How Unique Is a Face: An Investigative Study
Michal Balazia,
S L Happy,
Francois Bremond,
Antitza Dantcheva

Auto-TLDR; Uniqueness of Face Recognition: Exploring the Impact of Factors such as image resolution, feature representation, database size, age and gender
Similar papers
Attribute-Based Quality Assessment for Demographic Estimation in Face Videos
Fabiola Becerra-Riera, Annette Morales-González, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Jean-Luc Dugelay
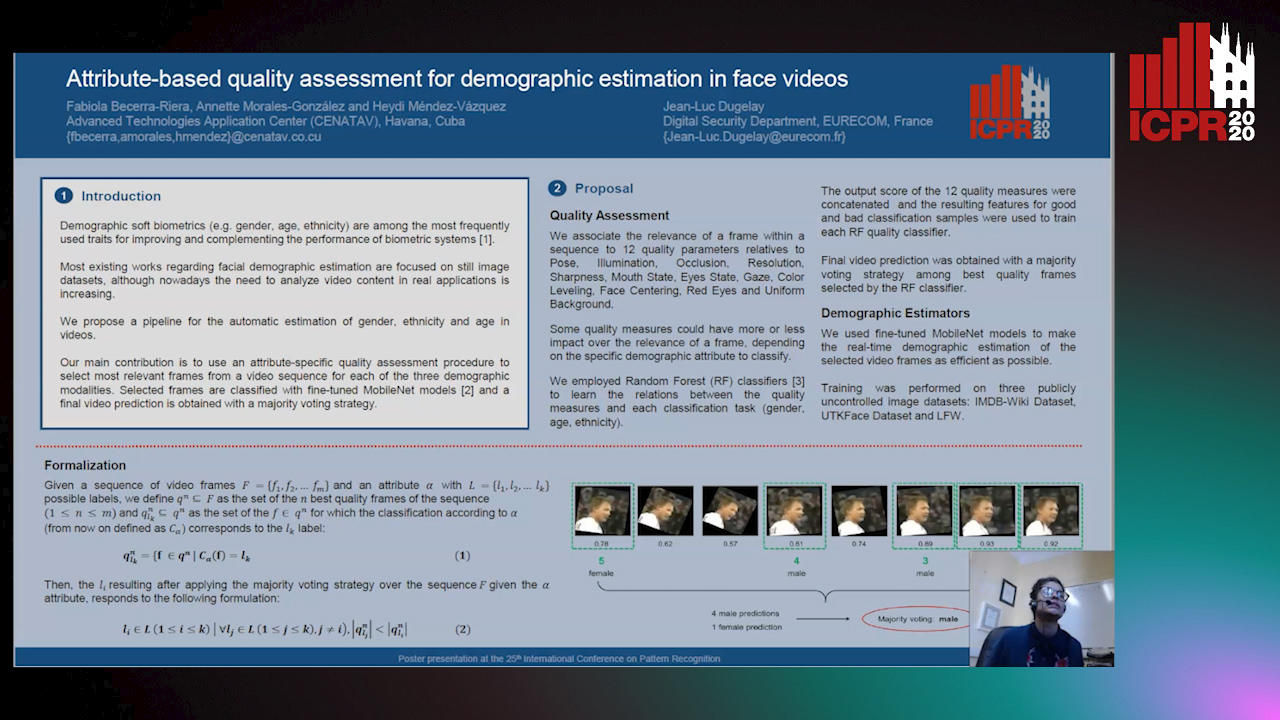
Auto-TLDR; Facial Demographic Estimation in Video Scenarios Using Quality Assessment
Lookalike Disambiguation: Improving Face Identification Performance at Top Ranks

Auto-TLDR; Lookalike Face Identification Using a Disambiguator for Lookalike Images
A Flatter Loss for Bias Mitigation in Cross-Dataset Facial Age Estimation
Ali Akbari, Muhammad Awais, Zhenhua Feng, Ammarah Farooq, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; Cross-dataset Age Estimation for Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
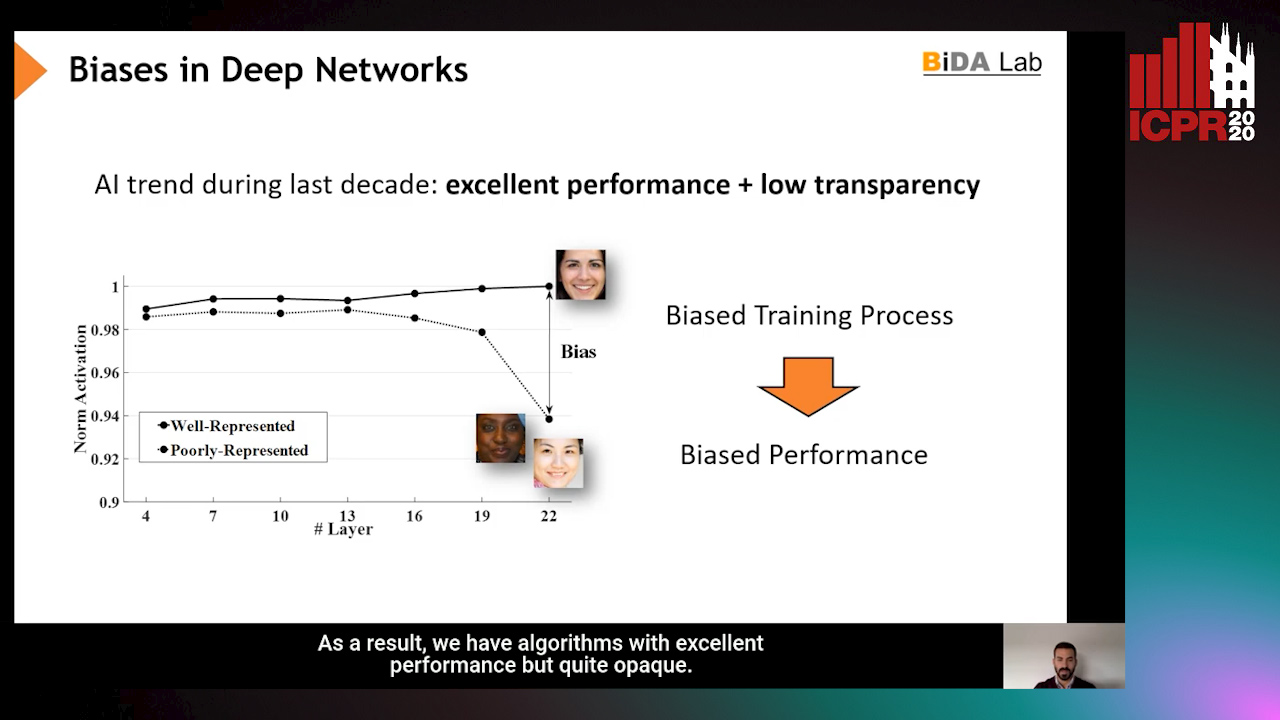
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
One-Shot Representational Learning for Joint Biometric and Device Authentication

Auto-TLDR; Joint Biometric and Device Recognition from a Single Biometric Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for Facial Template Protection
Hakyoung Lee, Cheng Yaw Low, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for C cancellable Biometrics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Emotional Blinded Face Representations
Alejandro Peña Almansa, Julian Fierrez, Agata Lapedriza, Aythami Morales

Auto-TLDR; Blind Face Representations for Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fingerprints, Forever Young?
Roman Kessler, Olaf Henniger, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; Mated Similarity Scores for Fingerprint Recognition: A Hierarchical Linear Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection of Makeup Presentation Attacks Based on Deep Face Representations
Christian Rathgeb, Pawel Drozdowski, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; An Attack Detection Scheme for Face Recognition Using Makeup Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Deep Gait Relative Attribute Using a Signed Quadratic Contrastive Loss
Yuta Hayashi, Shehata Allam, Yasushi Makihara, Daigo Muramatsu, Yasushi Yagi

Auto-TLDR; Signal-Contrastive Loss for Gait Attributes Estimation
Viability of Optical Coherence Tomography for Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Auto-TLDR; Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging for Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Detection in Finger Vein Biometrics Using CNNs
Bernhard Prommegger, Georg Wimmer, Andreas Uhl
Auto-TLDR; A CNN based rotation detector for finger vein recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Iris Presentation Attack Detection Algorithm under Cross-Database Settings
Mehak Gupta, Vishal Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MVNet: A Deep Learning-based PAD Network for Iris Recognition against Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Finger Vein Recognition and Intra-Subject Similarity Evaluation of Finger Veins Using the CNN Triplet Loss
Georg Wimmer, Bernhard Prommegger, Andreas Uhl

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein recognition using CNNs and hard triplet online selection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixNet for Generalized Face Presentation Attack Detection
Nilay Sanghvi, Sushant Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MixNet: A Deep Learning-based Network for Detection of Presentation Attacks in Cross-Database and Unseen Setting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identifying Missing Children: Face Age-Progression Via Deep Feature Aging
Debayan Deb, Divyansh Aggarwal, Anil Jain

Auto-TLDR; Aging Face Features for Missing Children Identification
ClusterFace: Joint Clustering and Classification for Set-Based Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Joint Clustering and Classification for Face Recognition in the Wild
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human or Machine? It Is Not What You Write, but How You Write It
Luis Leiva, Moises Diaz, M.A. Ferrer, Réjean Plamondon

Auto-TLDR; Behavioral Biometrics via Handwritten Symbols for Identification and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Quantitative Evaluation Framework of Video De-Identification Methods
Sathya Bursic, Alessandro D'Amelio, Marco Granato, Giuliano Grossi, Raffaella Lanzarotti

Auto-TLDR; Face de-identification using photo-reality and facial expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can You Really Trust the Sensor's PRNU? How Image Content Might Impact the Finger Vein Sensor Identification Performance
Dominik Söllinger, Luca Debiasi, Andreas Uhl

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein imagery can cause the PRNU estimate to be biased by image content
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Image Quality Assessment for Model and Human Perception
Ken Chen, Yichao Wu, Zhenmao Li, Yudong Wu, Ding Liang

Auto-TLDR; A labour-saving method for FIQA training with contradictory data from multiple sources
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HP2IFS: Head Pose Estimation Exploiting Partitioned Iterated Function Systems
Carmen Bisogni, Michele Nappi, Chiara Pero, Stefano Ricciardi
Auto-TLDR; PIFS based head pose estimation using fractal coding theory and Partitioned Iterated Function Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Important Are Faces for Person Re-Identification?
Julia Dietlmeier, Joseph Antony, Kevin Mcguinness, Noel E O'Connor

Auto-TLDR; Anonymization of Person Re-identification Datasets with Face Detection and Blurring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Attention and Global Representation Collaborating for Fine-Grained Classification
He Zhang, Yunming Bai, Hui Zhang, Jing Liu, Xingguang Li, Zhaofeng He

Auto-TLDR; Weighted Region Network for Cosmetic Contact Lenses Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Unsupervised Approach towards Varying Human Skin Tone Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Debapriya Roy, Diganta Mukherjee, Bhabatosh Chanda

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Skin Tone Change Using Augmented Reality Based Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SSDL: Self-Supervised Domain Learning for Improved Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Domain Learning for Face Recognition in unconstrained environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Exploring Seismocardiogram Biometrics with Wavelet Transform
Po-Ya Hsu, Po-Han Hsu, Hsin-Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Seismocardiogram Biometric Matching Using Wavelet Transform and Deep Learning Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Person Recognition with HGR Maximal Correlation on Multimodal Data
Yihua Liang, Fei Ma, Yang Li, Shao-Lun Huang
Auto-TLDR; A correlation-based multimodal person recognition framework that learns discriminative embeddings of persons by joint learning visual features and audio features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facial Expression Recognition Using Residual Masking Network
Luan Pham, Vu Huynh, Tuan Anh Tran

Auto-TLDR; Deep Residual Masking for Automatic Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cancelable Biometrics Vault: A Secure Key-Binding Biometric Cryptosystem Based on Chaffing and Winnowing
Osama Ouda, Karthik Nandakumar, Arun Ross

Auto-TLDR; Cancelable Biometrics Vault for Key-binding Biometric Cryptosystem Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese-Structure Deep Neural Network Recognizing Changes in Facial Expression According to the Degree of Smiling
Kazuaki Kondo, Taichi Nakamura, Yuichi Nakamura, Shin'Ichi Satoh

Auto-TLDR; A Siamese-Structure Deep Neural Network for Happiness Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond Cross-Entropy: Learning Highly Separable Feature Distributions for Robust and Accurate Classification
Arslan Ali, Andrea Migliorati, Tiziano Bianchi, Enrico Magli

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian class-conditional simplex loss for adversarial robust multiclass classifiers
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Task Learning for Calorie Prediction on a Novel Large-Scale Recipe Dataset Enriched with Nutritional Information
Robin Ruede, Verena Heusser, Lukas Frank, Monica Haurilet, Alina Roitberg, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Pic2kcal: Learning Food Recipes from Images for Calorie Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Jianrong Wang, Tong Wu, Shanyu Wang, Mei Yu, Qiang Fang, Ju Zhang, Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent and Text-Dependent Speaker Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar