Tracking Eye Movements
Meng Li, Beibei Liu, Yujiang Hu, Yufei Wang

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Approach to Detecting Deepfake Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inner Eye Canthus Localization for Human Body Temperature Screening
Claudio Ferrari, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Localization of the Inner Eye Canthus in Thermal Face Images using 3D Morphable Face Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HP2IFS: Head Pose Estimation Exploiting Partitioned Iterated Function Systems
Carmen Bisogni, Michele Nappi, Chiara Pero, Stefano Ricciardi
Auto-TLDR; PIFS based head pose estimation using fractal coding theory and Partitioned Iterated Function Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Facial Action Units
Malaika Vijay, Nandagopal Netrakanti Vinayak, Maanvi Nunna, Subramanyam Natarajan

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Detection of Driver Drowsiness using Facial Action Units using Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Distortion-Adaptive Grape Bunch Counting for Omnidirectional Images
Ryota Akai, Yuzuko Utsumi, Yuka Miwa, Masakazu Iwamura, Koichi Kise
Auto-TLDR; Object Counting for Omnidirectional Images Using Stereographic Projection
Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Video Detection of the Active Speaker in Meetings
Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle, Lionel Pibre, Isabelle Ferrané

Auto-TLDR; Active Speaker Detection with Visual and Contextual Information from Meeting Context
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Eye Tracking Data Segmentation, Generation, and Reconstruction
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Enkelejda Kasneci
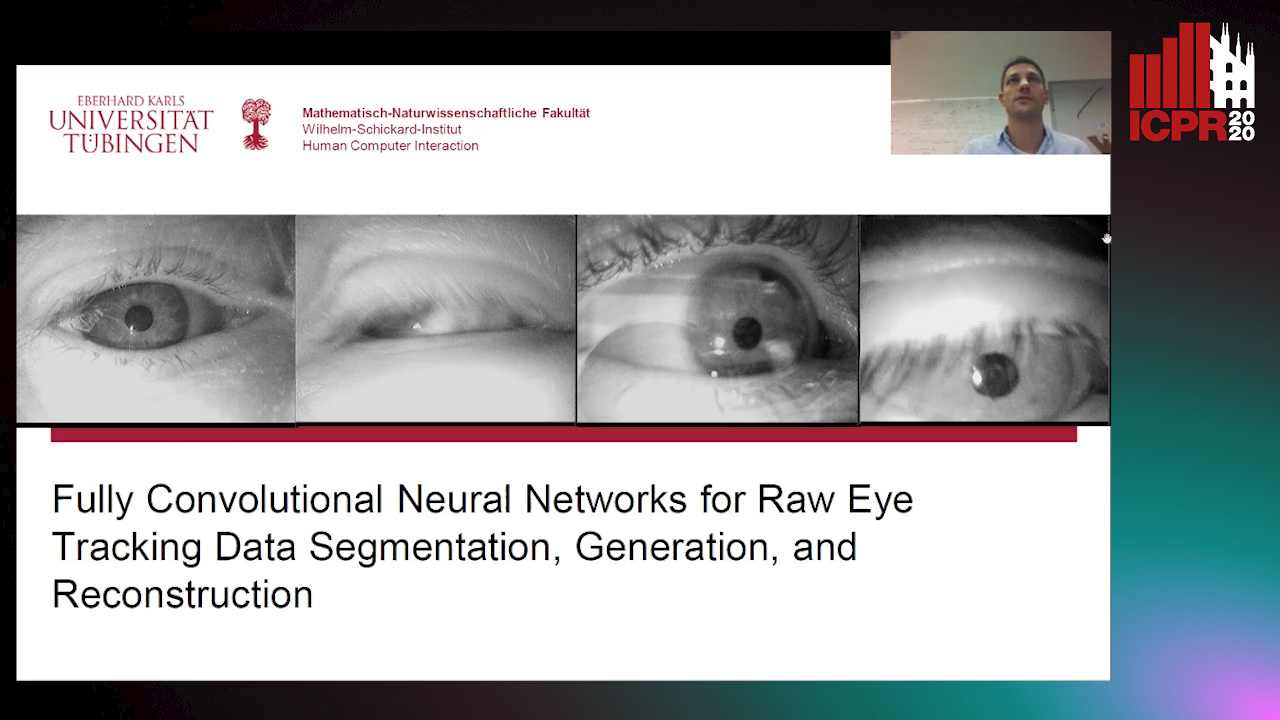
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Eye Tracking Data with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
OmniFlowNet: A Perspective Neural Network Adaptation for Optical Flow Estimation in Omnidirectional Images
Charles-Olivier Artizzu, Haozhou Zhang, Guillaume Allibert, Cédric Demonceaux

Auto-TLDR; OmniFlowNet: A Convolutional Neural Network for Omnidirectional Optical Flow Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao, Yan-Jing Lei, Chia-Hao Chang, Chu-Song Chen, Ming-Sui Lee, Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Optical Flow Estimation in 360 Videos
Keshav Bhandari, Ziliang Zong, Yan Yan
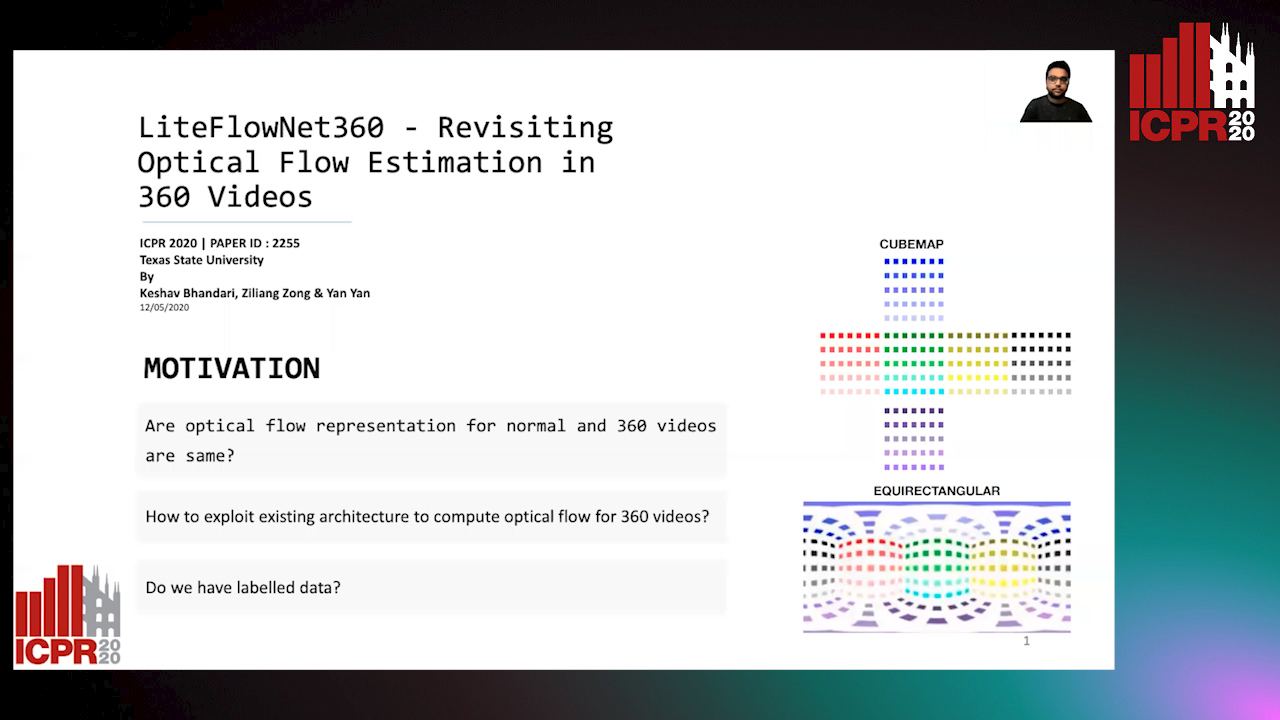
Auto-TLDR; LiteFlowNet360: A Domain Adaptation Framework for 360 Video Optical Flow Estimation
Joint Face Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction with Efficient Convolution Neural Networks
Keqiang Li, Huaiyu Wu, Xiuqin Shang, Zhen Shen, Gang Xiong, Xisong Dong, Bin Hu, Fei-Yue Wang

Auto-TLDR; Mobile-FRNet: Efficient 3D Morphable Model Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single 2D Facial Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Photometric Stereo with Twin-Fisheye Cameras
Jordan Caracotte, Fabio Morbidi, El Mustapha Mouaddib

Auto-TLDR; Photometric stereo problem for low-cost 360-degree cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Visual Voice Activity Detection with an Automatically Annotated Dataset
Stéphane Lathuiliere, Pablo Mesejo, Radu Horaud

Auto-TLDR; Deep Visual Voice Activity Detection with Optical Flow
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
A Flatter Loss for Bias Mitigation in Cross-Dataset Facial Age Estimation
Ali Akbari, Muhammad Awais, Zhenhua Feng, Ammarah Farooq, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; Cross-dataset Age Estimation for Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Ordinal Regression with Label Diversity
Axel Berg, Magnus Oskarsson, Mark Oconnor

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Regression via Classification for Neural Network Learning
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Learning of Landmarks Based on Inter-Intra Subject Consistencies
Weijian Li, Haofu Liao, Shun Miao, Le Lu, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Facial Landmark Discovery using Inter-subject Landmark consistencies
Quantified Facial Temporal-Expressiveness Dynamics for Affect Analysis
Md Taufeeq Uddin, Shaun Canavan

Auto-TLDR; quantified facial Temporal-expressiveness Dynamics for quantified affect analysis
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Locally-Connected, Irregular Deep Neural Networks for Biomimetic Active Vision in a Simulated Human
Masaki Nakada, Honglin Chen, Arjun Lakshmipathy, Demetri Terzopoulos

Auto-TLDR; Local-connected, Irregular Deep Neural Networks for biomimetic active vision
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Severe Occlusion: Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation with Gated Convolution
Renshu Gu, Gaoang Wang, Jenq-Neng Hwang

Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation for Multi-Human Videos with Occlusion
Recognizing American Sign Language Nonmanual Signal Grammar Errors in Continuous Videos
Elahe Vahdani, Longlong Jing, Ying-Li Tian, Matt Huenerfauth

Auto-TLDR; ASL-HW-RGBD: Recognizing Grammatical Errors in Continuous Sign Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Nina Weng, Jiahao Wang, Annan Li, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; 2S-TCN: A Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Jianrong Wang, Tong Wu, Shanyu Wang, Mei Yu, Qiang Fang, Ju Zhang, Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent and Text-Dependent Speaker Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Derivation of Geometrically and Semantically Annotated UAV Datasets at Large Scales from 3D City Models
Sidi Wu, Lukas Liebel, Marco Körner
Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Dataset of Synthetic UAV Imagery for Geometric and Semantic Annotation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RISEdb: A Novel Indoor Localization Dataset
Carlos Sanchez Belenguer, Erik Wolfart, Álvaro Casado Coscollá, Vitor Sequeira

Auto-TLDR; Indoor Localization Using LiDAR SLAM and Smartphones: A Benchmarking Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Light3DPose: Real-Time Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation from Multiple Views
Alessio Elmi, Davide Mazzini, Pietro Tortella

Auto-TLDR; 3D Pose Estimation of Multiple People from a Few calibrated Camera Views using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anticipating Activity from Multimodal Signals
Tiziana Rotondo, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Davide Giacalone, Sebastiano Mauro Strano, Valeria Tomaselli, Sebastiano Battiato

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Multimodal Signal Embedding Space for Multi-Action Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial Bias in Vision-Based Voice Activity Detection
Kalin Stefanov, Mohammad Adiban, Giampiero Salvi
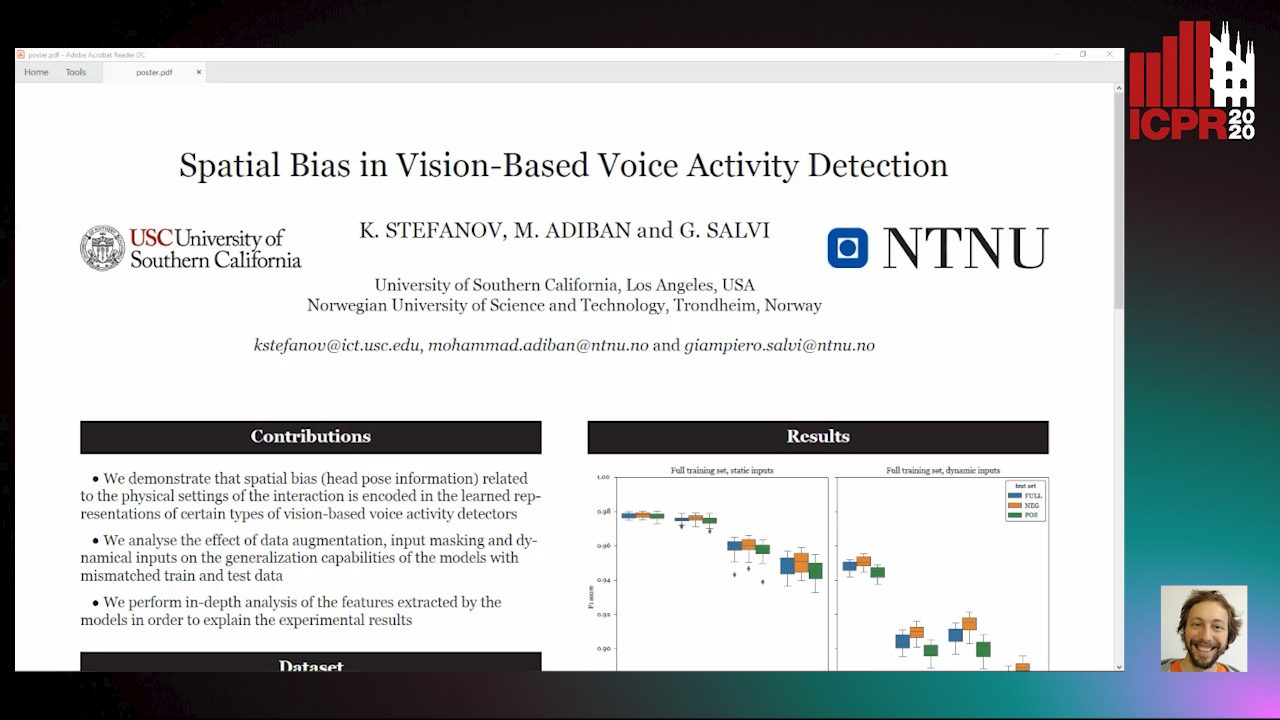
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Bias in Vision-based Voice Activity Detection in Multiparty Human-Human Interactions
Object Features and Face Detection Performance: Analyses with 3D-Rendered Synthetic Data
Jian Han, Sezer Karaoglu, Hoang-An Le, Theo Gevers

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Data for Face Detection Using 3DU Face Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2D: A Self-Supervised Method for Depth Estimation from Polarimetry
Marc Blanchon, Desire Sidibe, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Daniel Braun, Fabrice Meriaudeau

Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Regularization for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Camera Calibration Using Parallel Line Segments

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Surveillance Cameras using Parallel 3D Line Segment Projections
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Non-Rigid Surface Reconstruction from Spatio-Temporal Image Patches
Matteo Pedone, Abdelrahman Mostafa, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Dense Spatio-Temporal Depth Maps of Deformable Objects from Video Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar