Disentangled Representation Based Face Anti-Spoofing
Zhao Liu,
Zunlei Feng,
Yong Li,
Zeyu Zou,
Rong Zhang,
Mingli Song,
Jianping Shen

Auto-TLDR; Face Anti-Spoofing using Motion Information and Disentangled Frame Work
Similar papers
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Dynamic Color Texture Analysis Using Local Directional Number Pattern
Junwei Zhou, Ke Shu, Peng Liu, Jianwen Xiang, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; LDN-TOP Representation followed by ProCRC Classification for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixNet for Generalized Face Presentation Attack Detection
Nilay Sanghvi, Sushant Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MixNet: A Deep Learning-based Network for Detection of Presentation Attacks in Cross-Database and Unseen Setting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination Via Mutual Information Disentanglement
Haoxue Wu, Huaibo Huang, Aijing Yu, Jie Cao, Zhen Lei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination with Structural Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection of Makeup Presentation Attacks Based on Deep Face Representations
Christian Rathgeb, Pawel Drozdowski, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; An Attack Detection Scheme for Face Recognition Using Makeup Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Unsupervised Disentangling of Viewpoint and Residues Variations by Substituting Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Minsu Kim, Joanna Hong, Junho Kim, Hong Joo Lee, Yong Man Ro
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Disentangling of Identity, viewpoint, and Residue Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Iris Presentation Attack Detection Algorithm under Cross-Database Settings
Mehak Gupta, Vishal Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MVNet: A Deep Learning-based PAD Network for Iris Recognition against Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual-MTGAN: Stochastic and Deterministic Motion Transfer for Image-To-Video Synthesis
Fu-En Yang, Jing-Cheng Chang, Yuan-Hao Lee, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
Auto-TLDR; Dual Motion Transfer GAN for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Viability of Optical Coherence Tomography for Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Auto-TLDR; Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging for Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamically Mitigating Data Discrepancy with Balanced Focal Loss for Replay Attack Detection
Yongqiang Dou, Haocheng Yang, Maolin Yang, Yanyan Xu, Dengfeng Ke

Auto-TLDR; Anti-Spoofing with Balanced Focal Loss Function and Combination Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local-Global Interactive Network for Face Age Transformation
Jie Song, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Yongchi Zhang, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Local-Global Interaction Framework for Long-span Face Age Transformation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Attention and Global Representation Collaborating for Fine-Grained Classification
He Zhang, Yunming Bai, Hui Zhang, Jing Liu, Xingguang Li, Zhaofeng He

Auto-TLDR; Weighted Region Network for Cosmetic Contact Lenses Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Face Manipulation Via Hallucination
Keerthy Kusumam, Enrique Sanchez, Georgios Tzimiropoulos

Auto-TLDR; Unpaired Face Image Manipulation using Autoencoders
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Compressive Autoencoders for Full-Image-To-Image Hiding
Xiyao Liu, Ziping Ma, Xingbei Guo, Jialu Hou, Lei Wang, Gerald Schaefer, Hui Fang

Auto-TLDR; J-CAE: Joint Compressive Autoencoder for Image Hiding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition by Using a Disentangled Identity-Invariant Expression Representation
Auto-TLDR; Transfer-based Expression Recognition Generative Adversarial Network (TER-GAN)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coherence and Identity Learning for Arbitrary-Length Face Video Generation
Shuquan Ye, Chu Han, Jiaying Lin, Guoqiang Han, Shengfeng He

Auto-TLDR; Face Video Synthesis Using Identity-Aware GAN and Face Coherence Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion-Supervised Co-Part Segmentation
Aliaksandr Siarohin, Subhankar Roy, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Sergey Tulyakov, Elisa Ricci, Nicu Sebe

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Co-Part Segmentation Using Motion Information from Videos
Are Spoofs from Latent Fingerprints a Real Threat for the Best State-Of-Art Liveness Detectors?
Roberto Casula, Giulia Orrù, Daniele Angioni, Xiaoyi Feng, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; ScreenSpoof: Attacks using latent fingerprints against state-of-art fingerprint liveness detectors and verification systems
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Deep Multi-Task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis Based on Selective Feature Sharing
Rui Zhao, Tianshan Liu, Jun Xiao, P. K. Daniel Lun, Kin-Man Lam

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-Class Recognition
Pramuditha Perera, Vishal Patel
Auto-TLDR; Combining Generative Features and One-Class Classification for Effective One-class Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exposing Deepfake Videos by Tracking Eye Movements
Meng Li, Beibei Liu, Yujiang Hu, Yufei Wang

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Approach to Detecting Deepfake Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Makeup Style Transfer on Low-Quality Images with Weighted Multi-Scale Attention
Daniel Organisciak, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H.

Auto-TLDR; Facial Makeup Style Transfer for Low-Resolution Images Using Multi-Scale Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ResMax: Detecting Voice Spoofing Attacks with Residual Network and Max Feature Map
Il-Youp Kwak, Sungsu Kwag, Junhee Lee, Jun Ho Huh, Choong-Hoon Lee, Youngbae Jeon, Jeonghwan Hwang, Ji Won Yoon

Auto-TLDR; ASVspoof 2019: A Lightweight Automatic Speaker Verification Spoofing and Countermeasures System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Interpretable Representation for 3D Point Clouds
Feng-Guang Su, Ci-Siang Lin, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang

Auto-TLDR; Disentangling Body-type and Pose Information from 3D Point Clouds Using Adversarial Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Controllable Face Aging

Auto-TLDR; A controllable face aging method via attribute disentanglement generative adversarial network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition in Compressed Video
Xiaofeng Liu, Linghao Jin, Xu Han, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Facial Expression Representation in Compressed Video with Mutual Information Minimization
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AdvHat: Real-World Adversarial Attack on ArcFace Face ID System
Stepan Komkov, Aleksandr Petiushko

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Sticker Attack on ArcFace in Shooting Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion and Region Aware Adversarial Learning for Fall Detection with Thermal Imaging
Vineet Mehta, Abhinav Dhall, Sujata Pal, Shehroz Khan

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Fall Detection with Adversarial Network using Thermal Imaging Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
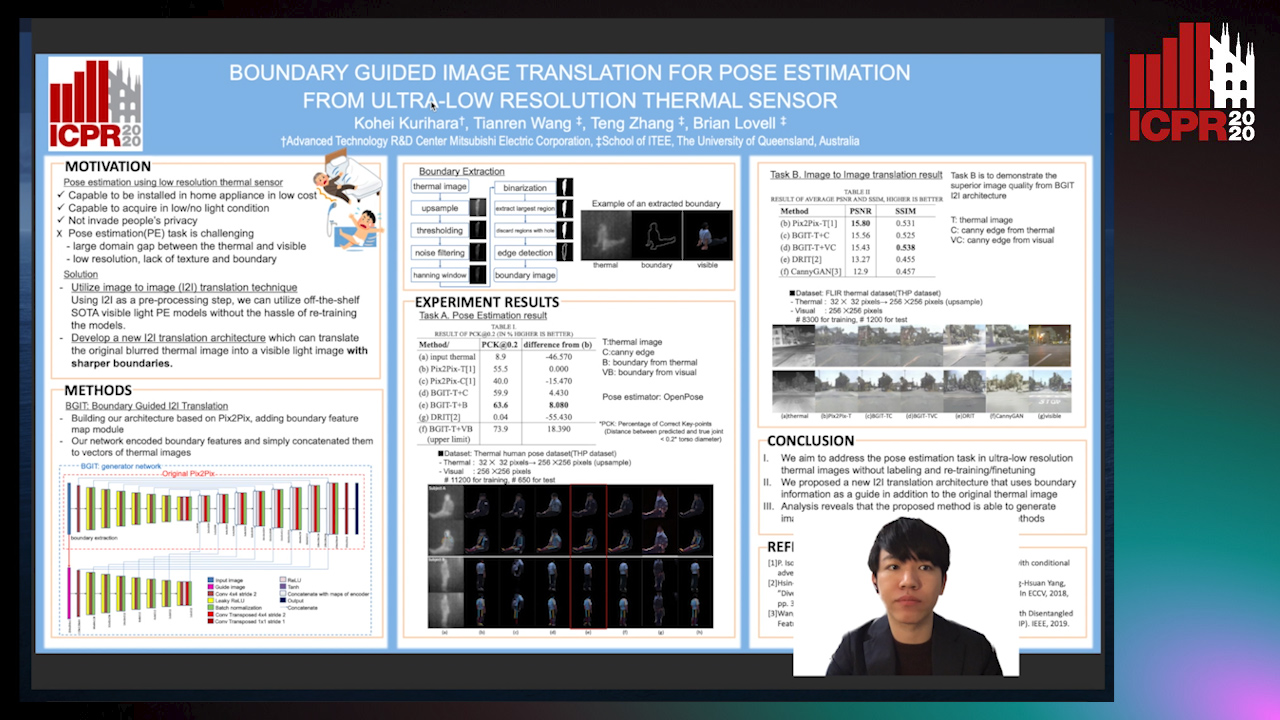
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Contrastive Photo-To-Caricature Translation Based on Auto-Distortion
Yuhe Ding, Xin Ma, Mandi Luo, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised contrastive photo-to-caricature translation with style loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Preserved Face Beauty Transformation with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks

Auto-TLDR; Identity-preserved face beauty transformation using conditional GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar