Learning Metric Features for Writer-Independent Signature Verification Using Dual Triplet Loss
Auto-TLDR; A dual triplet loss based method for offline writer-independent signature verification
Similar papers
An Investigation of Feature Selection and Transfer Learning for Writer-Independent Offline Handwritten Signature Verification
Victor Souza, Adriano Oliveira, Rafael Menelau Oliveira E Cruz, Robert Sabourin

Auto-TLDR; Overfitting of SigNet using Binary Particle Swarm Optimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cut and Compare: End-To-End Offline Signature Verification Network

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Cut-and-Compare Network for Offline Signature Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Total Whitening for Online Signature Verification Based on Deep Representation
Xiaomeng Wu, Akisato Kimura, Kunio Kashino, Seiichi Uchida

Auto-TLDR; Total Whitening for Online Signature Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Writer Identification Using Deep Neural Networks: Impact of Patch Size and Number of Patches
Akshay Punjabi, José Ramón Prieto Fontcuberta, Enrique Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Writer Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
One-Shot Representational Learning for Joint Biometric and Device Authentication

Auto-TLDR; Joint Biometric and Device Recognition from a Single Biometric Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Handwritten Signature and Text Based User Verification Using Smartwatch
Raghavendra Ramachandra, Sushma Venkatesh, Raja Kiran, Christoph Busch
Auto-TLDR; A novel technique for user verification using a smartwatch based on writing pattern or signing pattern
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human or Machine? It Is Not What You Write, but How You Write It
Luis Leiva, Moises Diaz, M.A. Ferrer, Réjean Plamondon

Auto-TLDR; Behavioral Biometrics via Handwritten Symbols for Identification and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Haruka Aoki, Koki Tsubota, Hikaru Ikuta, Kiyoharu Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; Deep Metric Learning for Japanese Typographic Font Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection of Makeup Presentation Attacks Based on Deep Face Representations
Christian Rathgeb, Pawel Drozdowski, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; An Attack Detection Scheme for Face Recognition Using Makeup Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Finger Vein Recognition and Intra-Subject Similarity Evaluation of Finger Veins Using the CNN Triplet Loss
Georg Wimmer, Bernhard Prommegger, Andreas Uhl

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein recognition using CNNs and hard triplet online selection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Learning Algorithm for Efficient Person Re-Identification
Zhen Li, Hanyang Shao, Liang Niu, Nian Xue

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Learning Algorithm for Large-Scale Person Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Dynamic Color Texture Analysis Using Local Directional Number Pattern
Junwei Zhou, Ke Shu, Peng Liu, Jianwen Xiang, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; LDN-TOP Representation followed by ProCRC Classification for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Weak Coupling of Semi-Supervised Learning with Generative Adversarial Networks for Malware Classification
Shuwei Wang, Qiuyun Wang, Zhengwei Jiang, Xuren Wang, Rongqi Jing

Auto-TLDR; IMIR: An Improved Malware Image Rescaling Algorithm Using Semi-supervised Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Learning Multiple Curvature Descriptor for 3D Palmprint Recognition
Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Jie Wen, Chunwei Tian, Peng Liu, Shuping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Joint Feature Learning for 3D palmprint recognition using curvature data vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-People Mobile-Phone Based Airwriting Character Recognition
Yunzhe Li, Hui Zheng, He Zhu, Haojun Ai, Xiaowei Dong

Auto-TLDR; Cross-People Airwriting Recognition via Motion Sensor Signal via Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SSDL: Self-Supervised Domain Learning for Improved Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Domain Learning for Face Recognition in unconstrained environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recursive Recognition of Offline Handwritten Mathematical Expressions
Marco Cotogni, Claudio Cusano, Antonino Nocera

Auto-TLDR; Online Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition with Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixNet for Generalized Face Presentation Attack Detection
Nilay Sanghvi, Sushant Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MixNet: A Deep Learning-based Network for Detection of Presentation Attacks in Cross-Database and Unseen Setting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota, Alexander Stone, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
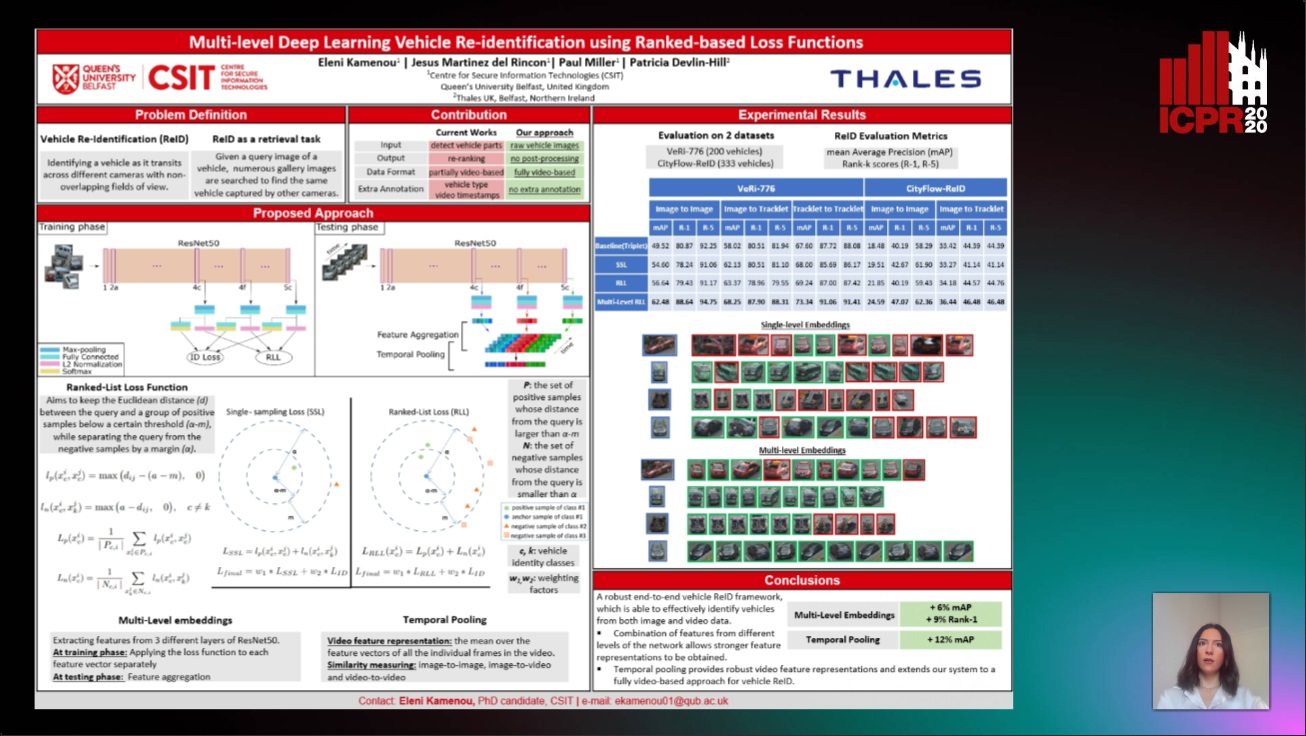
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supporting Skin Lesion Diagnosis with Content-Based Image Retrieval
Stefano Allegretti, Federico Bolelli, Federico Pollastri, Sabrina Longhitano, Giovanni Pellacani, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; Skin Images Retrieval Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Skin Lesion Classification and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose Variation Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Lei Zhang, Na Jiang, Qishuai Diao, Yue Xu, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu

Auto-TLDR; Pose Transfer Generative Adversarial Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Equation Attention Relationship Network (EARN) : A Geometric Deep Metric Framework for Learning Similar Math Expression Embedding
Saleem Ahmed, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; Representational Learning for Similarity Based Retrieval of Mathematical Expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Nonlinear Ranking Loss on Riemannian Potato Embedding
Byung Hyung Kim, Yoonje Suh, Honggu Lee, Sungho Jo

Auto-TLDR; Riemannian Potato for Rank-based Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Word Recognition Using Multiple Hypotheses and Deep Embeddings
Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; EmbedNet: fuse recognition-based and recognition-free approaches for word recognition using learning-based methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Seismocardiogram Biometrics with Wavelet Transform
Po-Ya Hsu, Po-Han Hsu, Hsin-Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Seismocardiogram Biometric Matching Using Wavelet Transform and Deep Learning Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Robust Face Recognition by Deep Meta Capsule Network-Based Equivariant Embedding
Fangyu Wu, Jeremy Simon Smith, Wenjin Lu, Bailing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Deep Meta Capsule Network-based Equivariant Embedding Model for Pose-Robust Face Recognition
Batch-Incremental Triplet Sampling for Training Triplet Networks Using Bayesian Updating Theorem
Milad Sikaroudi, Benyamin Ghojogh, Fakhri Karray, Mark Crowley, Hamid Reza Tizhoosh
Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Updating Triplet Mining with Bayesian updating
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D License Plate Recognition based on Automatic Perspective Rectification
Hui Xu, Zhao-Hong Guo, Da-Han Wang, Xiang-Dong Zhou, Yu Shi

Auto-TLDR; Perspective Rectification Network for License Plate Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for Facial Template Protection
Hakyoung Lee, Cheng Yaw Low, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for C cancellable Biometrics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multimodal Side-Tuning for Document Classification
Stefano Zingaro, Giuseppe Lisanti, Maurizio Gabbrielli

Auto-TLDR; Side-tuning for Multimodal Document Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Identification and Retrieval of Near-Duplicate Biological Images: A New Dataset and Protocol
Thomas E. Koker, Sai Spandana Chintapalli, San Wang, Blake A. Talbot, Daniel Wainstock, Marcelo Cicconet, Mary C. Walsh
Auto-TLDR; BINDER: Bio-Image Near-Duplicate Examples Repository for Image Identification and Retrieval
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Teacher-Student Training and Triplet Loss for Facial Expression Recognition under Occlusion
Mariana-Iuliana Georgescu, Radu Ionescu

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation for Facial Expression Recognition under Occlusion
SL-DML: Signal Level Deep Metric Learning for Multimodal One-Shot Action Recognition
Raphael Memmesheimer, Nick Theisen, Dietrich Paulus

Auto-TLDR; One-Shot Action Recognition using Metric Learning
Online Trajectory Recovery from Offline Handwritten Japanese Kanji Characters of Multiple Strokes
Hung Tuan Nguyen, Tsubasa Nakamura, Cuong Tuan Nguyen, Masaki Nakagawa

Auto-TLDR; Recovering Dynamic Online Trajectories from Offline Japanese Kanji Character Images for Handwritten Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
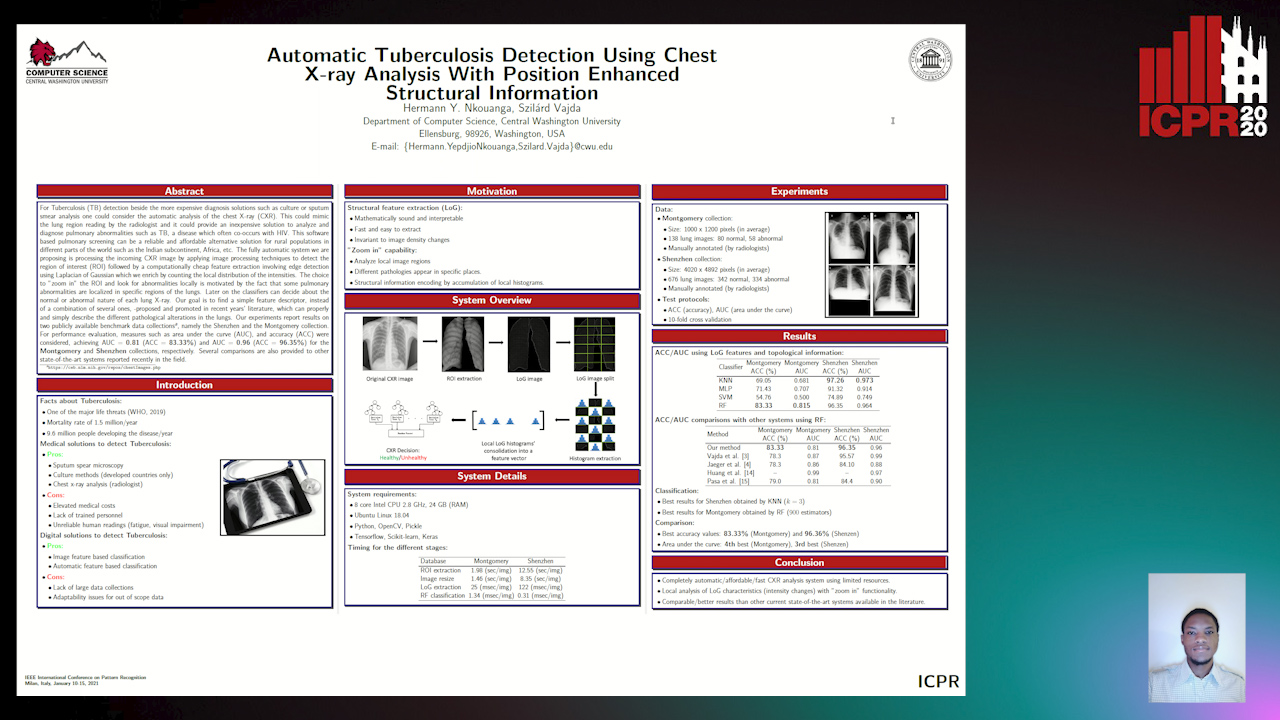
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Embeddings for Image Clustering: An Empirical Study of Triplet Loss Approaches
Kalun Ho, Janis Keuper, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; Clustering Objectives for K-means and Correlation Clustering Using Triplet Loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Emotional Blinded Face Representations
Alejandro Peña Almansa, Julian Fierrez, Agata Lapedriza, Aythami Morales

Auto-TLDR; Blind Face Representations for Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar