Improving Gravitational Wave Detection with 2D Convolutional Neural Networks
Siyu Fan,
Yisen Wang,
Yuan Luo,
Alexander Michael Schmitt,
Shenghua Yu

Auto-TLDR; Two-dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks for Gravitational Wave Detection from Time Series with Background Noise
Similar papers
Which are the factors affecting the performance of audio surveillance systems?
Antonio Greco, Antonio Roberto, Alessia Saggese, Mario Vento

Auto-TLDR; Sound Event Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Visual Representations on MIVIA Audio Events
ESResNet: Environmental Sound Classification Based on Visual Domain Models
Andrey Guzhov, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel
Auto-TLDR; Environmental Sound Classification with Short-Time Fourier Transform Spectrograms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EasiECG: A Novel Inter-Patient Arrhythmia Classification Method Using ECG Waves
Chuanqi Han, Ruoran Huang, Fang Yu, Xi Huang, Li Cui

Auto-TLDR; EasiECG: Attention-based Convolution Factorization Machines for Arrhythmia Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Network for End-To-End Text-Independent Speaker Identification
Wajdi Ghezaiel, Luc Brun, Olivier Lezoray
Auto-TLDR; Text-Independent Speaker Identification with Scattering Wavelet Network and Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Radar Image Reconstruction from Raw ADC Data Using Parametric Variational Autoencoder with Domain Adaptation
Michael Stephan, Thomas Stadelmayer, Avik Santra, Georg Fischer, Robert Weigel, Fabian Lurz
Auto-TLDR; Parametric Variational Autoencoder-based Human Target Detection and Localization for Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave Radar
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Application of Capsule Neural Network Based CNN for Speech Emotion Recognition

Auto-TLDR; CapCNN: A Capsule Neural Network for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ballroom Dance Recognition from Audio Recordings
Tomas Pavlin, Jan Cech, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; A CNN-based approach to classify ballroom dances given audio recordings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Wireless Localisation in WiFi Using Novel Deep Architectures
Peizheng Li, Han Cui, Aftab Khan, Usman Raza, Robert Piechocki, Angela Doufexi, Tim Farnham
Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Indoor Localisation of WiFi Devices in Indoor Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for Power Line Outage Identification
Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Networks for Power Line Outage Identification
Modulation Pattern Detection Using Complex Convolutions in Deep Learning
Jakob Krzyston, Rajib Bhattacharjea, Andrew Stark

Auto-TLDR; Complex Convolutional Neural Networks for Modulation Pattern Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Learning on Active Sonar Data Using Bayesian Optimization for Hyperparameter Tuning
Henrik Berg, Karl Thomas Hjelmervik

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Optimization for Sonar Operations in Littoral Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DenseRecognition of Spoken Languages
Jaybrata Chakraborty, Bappaditya Chakraborty, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; DenseNet: A Dense Convolutional Network Architecture for Speech Recognition in Indian Languages
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Using a Two-Step Feature Fusion Strategy

Auto-TLDR; A Two-Step Feature Fusion Network for Speech Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Engineering and Stacked Echo State Networks for Musical Onset Detection
Peter Steiner, Azarakhsh Jalalvand, Simon Stone, Peter Birkholz

Auto-TLDR; Echo State Networks for Onset Detection in Music Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Signal Generation Using 1d Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks for Fault Diagnosis of Electrical Machines
Russell Sabir, Daniele Rosato, Sven Hartmann, Clemens Gühmann

Auto-TLDR; Large Dataset Generation from Faulty AC Machines using Deep Convolutional GAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Marine Species in Echograms Via Traditional, Hybrid, and Deep Learning Frameworks
Porto Marques Tunai, Alireza Rezvanifar, Melissa Cote, Alexandra Branzan Albu, Kaan Ersahin, Todd Mudge, Stephane Gauthier
Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Deep Learning for Echogram Interpretation of Marine Species in Echograms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fine-Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Guide and Benchmark Analysis for Glaucoma Screening
Amed Mvoulana, Rostom Kachouri, Mohamed Akil
Auto-TLDR; Fine-tuning Convolutional Neural Networks for Glaucoma Screening
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FC-DCNN: A Densely Connected Neural Network for Stereo Estimation
Dominik Hirner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; FC-DCNN: A Lightweight Network for Stereo Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Merged 1D-2D Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Nerve Detection in Ultrasound Images
Mohammad Alkhatib, Adel Hafiane, Pierre Vieyres

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Deep Neural Networks to Detect Median Nerve in Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Weak Coupling of Semi-Supervised Learning with Generative Adversarial Networks for Malware Classification
Shuwei Wang, Qiuyun Wang, Zhengwei Jiang, Xuren Wang, Rongqi Jing

Auto-TLDR; IMIR: An Improved Malware Image Rescaling Algorithm Using Semi-supervised Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Planar 3D Transfer Learning for End to End Unimodal MRI Unbalanced Data Segmentation
Martin Kolarik, Radim Burget, Carlos M. Travieso-Gonzalez, Jan Kocica

Auto-TLDR; Planar 3D Res-U-Net Network for Unbalanced 3D Image Segmentation using Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recover
Temporal Pulses Driven Spiking Neural Network for Time and Power Efficient Object Recognition in Autonomous Driving
Wei Wang, Shibo Zhou, Jingxi Li, Xiaohua Li, Junsong Yuan, Zhanpeng Jin

Auto-TLDR; Spiking Neural Network for Real-Time Object Recognition on Temporal LiDAR Pulses
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VPU Specific CNNs through Neural Architecture Search
Ciarán Donegan, Hamza Yous, Saksham Sinha, Jonathan Byrne

Auto-TLDR; Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Edge Devices using Neural Architecture Search
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recursive Convolutional Neural Networks for Epigenomics
Aikaterini Symeonidi, Anguelos Nicolaou, Frank Johannes, Vincent Christlein
Auto-TLDR; Recursive Convolutional Neural Networks for Epigenomic Data Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant in MRA Using Dual-Attention Atrous Net
Subhashis Banerjee, Ashis Kumar Dhara, Johan Wikström, Robin Strand

Auto-TLDR; Dual-Attention Atrous Net for Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysm Remnant from MRA Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamically Mitigating Data Discrepancy with Balanced Focal Loss for Replay Attack Detection
Yongqiang Dou, Haocheng Yang, Maolin Yang, Yanyan Xu, Dengfeng Ke

Auto-TLDR; Anti-Spoofing with Balanced Focal Loss Function and Combination Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Bayesian Deep CNN Framework for Reconstructing K-T-Undersampled Resting-fMRI
Karan Taneja, Prachi Kulkarni, Shabbir Merchant, Suyash Awate
Auto-TLDR; K-t undersampled R-fMRI Reconstruction using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Epileptic Seizure Prediction: A Semi-Dilated Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
Ramy Hussein, Rabab K. Ward, Soojin Lee, Martin Mckeown
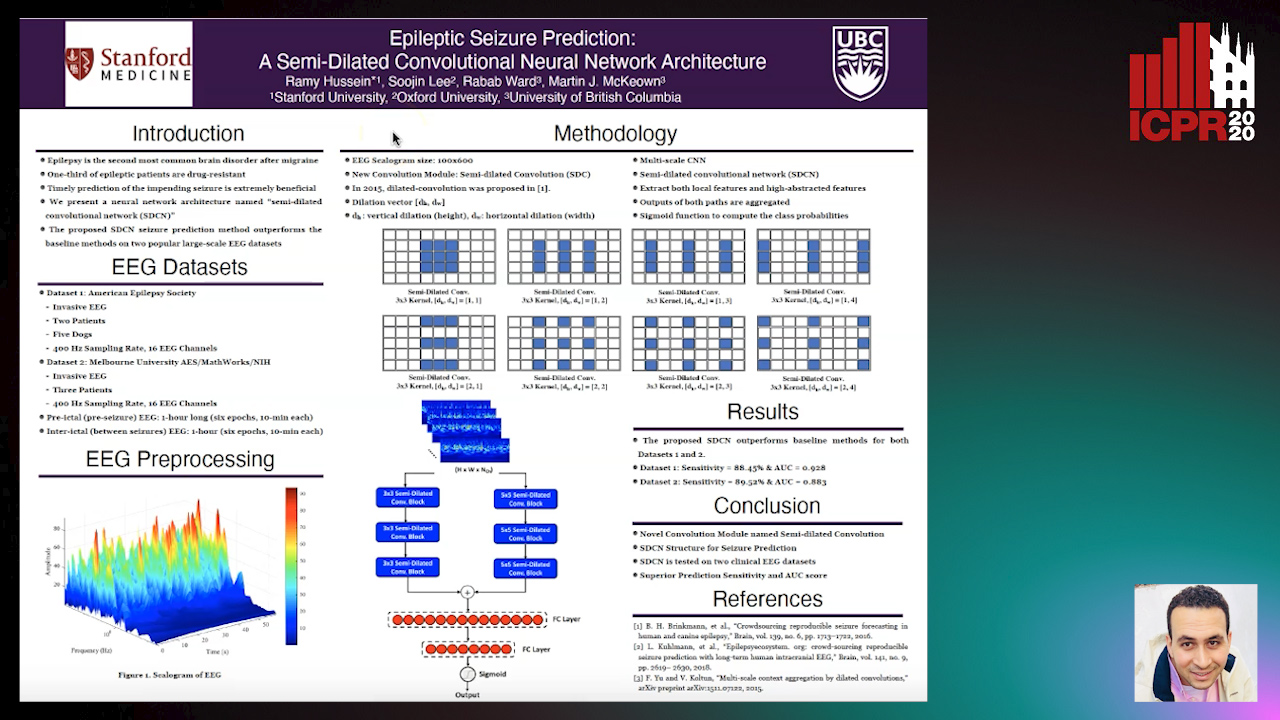
Auto-TLDR; Semi-Dilated Convolutional Network for Seizure Prediction using EEG Scalograms
AdaFilter: Adaptive Filter Design with Local Image Basis Decomposition for Optimizing Image Recognition Preprocessing
Aiga Suzuki, Keiichi Ito, Takahide Ibe, Nobuyuki Otsu
Auto-TLDR; Optimal Preprocessing Filtering for Pattern Recognition Using Higher-Order Local Auto-Correlation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale and Attention Based ResNet for Heartbeat Classification
Haojie Zhang, Gongping Yang, Yuwen Huang, Feng Yuan, Yilong Yin

Auto-TLDR; A Multi-Scale and Attention based ResNet for ECG heartbeat classification in intra-patient and inter-patient paradigms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Comparison of Neural Network Approaches for Melanoma Classification
Maria Frasca, Michele Nappi, Michele Risi, Genoveffa Tortora, Alessia Auriemma Citarella
Auto-TLDR; Classification of Melanoma Using Deep Neural Network Methodologies
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Scalable Deep Neural Network to Detect Low Quality Images without a Reference
Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network-based Algorithm for Non-reference Non-Reference Non-Referential Image Quality Metrics for Streaming Services
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty Guided Recognition of Tiny Craters on the Moon
Thorsten Wilhelm, Christian Wöhler
Auto-TLDR; Accurately Detecting Tiny Craters in Remote Sensed Images Using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Road Network Metric Learning for Estimated Time of Arrival
Yiwen Sun, Kun Fu, Zheng Wang, Changshui Zhang, Jieping Ye

Auto-TLDR; Road Network Metric Learning for Estimated Time of Arrival (RNML-ETA)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Binary Representation for Event-Based Action Recognition
Simone Undri Innocenti, Federico Becattini, Federico Pernici, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Binary Representation for Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Atmospheric Blocking Pattern Recognition in Global Climate Model Simulation Data
Grzegorz Muszynski, Prabhat Mr, Jan Balewski, Karthik Kashinath, Michael Wehner, Vitaliy Kurlin
Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Pattern Recognition of Atmospheric Blocking Events in Global Climate Model Simulation Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BAT Optimized CNN Model Identifies Water Stress in Chickpea Plant Shoot Images
Shiva Azimi, Taranjit Kaur, Tapan Gandhi

Auto-TLDR; BAT Optimized ResNet-18 for Stress Classification of chickpea shoot images under water deficiency
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Neural Compression and Filtering for Edge-assisted Real-time Object Detection in Challenged Networks
Yoshitomo Matsubara, Marco Levorato

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Networks for Remote Object Detection Using Edge Computing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Localization of Retinal Lesions Via Weakly-Supervised Learning

Auto-TLDR; Weakly Learning of Lesions in Fundus Images Using Multi-level Feature Maps and Classification Score
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Training for Audio Classifiers
Raymel Alfonso Sallo, Mohammad Esmaeilpour, Patrick Cardinal

Auto-TLDR; Adversarially Training for Robust Neural Networks against Adversarial Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar