Detective: An Attentive Recurrent Model for Sparse Object Detection
Amine Kechaou,
Manuel Martinez,
Monica Haurilet,
Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Detective: An attentive object detector that identifies objects in images in a sequential manner
Similar papers
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
MAGNet: Multi-Region Attention-Assisted Grounding of Natural Language Queries at Phrase Level
Amar Shrestha, Krittaphat Pugdeethosapol, Haowen Fang, Qinru Qiu

Auto-TLDR; MAGNet: A Multi-Region Attention-Aware Grounding Network for Free-form Textual Queries
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression by Learning Feature Embeddings

Auto-TLDR; FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression for Multiple Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ScarfNet: Multi-Scale Features with Deeply Fused and Redistributed Semantics for Enhanced Object Detection
Jin Hyeok Yoo, Dongsuk Kum, Jun Won Choi
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Fusion of Multi-scale Feature Maps for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Fast and Accurate Object Detector for Handwritten Digit String Recognition
Jun Guo, Wenjing Wei, Yifeng Ma, Cong Peng

Auto-TLDR; ChipNet: An anchor-free object detector for handwritten digit string recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Head Design for Object Detectors
Shivang Agarwal, Frederic Jurie
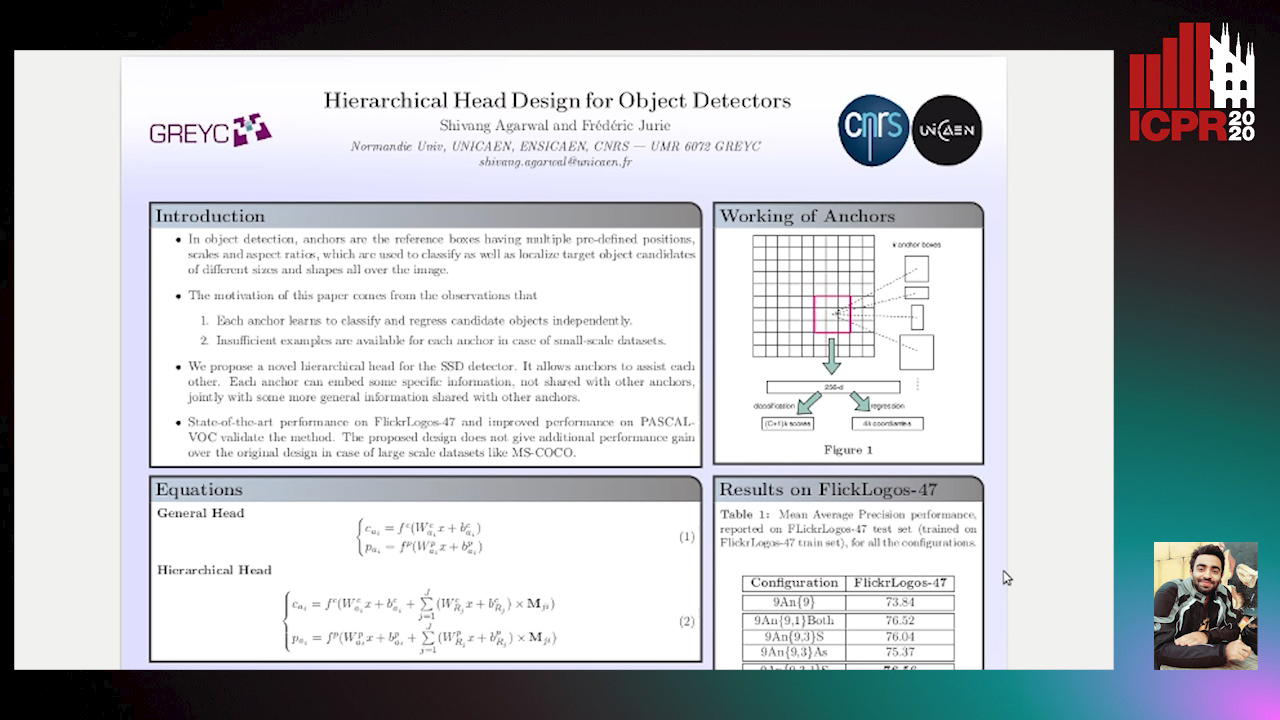
Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical Anchor for SSD Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Modified Single-Shot Multibox Detector for Beyond Real-Time Object Detection
Georgios Orfanidis, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Stefanos Vrochidis, Anastasios Tefas, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; Single Shot Detector in Resource-Restricted Systems with Lighter SSD Variations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CASNet: Common Attribute Support Network for Image Instance and Panoptic Segmentation
Xiaolong Liu, Yuqing Hou, Anbang Yao, Yurong Chen, Keqiang Li

Auto-TLDR; Common Attribute Support Network for instance segmentation and panoptic segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Convolutional STN for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
Akhil Meethal, Marco Pedersoli, Soufiane Belharbi, Eric Granger

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Localization for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Iterative Bounding Box Annotation for Object Detection
Bishwo Adhikari, Heikki Juhani Huttunen
Auto-TLDR; Semi-Automatic Bounding Box Annotation for Object Detection in Digital Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-View Object Detection Using Epipolar Constraints within Cluttered X-Ray Security Imagery
Brian Kostadinov Shalon Isaac-Medina, Chris G. Willcocks, Toby Breckon
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Epipolar Constraints for Multi-View Object Detection in X-ray Security Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Utilising Visual Attention Cues for Vehicle Detection and Tracking
Feiyan Hu, Venkatesh Gurram Munirathnam, Noel E O'Connor, Alan Smeaton, Suzanne Little
Auto-TLDR; Visual Attention for Object Detection and Tracking in Driver-Assistance Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CenterRepp: Predict Central Representative Point Set's Distribution for Detection
Yulin He, Limeng Zhang, Wei Chen, Xin Luo, Chen Li, Xiaogang Jia

Auto-TLDR; CRPDet: CenterRepp Detector for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Cascade Point Search Network for High Precision Bar Chart Component Detection
Junyu Luo, Jinpeng Wang, Chin-Yew Lin
Auto-TLDR; Object Detection of Chart Components in Chart Images Using Point-based and Region-Based Object Detection Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Object Detection Using Object's Motion Context and Spatio-Temporal Feature Aggregation
Jaekyum Kim, Junho Koh, Byeongwon Lee, Seungji Yang, Jun Won Choi

Auto-TLDR; Video Object Detection Using Spatio-Temporal Aggregated Features and Gated Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
Context for Object Detection Via Lightweight Global and Mid-Level Representations
Mesut Erhan Unal, Adriana Kovashka
Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Object Detection with Semantic Similarity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One-Stage Multi-Task Detector for 3D Cardiac MR Imaging
Weizeng Lu, Xi Jia, Wei Chen, Nicolò Savioli, Antonio De Marvao, Linlin Shen, Declan O'Regan, Jinming Duan

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Real-Time, simultaneous landmark location and bounding box detection in 3D space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Feature Enhancement Network with External Memory for Object Detection in Surveillance Video
Masato Fujitake, Akihiro Sugimoto

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Attention Based External Memory Network for Surveillance Object Detection
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
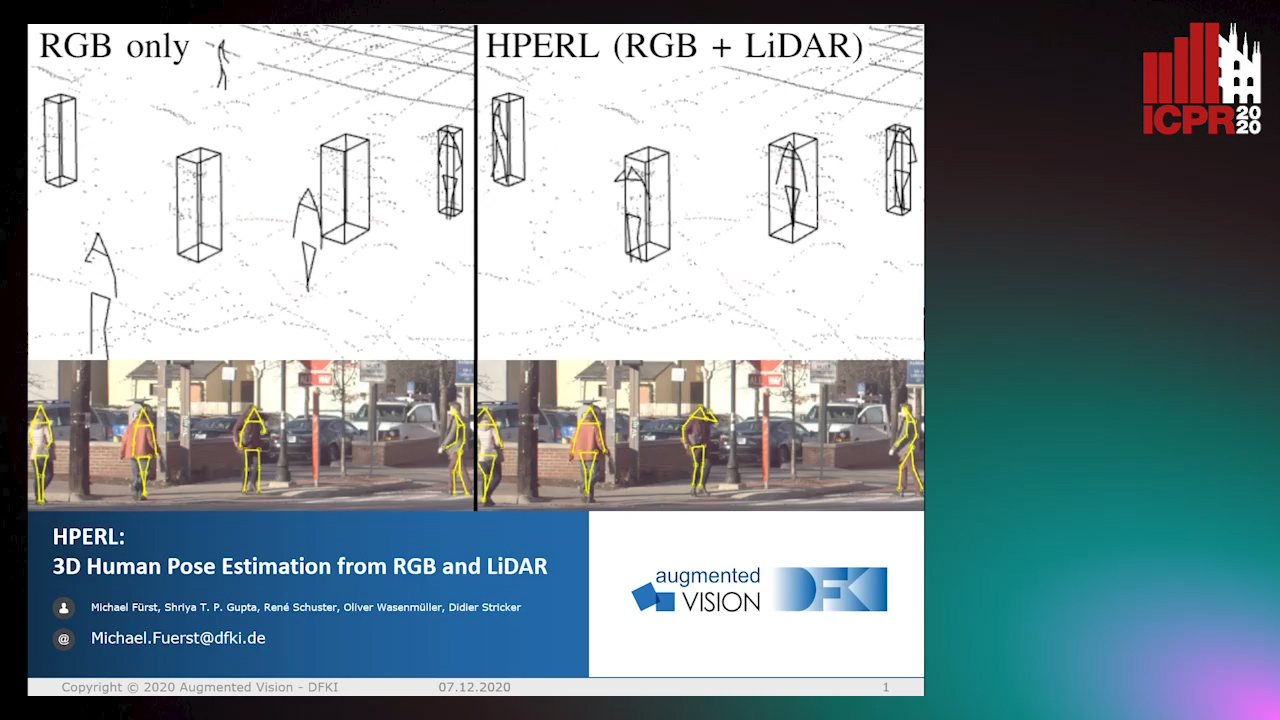
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Using Dual Graph Network
Shengjia Chen, Zhixin Li, Feicheng Huang, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; A Graph Convolutional Network for Object Detection with Key Relation Information
DualBox: Generating BBox Pair with Strong Correspondence Via Occlusion Pattern Clustering and Proposal Refinement
Zheng Ge, Chuyu Hu, Xin Huang, Baiqiao Qiu, Osamu Yoshie

Auto-TLDR; R2NMS: Combining Full and Visible Body Bounding Box for Dense Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PRF-Ped: Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detector with Prior-Based Receptive Field
Yuzhi Tan, Hongxun Yao, Haoran Li, Xiusheng Lu, Haozhe Xie

Auto-TLDR; Bidirectional Feature Enhancement Module for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VTT: Long-Term Visual Tracking with Transformers
Tianling Bian, Yang Hua, Tao Song, Zhengui Xue, Ruhui Ma, Neil Robertson, Haibing Guan

Auto-TLDR; Visual Tracking Transformer with transformers for long-term visual tracking
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EAGLE: Large-Scale Vehicle Detection Dataset in Real-World Scenarios Using Aerial Imagery
Seyed Majid Azimi, Reza Bahmanyar, Corentin Henry, Kurz Franz

Auto-TLDR; EAGLE: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multi-class Vehicle Detection with Object Orientation Information in Airborne Imagery
Correlation-Based ConvNet for Small Object Detection in Videos
Brais Bosquet, Manuel Mucientes, Victor Brea

Auto-TLDR; STDnet-ST: An End-to-End Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Network for Small Object Detection in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple-Step Sampling for Dense Object Detection and Counting

Auto-TLDR; Multiple-Step Sampling for Dense Objects Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection in the DCT Domain: Is Luminance the Solution?
Benjamin Deguerre, Clement Chatelain, Gilles Gasso

Auto-TLDR; Jpeg Deep: Object Detection Using Compressed JPEG Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
StrongPose: Bottom-up and Strong Keypoint Heat Map Based Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; StrongPose: A bottom-up box-free approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FourierNet: Compact Mask Representation for Instance Segmentation Using Differentiable Shape Decoders
Hamd Ul Moqeet Riaz, Nuri Benbarka, Andreas Zell

Auto-TLDR; FourierNet: A Single shot, anchor-free, fully convolutional instance segmentation method that predicts a shape vector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
SynDHN: Multi-Object Fish Tracker Trained on Synthetic Underwater Videos
Mygel Andrei Martija, Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Underwater Multi-Object Tracking in the Wild with Deep Hungarian Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CDeC-Net: Composite Deformable Cascade Network for Table Detection in Document Images
Madhav Agarwal, Ajoy Mondal, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; CDeC-Net: An End-to-End Trainable Deep Network for Detecting Tables in Document Images
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enriching Video Captions with Contextual Text
Philipp Rimle, Pelin Dogan, Markus Gross
Auto-TLDR; Contextualized Video Captioning Using Contextual Text
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar