Exploring Seismocardiogram Biometrics with Wavelet Transform
Po-Ya Hsu,
Po-Han Hsu,
Hsin-Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Seismocardiogram Biometric Matching Using Wavelet Transform and Deep Learning Models
Similar papers
A Low-Complexity R-Peak Detection Algorithm with Adaptive Thresholding for Wearable Devices
Tiago Rodrigues, Hugo Plácido Da Silva, Ana Luisa Nobre Fred, Sirisack Samoutphonh

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time and Low-Complexity R-peak Detection for Single Lead ECG Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EasiECG: A Novel Inter-Patient Arrhythmia Classification Method Using ECG Waves
Chuanqi Han, Ruoran Huang, Fang Yu, Xi Huang, Li Cui

Auto-TLDR; EasiECG: Attention-based Convolution Factorization Machines for Arrhythmia Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Network for End-To-End Text-Independent Speaker Identification
Wajdi Ghezaiel, Luc Brun, Olivier Lezoray
Auto-TLDR; Text-Independent Speaker Identification with Scattering Wavelet Network and Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Epileptic Seizure Prediction: A Semi-Dilated Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
Ramy Hussein, Rabab K. Ward, Soojin Lee, Martin Mckeown
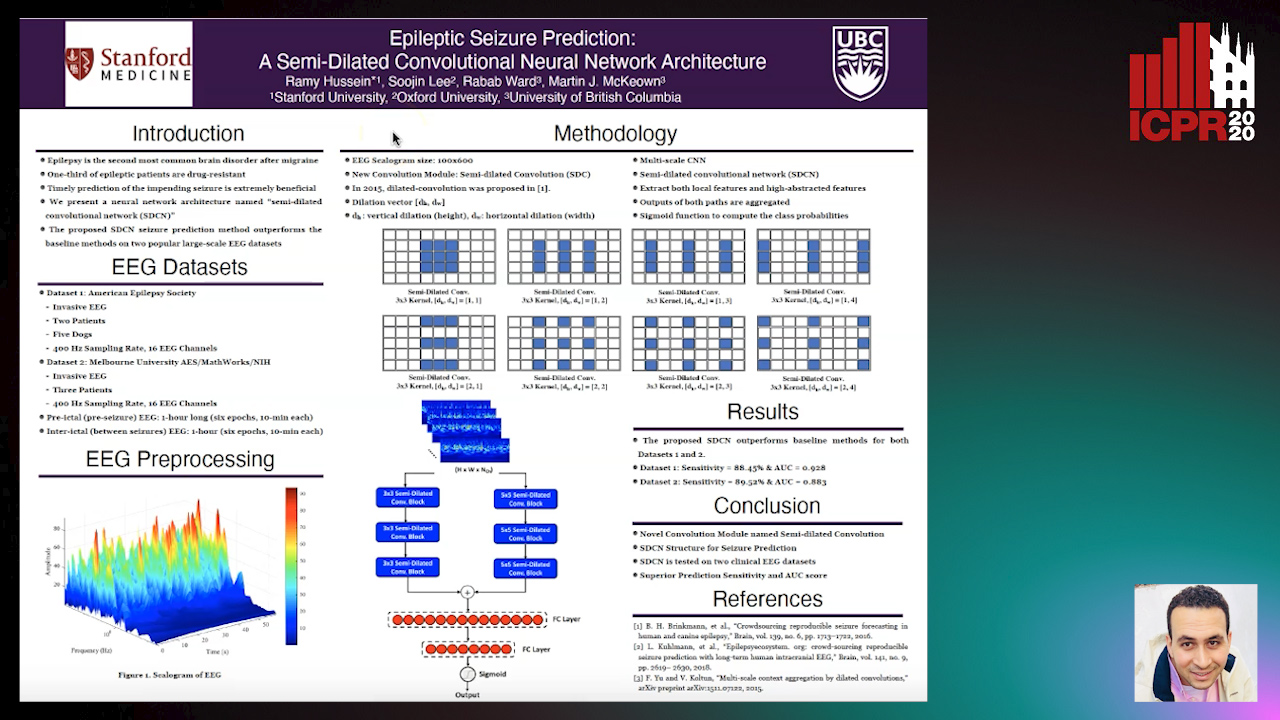
Auto-TLDR; Semi-Dilated Convolutional Network for Seizure Prediction using EEG Scalograms
Generalized Iris Presentation Attack Detection Algorithm under Cross-Database Settings
Mehak Gupta, Vishal Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MVNet: A Deep Learning-based PAD Network for Iris Recognition against Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Classification of Human Granulosa Cells in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Vibrational Spectroscopy Imaging
Marina Paolanti, Emanuele Frontoni, Giorgia Gioacchini, Giorgini Elisabetta, Notarstefano Valentina, Zacà Carlotta, Carnevali Oliana, Andrea Borini, Marco Mameli

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Oocyte Quality in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
One-Shot Representational Learning for Joint Biometric and Device Authentication

Auto-TLDR; Joint Biometric and Device Recognition from a Single Biometric Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale and Attention Based ResNet for Heartbeat Classification
Haojie Zhang, Gongping Yang, Yuwen Huang, Feng Yuan, Yilong Yin

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Scale and Attention based ResNet for ECG heartbeat classification in intra-patient and inter-patient paradigms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Explainable Online Validation of Machine Learning Models for Practical Applications
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Thomas Motz, Michael Scheidt, Andreas Markus Hartel, Andreas Koch, Enkelejda Kasneci

Auto-TLDR; A Reformulation of Regression and Classification for Machine Learning Algorithm Validation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EEG-Based Cognitive State Assessment Using Deep Ensemble Model and Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern
Debashis Das Chakladar, Shubhashis Dey, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Ensemble Model for Cognitive State Assessment using EEG-based Cognitive State Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Finger Vein Recognition and Intra-Subject Similarity Evaluation of Finger Veins Using the CNN Triplet Loss
Georg Wimmer, Bernhard Prommegger, Andreas Uhl

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein recognition using CNNs and hard triplet online selection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for Facial Template Protection
Hakyoung Lee, Cheng Yaw Low, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for C cancellable Biometrics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Influence of Event Duration on Automatic Wheeze Classification
Bruno M Rocha, Diogo Pessoa, Alda Marques, Paulo Carvalho, Rui Pedro Paiva

Auto-TLDR; Experimental Design of the Non-wheeze Class for Wheeze Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wireless Localisation in WiFi Using Novel Deep Architectures
Peizheng Li, Han Cui, Aftab Khan, Usman Raza, Robert Piechocki, Angela Doufexi, Tim Farnham
Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Indoor Localisation of WiFi Devices in Indoor Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Personalized Models in Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning
Hamza Amrani, Daniela Micucci, Paolo Napoletano

Auto-TLDR; Incremental Learning for Personalized Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BAT Optimized CNN Model Identifies Water Stress in Chickpea Plant Shoot Images
Shiva Azimi, Taranjit Kaur, Tapan Gandhi

Auto-TLDR; BAT Optimized ResNet-18 for Stress Classification of chickpea shoot images under water deficiency
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Transfer Learning for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Nicole Cilia, Claudio De Stefano, Francesco Fontanella, Claudio Marrocco, Mario Molinara, Alessandra Scotto Di Freca

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Detection of Handwriting Alterations for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis using Dynamic Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Dynamic Color Texture Analysis Using Local Directional Number Pattern
Junwei Zhou, Ke Shu, Peng Liu, Jianwen Xiang, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; LDN-TOP Representation followed by ProCRC Classification for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Unique Is a Face: An Investigative Study
Michal Balazia, S L Happy, Francois Bremond, Antitza Dantcheva

Auto-TLDR; Uniqueness of Face Recognition: Exploring the Impact of Factors such as image resolution, feature representation, database size, age and gender
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Level Three Synthetic Fingerprint Generation
Andre Wyzykowski, Mauricio Pamplona Segundo, Rubisley Lemes

Auto-TLDR; Synthesis of High-Resolution Fingerprints with Pore Detection Using CycleGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Raw Eye Tracking Data Segmentation, Generation, and Reconstruction
Wolfgang Fuhl, Yao Rong, Enkelejda Kasneci
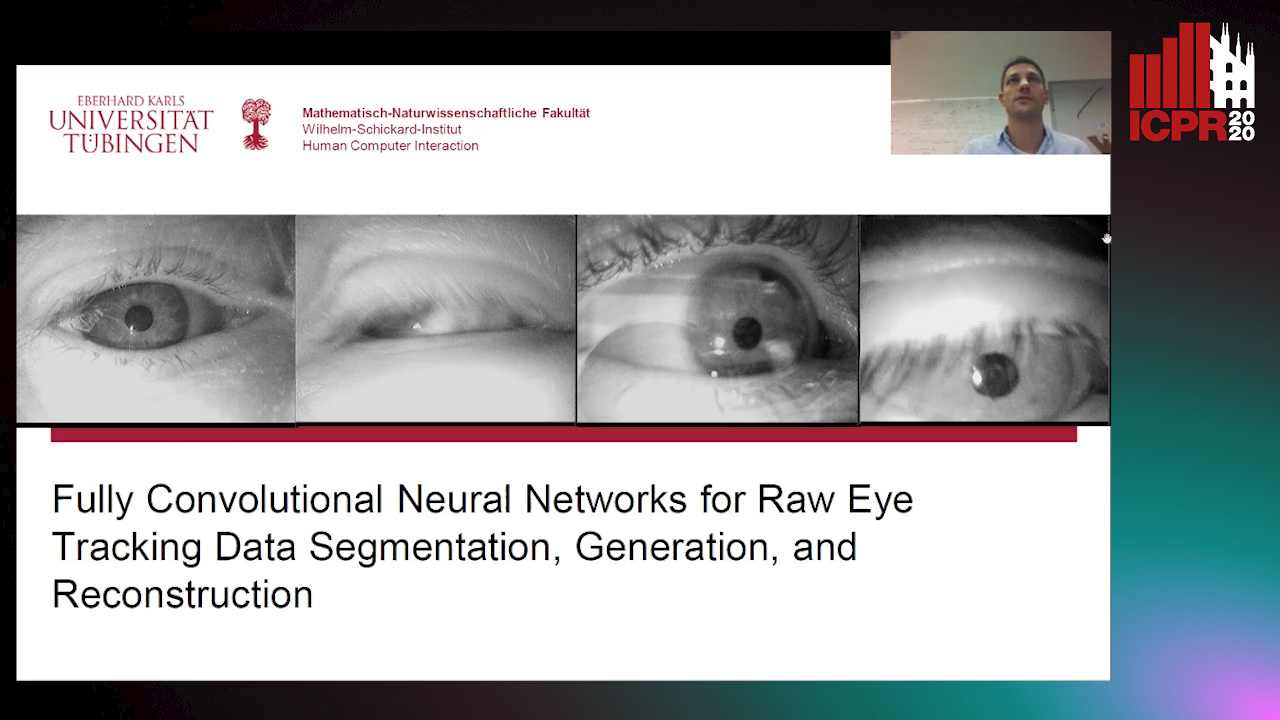
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Eye Tracking Data with Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Creating Classifier Ensembles through Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Aerial Scene Classification
Álvaro Roberto Ferreira Jr., Gustavo Gustavo Henrique De Rosa, Joao Paulo Papa, Gustavo Carneiro, Fabio Augusto Faria

Auto-TLDR; Univariate Marginal Distribution Algorithm for Aerial Scene Classification Using Meta-Heuristic Optimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
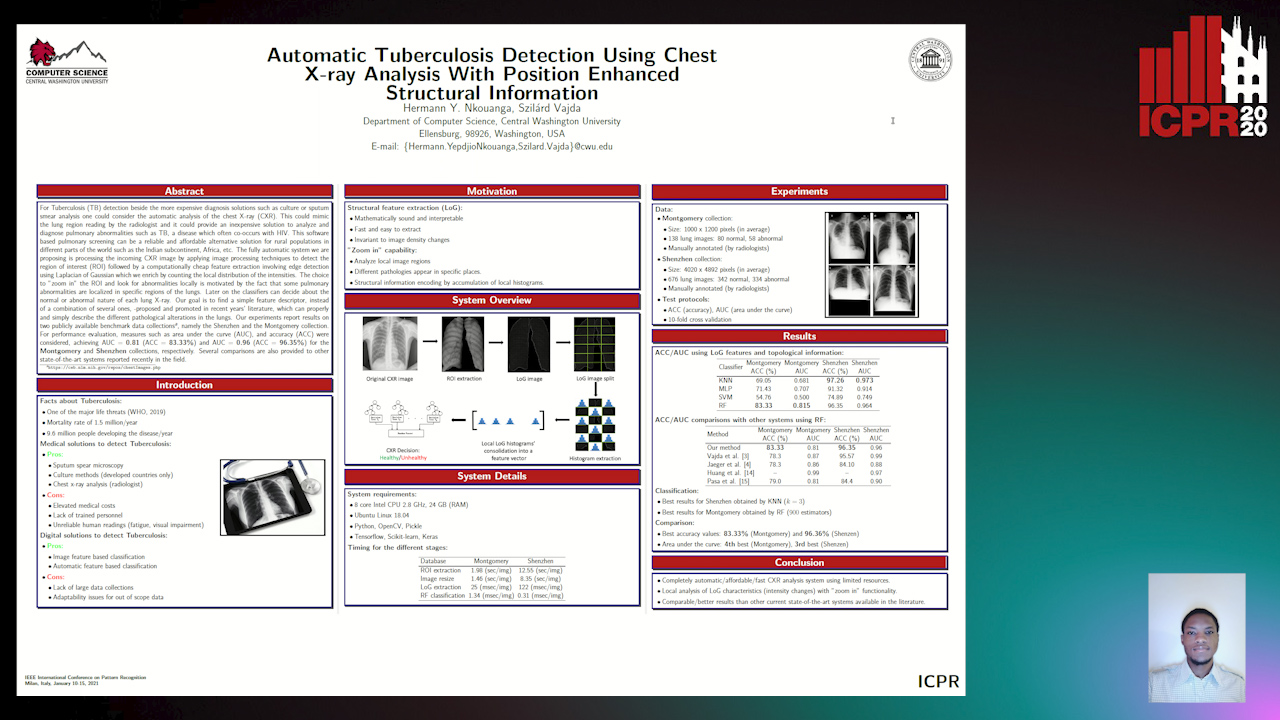
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
Detection of Makeup Presentation Attacks Based on Deep Face Representations
Christian Rathgeb, Pawel Drozdowski, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; An Attack Detection Scheme for Face Recognition Using Makeup Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Investigation of Feature Selection and Transfer Learning for Writer-Independent Offline Handwritten Signature Verification
Victor Souza, Adriano Oliveira, Rafael Menelau Oliveira E Cruz, Robert Sabourin

Auto-TLDR; Overfitting of SigNet using Binary Particle Swarm Optimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Viability of Optical Coherence Tomography for Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Auto-TLDR; Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging for Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Level Attention-Based Fusion Learning for RGB-D Face Recognition
Hardik Uppal, Alireza Sepas-Moghaddam, Michael Greenspan, Ali Etemad

Auto-TLDR; Fused RGB-D Facial Recognition using Attention-Aware Feature Fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Gravitational Wave Detection with 2D Convolutional Neural Networks
Siyu Fan, Yisen Wang, Yuan Luo, Alexander Michael Schmitt, Shenghua Yu

Auto-TLDR; Two-dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks for Gravitational Wave Detection from Time Series with Background Noise
Attribute-Based Quality Assessment for Demographic Estimation in Face Videos
Fabiola Becerra-Riera, Annette Morales-González, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Jean-Luc Dugelay
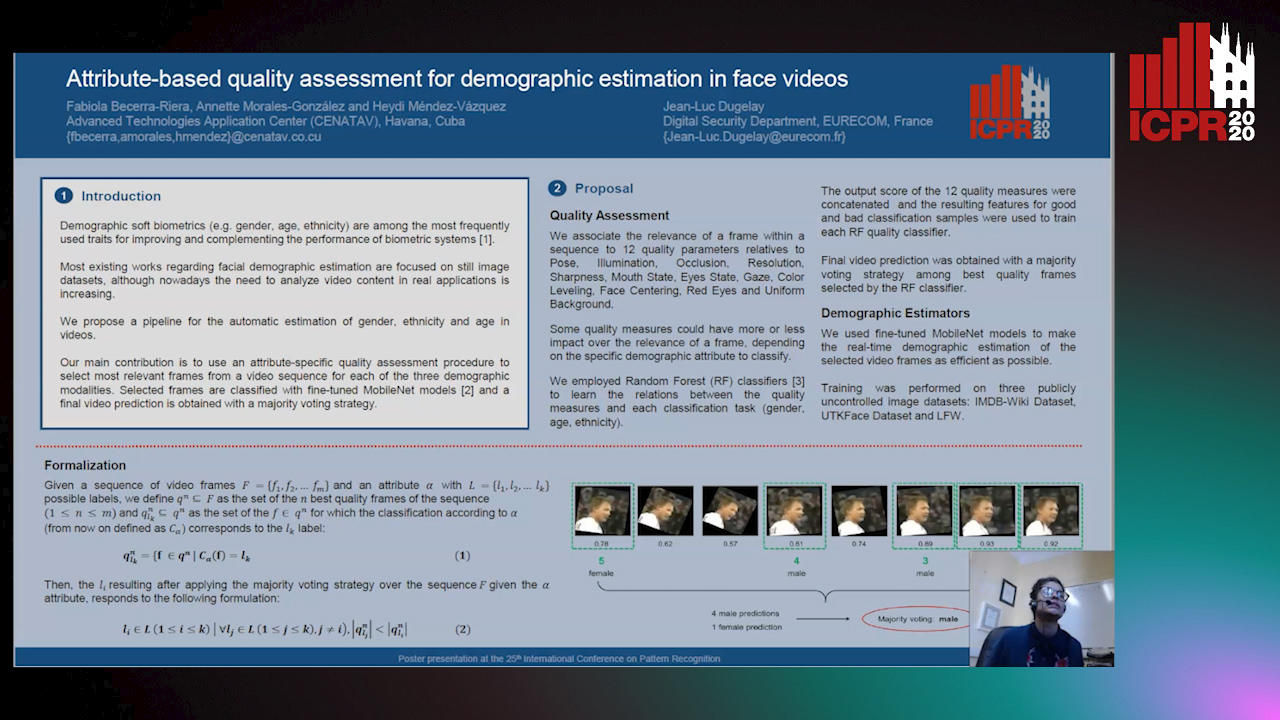
Auto-TLDR; Facial Demographic Estimation in Video Scenarios Using Quality Assessment
ResMax: Detecting Voice Spoofing Attacks with Residual Network and Max Feature Map
Il-Youp Kwak, Sungsu Kwag, Junhee Lee, Jun Ho Huh, Choong-Hoon Lee, Youngbae Jeon, Jeonghwan Hwang, Ji Won Yoon

Auto-TLDR; ASVspoof 2019: A Lightweight Automatic Speaker Verification Spoofing and Countermeasures System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Metric Features for Writer-Independent Signature Verification Using Dual Triplet Loss
Auto-TLDR; A dual triplet loss based method for offline writer-independent signature verification
Rotation Detection in Finger Vein Biometrics Using CNNs
Bernhard Prommegger, Georg Wimmer, Andreas Uhl
Auto-TLDR; A CNN based rotation detector for finger vein recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Handwritten Signature and Text Based User Verification Using Smartwatch
Raghavendra Ramachandra, Sushma Venkatesh, Raja Kiran, Christoph Busch
Auto-TLDR; A novel technique for user verification using a smartwatch based on writing pattern or signing pattern
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Appliance Identification Using a Histogram Post-Processing of 2D Local Binary Patterns for Smart Grid Applications
Yassine Himeur, Abdullah Alsalemi, Faycal Bensaali, Abbes Amira

Auto-TLDR; LBP-BEVM based Local Binary Patterns for Appliances Identification in the Smart Grid
A Novel Random Forest Dissimilarity Measure for Multi-View Learning
Hongliu Cao, Simon Bernard, Robert Sabourin, Laurent Heutte
Auto-TLDR; Multi-view Learning with Random Forest Relation Measure and Instance Hardness
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AdaFilter: Adaptive Filter Design with Local Image Basis Decomposition for Optimizing Image Recognition Preprocessing
Aiga Suzuki, Keiichi Ito, Takahide Ibe, Nobuyuki Otsu
Auto-TLDR; Optimal Preprocessing Filtering for Pattern Recognition Using Higher-Order Local Auto-Correlation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar