Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Jianrong Wang,
Tong Wu,
Shanyu Wang,
Mei Yu,
Qiang Fang,
Ju Zhang,
Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent and Text-Dependent Speaker Recognition
Similar papers
Audio-Video Detection of the Active Speaker in Meetings
Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle, Lionel Pibre, Isabelle Ferrané

Auto-TLDR; Active Speaker Detection with Visual and Contextual Information from Meeting Context
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using a Two-Step Feature Fusion Strategy

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Step Feature Fusion Network for Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial Bias in Vision-Based Voice Activity Detection
Kalin Stefanov, Mohammad Adiban, Giampiero Salvi
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Bias in Vision-based Voice Activity Detection in Multiparty Human-Human Interactions
Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Nina Weng, Jiahao Wang, Annan Li, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; 2S-TCN: A Two-Stream Temporal Convolutional Network for Dynamic Facial Attractiveness Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Visual Voice Activity Detection with an Automatically Annotated Dataset
Stéphane Lathuiliere, Pablo Mesejo, Radu Horaud

Auto-TLDR; Deep Visual Voice Activity Detection with Optical Flow
Robust Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Based on Hybrid Fusion
Hong Liu, Wenhao Li, Bing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Hybrid Fusion Based AVSR with Residual Networks and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit for Robust Speech Recognition in Noise Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Talking Face Generation Via Learning Semantic and Temporal Synchronous Landmarks
Aihua Zheng, Feixia Zhu, Hao Zhu, Mandi Luo, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; A semantic and temporal synchronous landmark learning method for talking face generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Neural Lip-Sync Framework for Synthesizing Photorealistic Virtual News Anchors
Ruobing Zheng, Zhou Zhu, Bo Song, Ji Changjiang

Auto-TLDR; Lip-sync: Synthesis of a Virtual News Anchor for Low-Delayed Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Annotation of Corpora for Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions Analysis
Alex Mircoli, Claudia Diamantini, Domenico Potena, Emanuele Storti

Auto-TLDR; Automatic annotation of video subtitles on the basis of facial expressions using machine learning algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual Alignment between Audiovisual Features for End-To-End Audiovisual Speech Recognition
Hong Liu, Yawei Wang, Bing Yang

Auto-TLDR; Mutual Iterative Attention for Audio Visual Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Network for End-To-End Text-Independent Speaker Identification
Wajdi Ghezaiel, Luc Brun, Olivier Lezoray
Auto-TLDR; Text-Independent Speaker Identification with Scattering Wavelet Network and Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Person Recognition with HGR Maximal Correlation on Multimodal Data
Yihua Liang, Fei Ma, Yang Li, Shao-Lun Huang
Auto-TLDR; A correlation-based multimodal person recognition framework that learns discriminative embeddings of persons by joint learning visual features and audio features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Triplet Loss Based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Puneet Kumar, Sidharth Jain, Balasubramanian Raman, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Neural Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Audio-Visual Speaker Tracking with a Novel Particle Filter
Hong Liu, Yongheng Sun, Yidi Li, Bing Yang

Auto-TLDR; 3D audio-visual speaker tracking using particle filter based method
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Gaze Tracking in Mobile Tablets
Yiwei Bao, Yihua Cheng, Yunfei Liu, Feng Lu

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Feature Fusion Network for Multi-stream Gaze Estimation in Mobile Tablets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Let's Play Music: Audio-Driven Performance Video Generation
Hao Zhu, Yi Li, Feixia Zhu, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; APVG: Audio-driven Performance Video Generation Using Structured Temporal UNet
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing American Sign Language Nonmanual Signal Grammar Errors in Continuous Videos
Elahe Vahdani, Longlong Jing, Ying-Li Tian, Matt Huenerfauth

Auto-TLDR; ASL-HW-RGBD: Recognizing Grammatical Errors in Continuous Sign Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
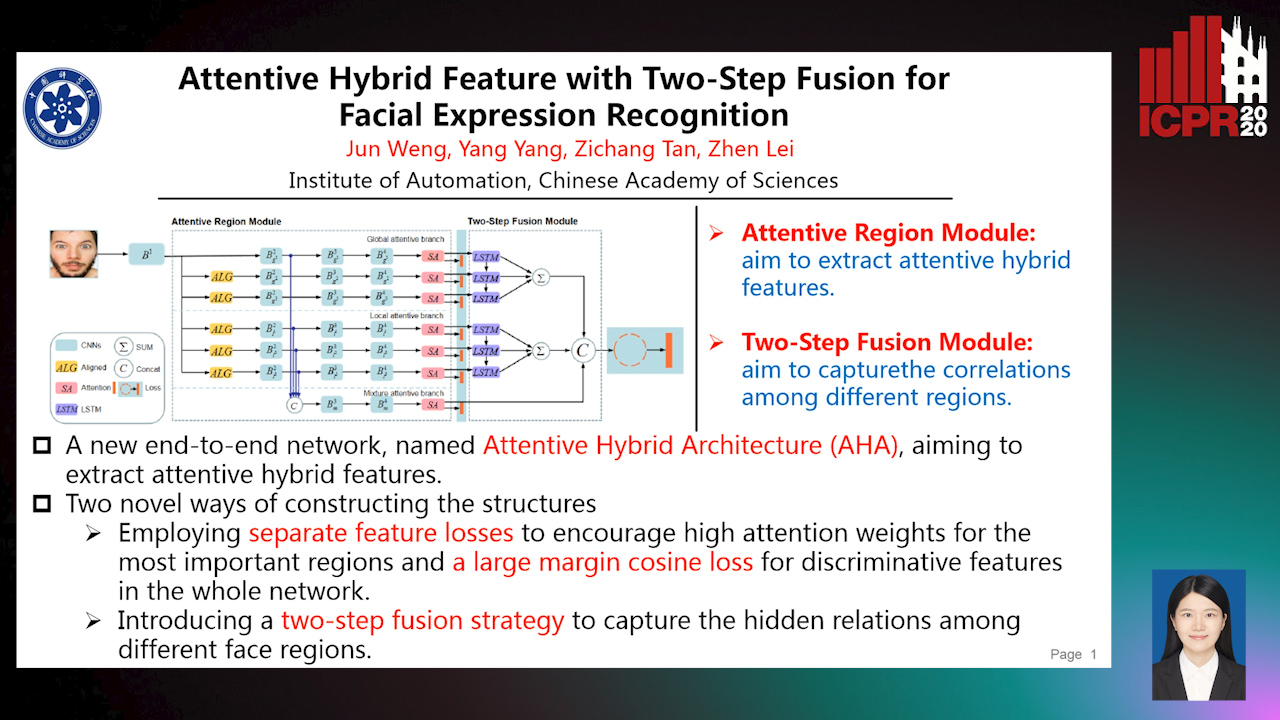
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
Cross-People Mobile-Phone Based Airwriting Character Recognition
Yunzhe Li, Hui Zheng, He Zhu, Haojun Ai, Xiaowei Dong

Auto-TLDR; Cross-People Airwriting Recognition via Motion Sensor Signal via Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpretable Emotion Classification Using Temporal Convolutional Models
Manasi Bharat Gund, Abhiram Ravi Bharadwaj, Ifeoma Nwogu
Auto-TLDR; Understanding the Dynamics of Facial Emotion Expression with Spatiotemporal Representations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Face Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction with Efficient Convolution Neural Networks
Keqiang Li, Huaiyu Wu, Xiuqin Shang, Zhen Shen, Gang Xiong, Xisong Dong, Bin Hu, Fei-Yue Wang

Auto-TLDR; Mobile-FRNet: Efficient 3D Morphable Model Alignment and 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single 2D Facial Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DenseRecognition of Spoken Languages
Jaybrata Chakraborty, Bappaditya Chakraborty, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; DenseNet: A Dense Convolutional Network Architecture for Speech Recognition in Indian Languages
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Toward Text-Independent Cross-Lingual Speaker Recognition Using English-Mandarin-Taiwanese Dataset

Auto-TLDR; Cross-lingual Speech for Biometric Recognition
Video-Based Facial Expression Recognition Using Graph Convolutional Networks
Daizong Liu, Hongting Zhang, Pan Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Network for Video-based Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFI: Multi-Range Feature Interchange for Video Action Recognition
Sikai Bai, Qi Wang, Xuelong Li

Auto-TLDR; Multi-range Feature Interchange Network for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inner Eye Canthus Localization for Human Body Temperature Screening
Claudio Ferrari, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Localization of the Inner Eye Canthus in Thermal Face Images using 3D Morphable Face Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
User-Independent Gaze Estimation by Extracting Pupil Parameter and Its Mapping to the Gaze Angle

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation using Pupil Shape for Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition in Compressed Video
Xiaofeng Liu, Linghao Jin, Xu Han, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Facial Expression Representation in Compressed Video with Mutual Information Minimization
JT-MGCN: Joint-Temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Joint-temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Spatiotemporal Fine-Tuning
Kenessary Koishybay, Medet Mukushev, Anara Sandygulova

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition with Iterative Gloss Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Learning Multiple Curvature Descriptor for 3D Palmprint Recognition
Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Jie Wen, Chunwei Tian, Peng Liu, Shuping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Joint Feature Learning for 3D palmprint recognition using curvature data vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Oriented Encoder: Integrating Multimodal and Multi-Scale Contexts for Video Captioning

Auto-TLDR; Visual Oriented Encoder for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
G-FAN: Graph-Based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
He Zhao, Yongjie Shi, Xin Tong, Jingsi Wen, Xianghua Ying, Jinshi Hongbin Zha

Auto-TLDR; Graph-based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar