Contrastive Data Learning for Facial Pose and Illumination Normalization

Auto-TLDR; Pose and Illumination Normalization with Contrast Data Learning for Face Recognition
Similar papers
Unsupervised Disentangling of Viewpoint and Residues Variations by Substituting Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Minsu Kim, Joanna Hong, Junho Kim, Hong Joo Lee, Yong Man Ro
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Disentangling of Identity, viewpoint, and Residue Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Face Manipulation Via Hallucination
Keerthy Kusumam, Enrique Sanchez, Georgios Tzimiropoulos

Auto-TLDR; Unpaired Face Image Manipulation using Autoencoders
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination Via Mutual Information Disentanglement
Haoxue Wu, Huaibo Huang, Aijing Yu, Jie Cao, Zhen Lei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Exemplar Guided Cross-Spectral Face Hallucination with Structural Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identifying Missing Children: Face Age-Progression Via Deep Feature Aging
Debayan Deb, Divyansh Aggarwal, Anil Jain

Auto-TLDR; Aging Face Features for Missing Children Identification
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Image Quality Assessment for Model and Human Perception
Ken Chen, Yichao Wu, Zhenmao Li, Yudong Wu, Ding Liang

Auto-TLDR; A labour-saving method for FIQA training with contradictory data from multiple sources
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Robust Face Recognition by Deep Meta Capsule Network-Based Equivariant Embedding
Fangyu Wu, Jeremy Simon Smith, Wenjin Lu, Bailing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Deep Meta Capsule Network-based Equivariant Embedding Model for Pose-Robust Face Recognition
Coherence and Identity Learning for Arbitrary-Length Face Video Generation
Shuquan Ye, Chu Han, Jiaying Lin, Guoqiang Han, Shengfeng He

Auto-TLDR; Face Video Synthesis Using Identity-Aware GAN and Face Coherence Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition by Using a Disentangled Identity-Invariant Expression Representation
Auto-TLDR; Transfer-based Expression Recognition Generative Adversarial Network (TER-GAN)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ClusterFace: Joint Clustering and Classification for Set-Based Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Joint Clustering and Classification for Face Recognition in the Wild
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
G-FAN: Graph-Based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
He Zhao, Yongjie Shi, Xin Tong, Jingsi Wen, Xianghua Ying, Jinshi Hongbin Zha

Auto-TLDR; Graph-based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local-Global Interactive Network for Face Age Transformation
Jie Song, Ping Wei, Huan Li, Yongchi Zhang, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Local-Global Interaction Framework for Long-span Face Age Transformation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Preserved Face Beauty Transformation with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks

Auto-TLDR; Identity-preserved face beauty transformation using conditional GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Multi-Task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis Based on Selective Feature Sharing
Rui Zhao, Tianshan Liu, Jun Xiao, P. K. Daniel Lun, Kin-Man Lam

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Facial Expression Recognition and Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Controllable Face Aging

Auto-TLDR; A controllable face aging method via attribute disentanglement generative adversarial network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pixel-based Facial Expression Synthesis
Auto-TLDR; pixel-based facial expression synthesis using GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attributes Aware Face Generation with Generative Adversarial Networks
Zheng Yuan, Jie Zhang, Shiguang Shan, Xilin Chen

Auto-TLDR; AFGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Attributes Aware Face Image Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Laplacian GAN with Edge Enhancement for Face Super Resolution
Auto-TLDR; Face Image Super-Resolution with Enhanced Edge Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Quantitative Evaluation Framework of Video De-Identification Methods
Sathya Bursic, Alessandro D'Amelio, Marco Granato, Giuliano Grossi, Raffaella Lanzarotti

Auto-TLDR; Face de-identification using photo-reality and facial expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SSDL: Self-Supervised Domain Learning for Improved Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Domain Learning for Face Recognition in unconstrained environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lookalike Disambiguation: Improving Face Identification Performance at Top Ranks

Auto-TLDR; Lookalike Face Identification Using a Disambiguator for Lookalike Images
Talking Face Generation Via Learning Semantic and Temporal Synchronous Landmarks
Aihua Zheng, Feixia Zhu, Hao Zhu, Mandi Luo, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; A semantic and temporal synchronous landmark learning method for talking face generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Important Are Faces for Person Re-Identification?
Julia Dietlmeier, Joseph Antony, Kevin Mcguinness, Noel E O'Connor

Auto-TLDR; Anonymization of Person Re-identification Datasets with Face Detection and Blurring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Attribute Regression Network for Face Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection of Makeup Presentation Attacks Based on Deep Face Representations
Christian Rathgeb, Pawel Drozdowski, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; An Attack Detection Scheme for Face Recognition Using Makeup Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Shape Consistent 2D Keypoint Estimation under Domain Shift
Levi Vasconcelos, Massimiliano Mancini, Davide Boscaini, Barbara Caputo, Elisa Ricci

Auto-TLDR; Deep Adaptation for Keypoint Prediction under Domain Shift
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Emotional Blinded Face Representations
Alejandro Peña Almansa, Julian Fierrez, Agata Lapedriza, Aythami Morales

Auto-TLDR; Blind Face Representations for Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Features and Face Detection Performance: Analyses with 3D-Rendered Synthetic Data
Jian Han, Sezer Karaoglu, Hoang-An Le, Theo Gevers

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Data for Face Detection Using 3DU Face Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Role of Cycle Consistency for Generating Better Human Action Videos from a Single Frame

Auto-TLDR; Generating Videos with Human Action Semantics using Cycle Constraints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
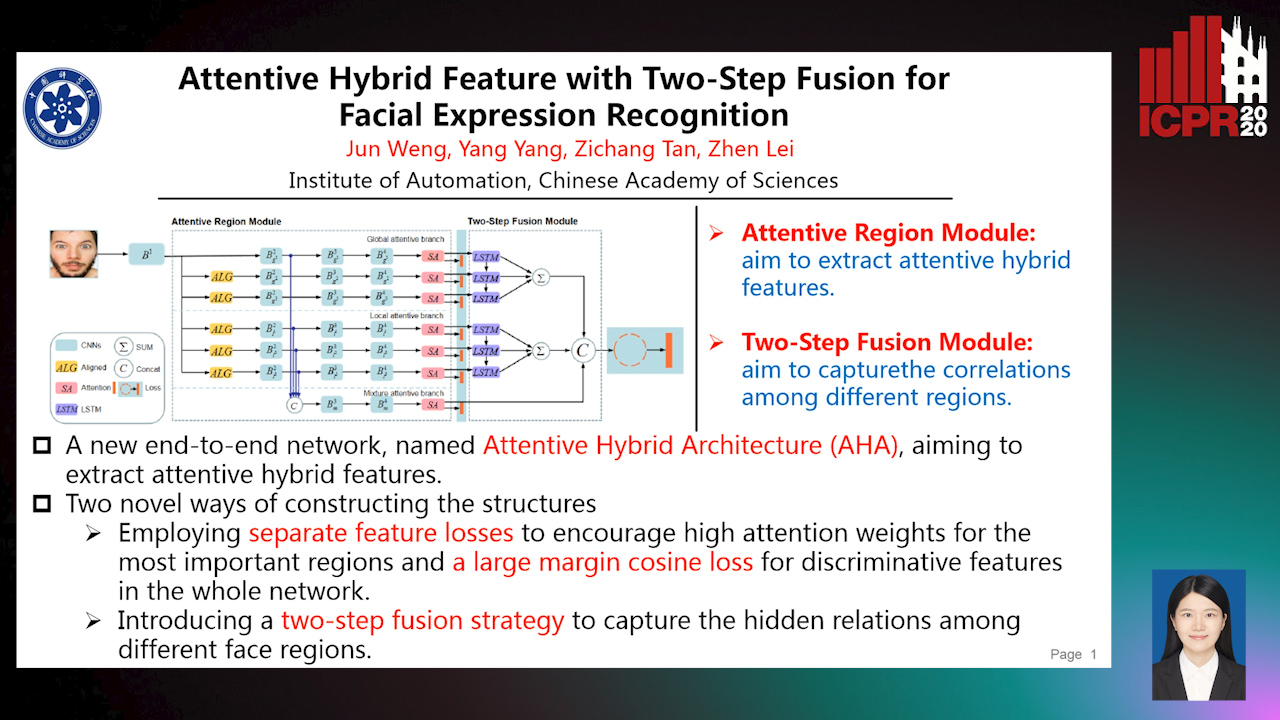
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Contrastive Photo-To-Caricature Translation Based on Auto-Distortion
Yuhe Ding, Xin Ma, Mandi Luo, Aihua Zheng, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised contrastive photo-to-caricature translation with style loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Free-Form Image Inpainting Via Contrastive Attention Network
Xin Ma, Xiaoqiang Zhou, Huaibo Huang, Zhenhua Chai, Xiaolin Wei, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Siamese inference for image inpainting
Cam-Softmax for Discriminative Deep Feature Learning
Tamas Suveges, Stephen James Mckenna

Auto-TLDR; Cam-Softmax: A Generalisation of Activations and Softmax for Deep Feature Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CANU-ReID: A Conditional Adversarial Network for Unsupervised Person Re-IDentification
Guillaume Delorme, Yihong Xu, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Radu Horaud, Xavier Alameda-Pineda

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Person Re-Identification with Clustering and Adversarial Learning
AVAE: Adversarial Variational Auto Encoder
Antoine Plumerault, Hervé Le Borgne, Celine Hudelot

Auto-TLDR; Combining VAE and GAN for Realistic Image Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Makeup Style Transfer on Low-Quality Images with Weighted Multi-Scale Attention
Daniel Organisciak, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H.

Auto-TLDR; Facial Makeup Style Transfer for Low-Resolution Images Using Multi-Scale Spatial Attention
Abstract Slides Poster Similar