Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification through Source-Guided Pseudo-Labeling
Fabian Dubourvieux,
Romaric Audigier,
Angélique Loesch,
Ainouz-Zemouche Samia,
Stéphane Canu
Auto-TLDR; Pseudo-labeling for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Similar papers
Progressive Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Image-Based Person Re-Identification
Mingliang Yang, Da Huang, Jing Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CANU-ReID: A Conditional Adversarial Network for Unsupervised Person Re-IDentification
Guillaume Delorme, Yihong Xu, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Radu Horaud, Xavier Alameda-Pineda

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Person Re-Identification with Clustering and Adversarial Learning
Domain Generalized Person Re-Identification Via Cross-Domain Episodic Learning
Ci-Siang Lin, Yuan Chia Cheng, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang

Auto-TLDR; Domain-Invariant Person Re-identification with Episodic Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Person Re-Identification by Attribute Similarity Guidance
Peixian Hong, Ancong Wu, Wei-Shi Zheng

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Similarity Guidance Guidance Loss for Semi-supervised Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Paced Bottom-Up Clustering Network with Side Information for Person Re-Identification
Mingkun Li, Chun-Guang Li, Ruo-Pei Guo, Jun Guo

Auto-TLDR; Self-Paced Bottom-up Clustering Network with Side Information for Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Online Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification with a Human in the Loop
Rita Delussu, Lorenzo Putzu, Giorgio Fumera, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Human-in-the-loop for Person Re-Identification in Infeasible Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Spatial-Aware GAN for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
Fangneng Zhan, Changgong Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Teacher-Student Competition for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Ruixin Xiao, Zhilei Liu, Baoyuan Wu
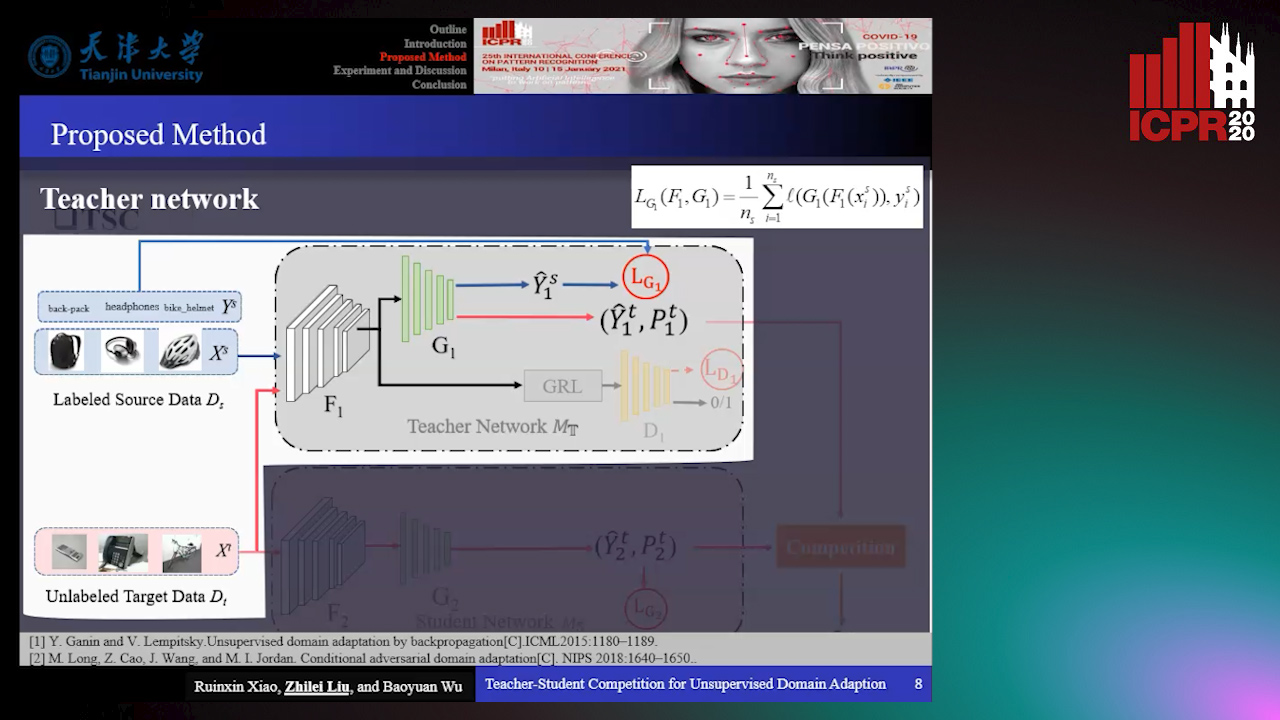
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaption with Teacher-Student Competition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Building Computationally Efficient and Well-Generalizing Person Re-Identification Models with Metric Learning
Vladislav Sovrasov, Dmitry Sidnev

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Generalization in Person Re-identification using Omni-Scale Network
Attention-Based Model with Attribute Classification for Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification
Simin Xu, Lingkun Luo, Shiqiang Hu

Auto-TLDR; An attention-based model with attribute classification for cross-domain person re-identification
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation Via Selective Pseudo Labeling and Progressive Self-Training

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation with Pseudo Labels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive L2 Regularization in Person Re-Identification
Xingyang Ni, Liang Fang, Heikki Juhani Huttunen

Auto-TLDR; AdaptiveReID: Adaptive L2 Regularization for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Energy-Constrained Self-Training for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Xiaofeng Liu, Xiongchang Liu, Bo Hu, Jun Lu, Jonghye Woo, Jane You

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Energy Function Minimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose Variation Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Lei Zhang, Na Jiang, Qishuai Diao, Yue Xu, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu

Auto-TLDR; Pose Transfer Generative Adversarial Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Class Conditional Alignment for Partial Domain Adaptation
Mohsen Kheirandishfard, Fariba Zohrizadeh, Farhad Kamangar
Auto-TLDR; Multi-class Adversarial Adaptation for Partial Domain Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multiple Domain Discriminators and Adaptive Self-Training
Teo Spadotto, Marco Toldo, Umberto Michieli, Pietro Zanuttigh

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Multi-Task Domain Adaptation

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multi-task Learning for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SSDL: Self-Supervised Domain Learning for Improved Face Recognition
Samadhi Poornima Kumarasinghe Wickrama Arachchilage, Ebroul Izquierdo

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Domain Learning for Face Recognition in unconstrained environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enlarging Discriminative Power by Adding an Extra Class in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Hai Tran, Sumyeong Ahn, Taeyoung Lee, Yung Yi

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation using Artificial Classes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Gaoang Wang, Chen Lin, Tianqiang Liu, Mingwei He, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; DAIL: Dataset-Aware and Invariant Learning for Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Progressive Learning Algorithm for Efficient Person Re-Identification
Zhen Li, Hanyang Shao, Liang Niu, Nian Xue

Auto-TLDR; Progressive Learning Algorithm for Large-Scale Person Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Unified Framework for Distance-Aware Domain Adaptation
Fei Wang, Youdong Ding, Huan Liang, Yuzhen Gao, Wenqi Che

Auto-TLDR; distance-aware domain adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Foreground-Focused Domain Adaption for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Unsupervised Object Detection
Shape Consistent 2D Keypoint Estimation under Domain Shift
Levi Vasconcelos, Massimiliano Mancini, Davide Boscaini, Barbara Caputo, Elisa Ricci

Auto-TLDR; Deep Adaptation for Keypoint Prediction under Domain Shift
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adversarially Constrained Interpolation for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Mohamed Azzam, Aurele Tohokantche Gnanha, Hau-San Wong, Si Wu

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Domain Mixup Strategy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAPC: Domain Adaptation People Counting Via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Na Jiang, Xingsen Wen, Zhiping Shi

Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation People counting via Style-Level Transfer Learning and Scene-Aware Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking ReID:Multi-Feature Fusion Person Re-Identification Based on Orientation Constraints
Mingjing Ai, Guozhi Shan, Bo Liu, Tianyang Liu
Auto-TLDR; Person Re-identification with Orientation Constrained Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Domain Generalization Baselines
Francesco Cappio Borlino, Antonio D'Innocente, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Style Transfer Data Augmentation for Domain Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Robust Learning with Different Label Noise Distributions
Diego Ortego, Eric Arazo, Paul Albert, Noel E O'Connor, Kevin Mcguinness

Auto-TLDR; Distribution Robust Pseudo-Labeling with Semi-supervised Learning
Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes Via Multi-Level Feature Alignment
Bin Zhang, Shengjie Zhao, Rongqing Zhang
Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Top-DB-Net: Top DropBlock for Activation Enhancement in Person Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; Top-DB-Net for Person Re-Identification using Top DropBlock
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Not 3D Re-ID: Simple Single Stream 2D Convolution for Robust Video Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; ResNet50-IBN for Video-based Person Re-Identification using Single Stream 2D Convolution Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Top-Rank Counter Metric for Person Re-Identification
Chen Chen, Hao Dou, Xiyuan Hu, Silong Peng

Auto-TLDR; Deep Top-Rank Counter Metric for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Graph Embedding
Lukas Hedegaard, Omar Ali Sheikh-Omar, Alexandros Iosifidis
Auto-TLDR; Domain Adaptation from the Perspective of Multi-view Graph Embedding and Dimensionality Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Randomized Transferable Machine

Auto-TLDR; Randomized Transferable Machine for Suboptimal Feature-based Transfer Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification Via Image Modality Conversion
Huangpeng Dai, Qing Xie, Yanchun Ma, Yongjian Liu, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; CE2L: A Novel Network for Cross-Modality Re-identification with Feature Alignment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
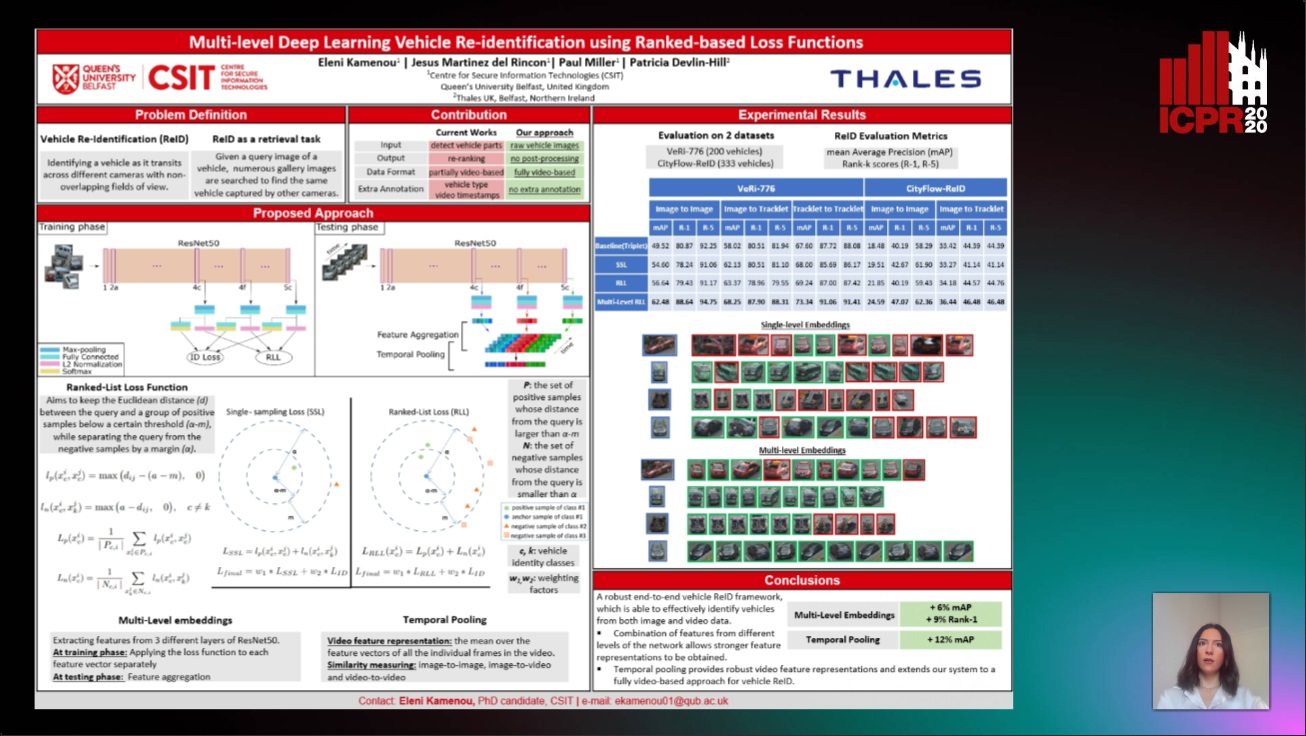
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Part-Aware Networks for Partial Person Re-Identification
Lijuan Huo, Chunfeng Song, Zhengyi Liu, Zhaoxiang Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Part-Aware Learning for Partial Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Manual-Label Free 3D Detection Via an Open-Source Simulator
Zhen Yang, Chi Zhang, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Huiming Guo

Auto-TLDR; DA-VoxelNet: A Novel Domain Adaptive VoxelNet for LIDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Open Set Domain Recognition Via Attention-Based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization
Xinxing He, Yuan Yuan, Zhiyu Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization for Open Set Domain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recurrent Deep Attention Network for Person Re-Identification
Changhao Wang, Jun Zhou, Xianfei Duan, Guanwen Zhang, Wei Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Deep Attention Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-Identification
Asad Munir, Niki Martinel, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; SCAN: Self and Channel Attention Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stochastic Label Refinery: Toward Better Target Label Distribution
Xi Fang, Jiancheng Yang, Bingbing Ni

Auto-TLDR; Stochastic Label Refinery for Deep Supervised Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Domain Adaptation with Consistency Training
Liang Xiao, Jiaolong Xu, Dawei Zhao, Zhiyu Wang, Li Wang, Yiming Nie, Bin Dai

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Embeddings for Image Clustering: An Empirical Study of Triplet Loss Approaches
Kalun Ho, Janis Keuper, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Margret Keuper
Auto-TLDR; Clustering Objectives for K-means and Correlation Clustering Using Triplet Loss
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Convolutional Feature Transfer via Camera-Specific Discriminative Pooling for Person Re-Identification
Tetsu Matsukawa, Einoshin Suzuki

Auto-TLDR; A small-scale CNN feature transfer method for person re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Simple Domain Shifting Network for Generating Low Quality Images
Guruprasad Hegde, Avinash Nittur Ramesh, Kanchana Vaishnavi Gandikota, Michael Möller, Roman Obermaisser
Auto-TLDR; Robotic Image Classification Using Quality degrading networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar