An Experimental Evaluation of Recent Face Recognition Losses for Deepfake Detection
Yu-Cheng Liu,
Chia-Ming Chang,
I-Hsuan Chen,
Yu Ju Ku,
Jun-Cheng Chen

Auto-TLDR; Deepfake Classification and Detection using Loss Functions for Face Recognition
Similar papers
Video Face Manipulation Detection through Ensemble of CNNs
Nicolo Bonettini, Edoardo Daniele Cannas, Sara Mandelli, Luca Bondi, Paolo Bestagini, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Face Manipulation Detection in Video Sequences Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Dual Loss for Manga Character Recognition with Imbalanced Training Data
Yonggang Li, Yafeng Zhou, Yongtao Wang, Xiaoran Qin, Zhi Tang

Auto-TLDR; Dual Adaptive Re-weighting Loss for Manga Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Angular Sparsemax for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cam-Softmax for Discriminative Deep Feature Learning
Tamas Suveges, Stephen James Mckenna

Auto-TLDR; Cam-Softmax: A Generalisation of Activations and Softmax for Deep Feature Spaces
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
G-FAN: Graph-Based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
He Zhao, Yongjie Shi, Xin Tong, Jingsi Wen, Xianghua Ying, Jinshi Hongbin Zha

Auto-TLDR; Graph-based Feature Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SATGAN: Augmenting Age Biased Dataset for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Wenshuang Liu, Wenting Chen, Yuanlue Zhu, Linlin Shen

Auto-TLDR; SATGAN: Stable Age Translation GAN for Cross-Age Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cc-Loss: Channel Correlation Loss for Image Classification
Zeyu Song, Dongliang Chang, Zhanyu Ma, Li Xiaoxu, Zheng-Hua Tan

Auto-TLDR; Channel correlation loss for ad- dressing image classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for Facial Template Protection
Hakyoung Lee, Cheng Yaw Low, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; SoftmaxOut Transformation-Permutation Network for C cancellable Biometrics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SSDL: Self-Supervised Domain Learning for Improved Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Domain Learning for Face Recognition in unconstrained environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fixed Simplex Coordinates for Angular Margin Loss in CapsNet
Rita Pucci, Christian Micheloni, Gian Luca Foresti, Niki Martinel

Auto-TLDR; angular margin loss for capsule networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
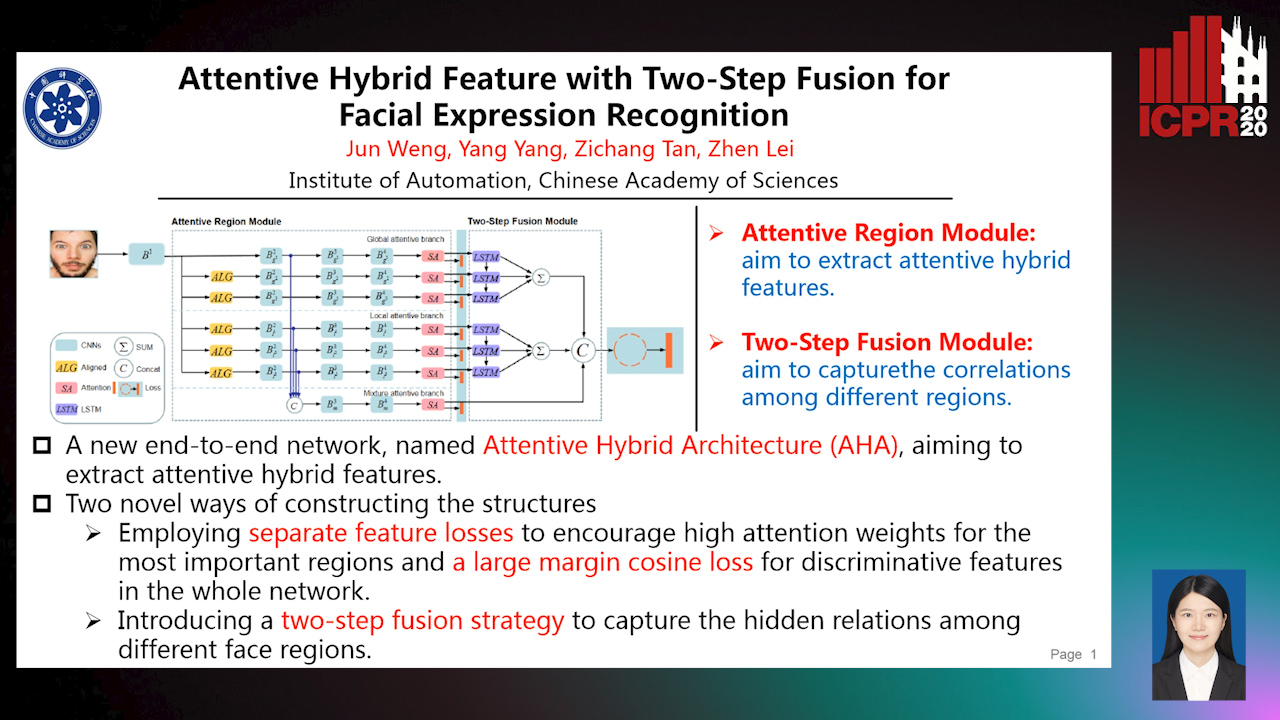
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Not 3D Re-ID: Simple Single Stream 2D Convolution for Robust Video Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; ResNet50-IBN for Video-based Person Re-Identification using Single Stream 2D Convolution Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Disentangled Representations for Identity Preserving Surveillance Face Camouflage
Jingzhi Li, Lutong Han, Hua Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Jingguo Ge, Xiaochu Cao

Auto-TLDR; Individual Face Privacy under Surveillance Scenario with Multi-task Loss Function
Contrastive Data Learning for Facial Pose and Illumination Normalization

Auto-TLDR; Pose and Illumination Normalization with Contrast Data Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lightweight Low-Resolution Face Recognition for Surveillance Applications
Yoanna Martínez-Díaz, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Luis S. Luevano, Leonardo Chang, Miguel Gonzalez-Mendoza

Auto-TLDR; Efficiency of Lightweight Deep Face Networks on Low-Resolution Surveillance Imagery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Disentangling of Viewpoint and Residues Variations by Substituting Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Minsu Kim, Joanna Hong, Junho Kim, Hong Joo Lee, Yong Man Ro
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Disentangling of Identity, viewpoint, and Residue Representations for Robust Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Label Contrastive Focal Loss for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Xiaoqiang Zheng, Zhenxia Yu, Lin Chen, Fan Zhu, Shilong Wang

Auto-TLDR; Multi-label Contrastive Focal Loss for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Image Quality Assessment for Model and Human Perception
Ken Chen, Yichao Wu, Zhenmao Li, Yudong Wu, Ding Liang

Auto-TLDR; A labour-saving method for FIQA training with contradictory data from multiple sources
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Teacher-Student Training and Triplet Loss for Facial Expression Recognition under Occlusion
Mariana-Iuliana Georgescu, Radu Ionescu

Auto-TLDR; Knowledge Distillation for Facial Expression Recognition under Occlusion
AdvHat: Real-World Adversarial Attack on ArcFace Face ID System
Stepan Komkov, Aleksandr Petiushko

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Sticker Attack on ArcFace in Shooting Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exposing Deepfake Videos by Tracking Eye Movements
Meng Li, Beibei Liu, Yujiang Hu, Yufei Wang

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Approach to Detecting Deepfake Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classifying Eye-Tracking Data Using Saliency Maps
Shafin Rahman, Sejuti Rahman, Omar Shahid, Md. Tahmeed Abdullah, Jubair Ahmed Sourov
Auto-TLDR; Saliency-based Feature Extraction for Automatic Classification of Eye-tracking Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-Supervised Learning
Jaewoo Park, Yoon Gyo Jung, Andrew Teoh

Auto-TLDR; Improving ImprovedGAN with Metric Learning for Semi-supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probability Guided Maxout
Claudio Ferrari, Stefano Berretti, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Probability Guided Maxout for CNN Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Flatter Loss for Bias Mitigation in Cross-Dataset Facial Age Estimation
Ali Akbari, Muhammad Awais, Zhenhua Feng, Ammarah Farooq, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; Cross-dataset Age Estimation for Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Visual Voice Activity Detection with an Automatically Annotated Dataset
Stéphane Lathuiliere, Pablo Mesejo, Radu Horaud

Auto-TLDR; Deep Visual Voice Activity Detection with Optical Flow
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
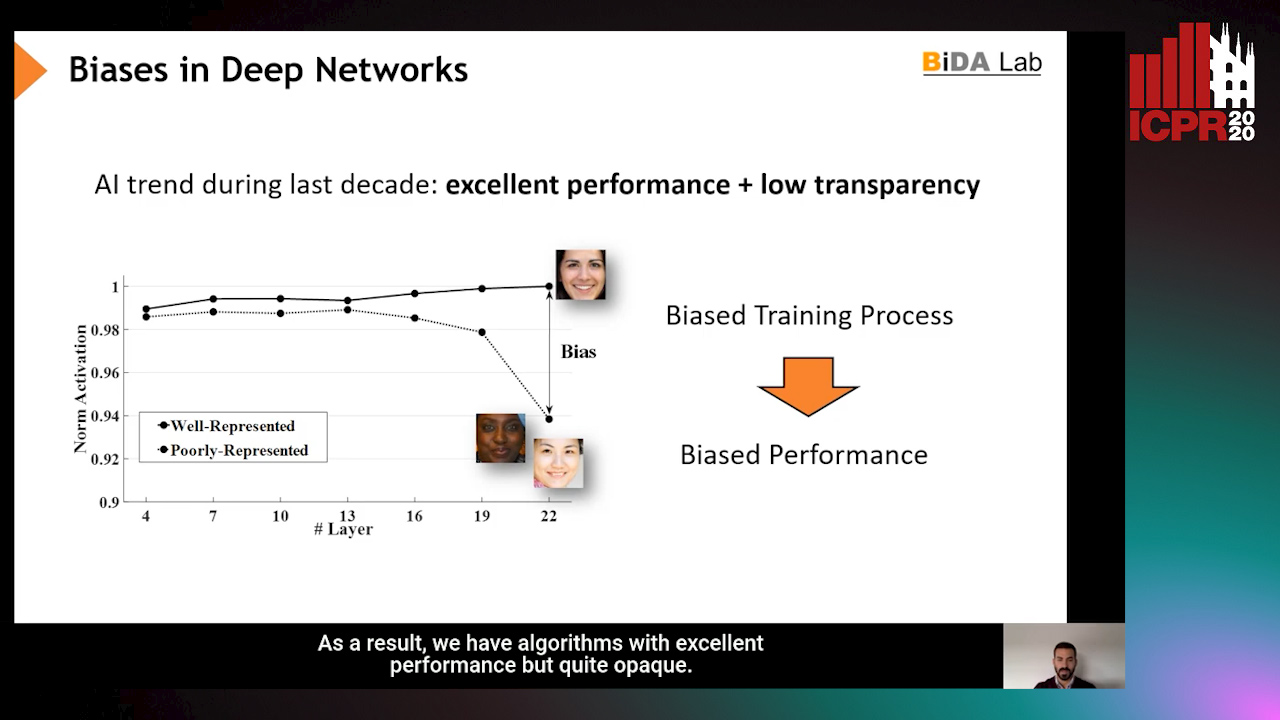
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
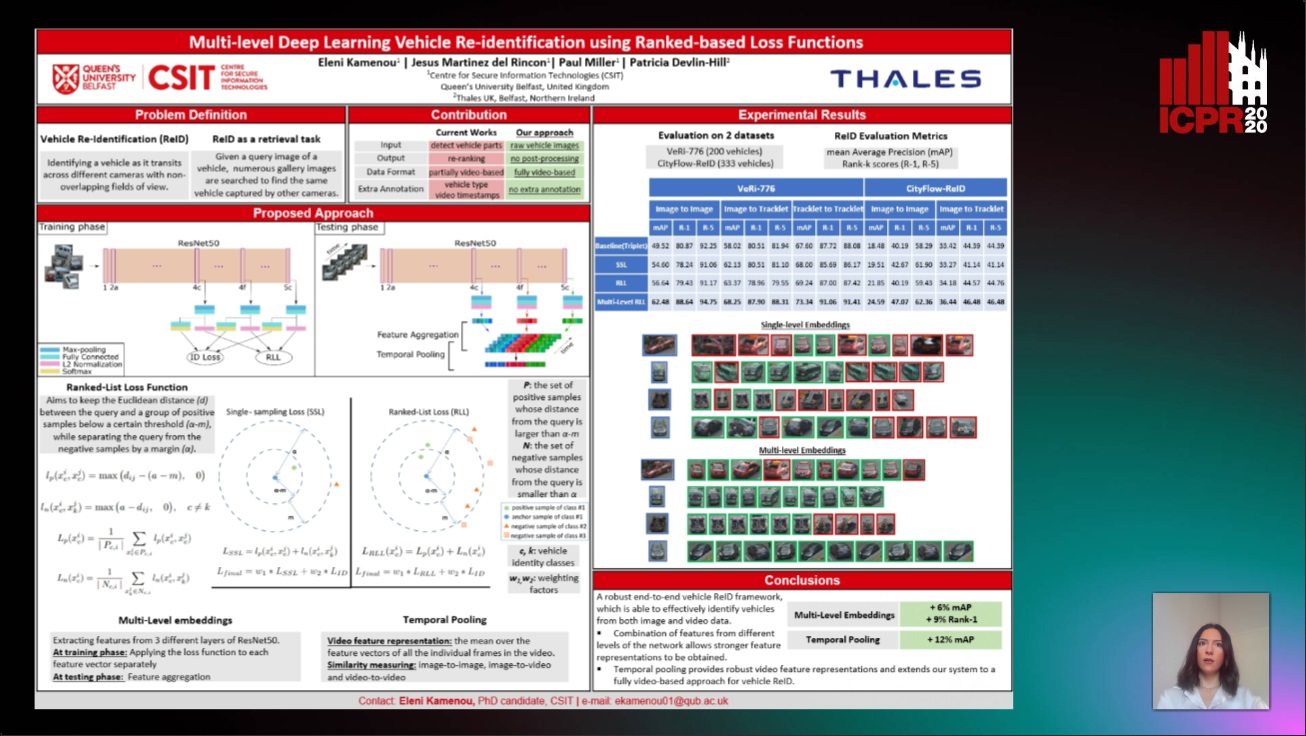
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Triplet Loss Based Emotion Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Puneet Kumar, Sidharth Jain, Balasubramanian Raman, Partha Pratim Roy, Masakazu Iwamura

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Neural Embedding System for Speech Emotion Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Person Recognition with HGR Maximal Correlation on Multimodal Data
Yihua Liang, Fei Ma, Yang Li, Shao-Lun Huang
Auto-TLDR; A correlation-based multimodal person recognition framework that learns discriminative embeddings of persons by joint learning visual features and audio features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Building Computationally Efficient and Well-Generalizing Person Re-Identification Models with Metric Learning
Vladislav Sovrasov, Dmitry Sidnev

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Generalization in Person Re-identification using Omni-Scale Network
ClusterFace: Joint Clustering and Classification for Set-Based Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Joint Clustering and Classification for Face Recognition in the Wild
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Cross Domain Multi-Modal Dataset for Robust Face Anti-Spoofing
Qiaobin Ji, Shugong Xu, Xudong Chen, Shan Cao, Shunqing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Cross domain multi-modal FAS dataset GREAT-FASD and several evaluation protocols for academic community
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved Deep Classwise Hashing with Centers Similarity Learning for Image Retrieval

Auto-TLDR; Deep Classwise Hashing for Image Retrieval Using Center Similarity Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking ReID:Multi-Feature Fusion Person Re-Identification Based on Orientation Constraints
Mingjing Ai, Guozhi Shan, Bo Liu, Tianyang Liu
Auto-TLDR; Person Re-identification with Orientation Constrained Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MixNet for Generalized Face Presentation Attack Detection
Nilay Sanghvi, Sushant Singh, Akshay Agarwal, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh

Auto-TLDR; MixNet: A Deep Learning-based Network for Detection of Presentation Attacks in Cross-Database and Unseen Setting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Semantic Representations Via Joint 3D Face Reconstruction and Facial Attribute Estimation
Zichun Weng, Youjun Xiang, Xianfeng Li, Juntao Liang, Wanliang Huo, Yuli Fu

Auto-TLDR; Joint Framework for 3D Face Reconstruction with Facial Attribute Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Quantitative Evaluation Framework of Video De-Identification Methods
Sathya Bursic, Alessandro D'Amelio, Marco Granato, Giuliano Grossi, Raffaella Lanzarotti

Auto-TLDR; Face de-identification using photo-reality and facial expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Robust Face Recognition by Deep Meta Capsule Network-Based Equivariant Embedding
Fangyu Wu, Jeremy Simon Smith, Wenjin Lu, Bailing Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Deep Meta Capsule Network-based Equivariant Embedding Model for Pose-Robust Face Recognition
Video Representation Fusion Network For Multi-Label Movie Genre Classification
Tianyu Bi, Dmitri Jarnikov, Johan Lukkien

Auto-TLDR; A Video Representation Fusion Network for Movie Genre Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar