Memetic Evolution of Training Sets with Adaptive Radial Basis Kernels for Support Vector Machines
Jakub Nalepa, Wojciech Dudzik, Michal Kawulok
Auto-TLDR; Memetic Algorithm for Evolving Support Vector Machines with Adaptive Kernels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Eye Tracking Data Segmentation, Generation, and Reconstruction
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Enkelejda Kasneci
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Eye Tracking Data with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cut and Compare: End-To-End Offline Signature Verification Network

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Cut-and-Compare Network for Offline Signature Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
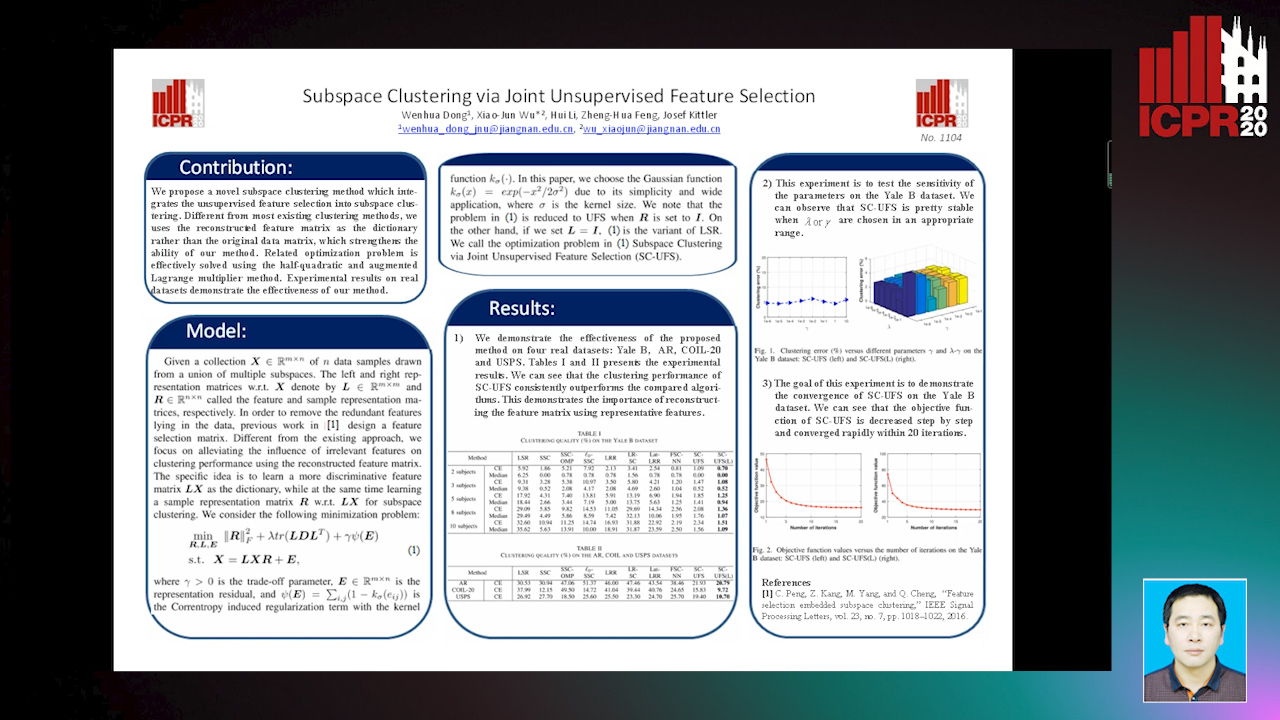
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering
Photometric Stereo with Twin-Fisheye Cameras
Jordan Caracotte, Fabio Morbidi, El Mustapha Mouaddib

Auto-TLDR; Photometric stereo problem for low-cost 360-degree cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Label Self-Adaption Hashing for Image Retrieval
Jianglin Lu, Zhihui Lai, Hailing Wang, Jie Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Label Self-Adaption Hashing for Large-Scale Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can You Really Trust the Sensor's PRNU? How Image Content Might Impact the Finger Vein Sensor Identification Performance
Dominik Söllinger, Luca Debiasi, Andreas Uhl

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein imagery can cause the PRNU estimate to be biased by image content
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Softer Pruning, Incremental Regularization
Linhang Cai, Zhulin An, Yongjun Xu

Auto-TLDR; Asymptotic SofteR Filter Pruning for Deep Neural Network Pruning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Effect of Spectrogram Reconstruction on Automatic Music Transcription: An Alternative Approach to Improve Transcription Accuracy
Kin Wai Cheuk, Yin-Jyun Luo, Emmanouil Benetos, Herremans Dorien
Auto-TLDR; Exploring the effect of spectrogram reconstruction loss on automatic music transcription
Image Inpainting with Contrastive Relation Network
Xiaoqiang Zhou, Junjie Li, Zilei Wang, Ran He, Tieniu Tan

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stage Inpainting with Graph-based Relation Network
Parallel Network to Learn Novelty from the Known
Shuaiyuan Du, Chaoyi Hong, Zhiyu Pan, Chen Feng, Zhiguo Cao
Auto-TLDR; Trainable Parallel Network for Pseudo-Novel Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Correlation Filter Tracking with Adaptive Training Sample Update Scheme
Shan Jiang, Shuxiao Li, Chengfei Zhu, Nan Yan

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Training Sample Update Scheme of Correlation Filter Based Trackers for Visual Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Radical Counter Network for Robust Chinese Character Recognition
Yunqing Li, Yixing Zhu, Jun Du, Changjie Wu, Jianshu Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Radical Counter Network for Chinese Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Position-Aware Safe Boundary Interpolation Oversampling

Auto-TLDR; PABIO: Position-Aware Safe Boundary Interpolation-Based Oversampling for Imbalanced Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Locality-Promoting Representation Learning
Auto-TLDR; Locality-promoting Regularization for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Connectivity with Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Learning Graph Convolutional Networks Using Topological Properties of Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Knowledge Distillation Beyond Model Compression
Fahad Sarfraz, Elahe Arani, Bahram Zonooz

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation from Teacher to Student
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RONELD: Robust Neural Network Output Enhancement for Active Lane Detection
Zhe Ming Chng, Joseph Mun Hung Lew, Jimmy Addison Lee
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Robust Neural Network Output Enhancement for Active Lane Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation Network for Fast Video Object Segmentation
Dexiang Hong, Guorong Li, Kai Xu, Li Su, Qingming Huang

Auto-TLDR; Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar