An Empirical Analysis of Visual Features for Multiple Object Tracking in Urban Scenes
Mehdi Miah,
Justine Pepin,
Nicolas Saunier,
Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau

Auto-TLDR; Evaluating Appearance Features for Multiple Object Tracking in Urban Scenes
Similar papers
Story Comparison for Estimating Field of View Overlap in a Video Collection
Thierry Malon, Sylvie Chambon, Alain Crouzil, Vincent Charvillat

Auto-TLDR; Finding Videos with Overlapping Fields of View Using Video Data
Not 3D Re-ID: Simple Single Stream 2D Convolution for Robust Video Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; ResNet50-IBN for Video-based Person Re-Identification using Single Stream 2D Convolution Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
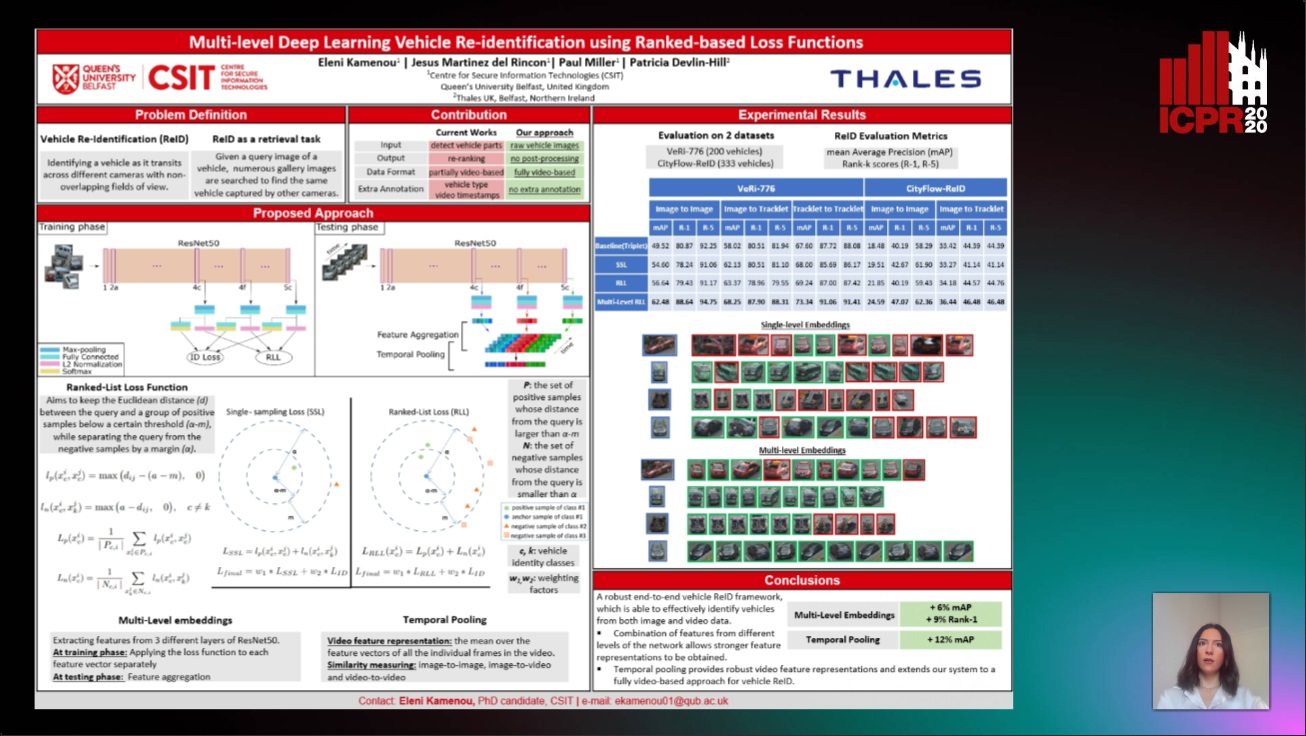
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SynDHN: Multi-Object Fish Tracker Trained on Synthetic Underwater Videos
Mygel Andrei Martija, Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Underwater Multi-Object Tracking in the Wild with Deep Hungarian Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Open-World Group Retrieval with Ambiguity Removal: A Benchmark
Ling Mei, Jian-Huang Lai, Zhanxiang Feng, Xiaohua Xie

Auto-TLDR; P2GSM-AR: Re-identifying changing groups of people under the open-world and group-ambiguity scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AerialMPTNet: Multi-Pedestrian Tracking in Aerial Imagery Using Temporal and Graphical Features
Maximilian Kraus, Seyed Majid Azimi, Emec Ercelik, Reza Bahmanyar, Peter Reinartz, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; AerialMPTNet: A novel approach for multi-pedestrian tracking in geo-referenced aerial imagery by fusing appearance features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Compact and Discriminative Multi-Object Tracking with Siamese CNNs
Claire Labit-Bonis, Jérôme Thomas, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fast, Light-Weight and All-in-One Single Object Tracking for Multi-Target Management
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SiamMT: Real-Time Arbitrary Multi-Object Tracking
Lorenzo Vaquero, Manuel Mucientes, Victor Brea

Auto-TLDR; SiamMT: A Deep-Learning-based Arbitrary Multi-Object Tracking System for Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Fully Convolutional Tracker with Motion Correction
Mathew Francis, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; A Siamese Ensemble for Visual Tracking with Appearance and Motion Components
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Building Computationally Efficient and Well-Generalizing Person Re-Identification Models with Metric Learning
Vladislav Sovrasov, Dmitry Sidnev

Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Generalization in Person Re-identification using Omni-Scale Network
How Important Are Faces for Person Re-Identification?
Julia Dietlmeier, Joseph Antony, Kevin Mcguinness, Noel E O'Connor

Auto-TLDR; Anonymization of Person Re-identification Datasets with Face Detection and Blurring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DAL: A Deep Depth-Aware Long-Term Tracker
Yanlin Qian, Song Yan, Alan Lukežič, Matej Kristan, Joni-Kristian Kamarainen, Jiri Matas
Auto-TLDR; Deep Depth-Aware Long-Term RGBD Tracking with Deep Discriminative Correlation Filter
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Duplex Spatiotemporal Filtering Network for Video-Based Person Re-Identification
Chong Zheng, Ping Wei, Nanning Zheng

Auto-TLDR; Duplex Spatiotemporal Filtering Network for Person Re-identification in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Top-DB-Net: Top DropBlock for Activation Enhancement in Person Re-Identification

Auto-TLDR; Top-DB-Net for Person Re-Identification using Top DropBlock
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Adaptive Fusion Model Based on Kalman Filtering and LSTM for Fast Tracking of Road Signs
Chengliang Wang, Xin Xie, Chao Liao

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of ThunderNet and Region Growing Detector for Road Sign Detection and Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Saliency Oriented Vehicle Scale Estimation
Qixin Chen, Tie Liu, Jiali Ding, Zejian Yuan, Yuanyuan Shang

Auto-TLDR; Regularized Intensity Matching for Vehicle Scale Estimation with salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive L2 Regularization in Person Re-Identification
Xingyang Ni, Liang Fang, Heikki Juhani Huttunen

Auto-TLDR; AdaptiveReID: Adaptive L2 Regularization for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPT: A Dataset for Identity Preserved Tracking in Closed Domains
Thomas Heitzinger, Martin Kampel
Auto-TLDR; Identity Preserved Tracking Using Depth Data for Privacy and Privacy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Segmentation for Pedestrian Detection from Motion in Temporal Domain

Auto-TLDR; Motion Profile: Recognizing Pedestrians along with their Motion Directions in a Temporal Way
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Visual Object Tracking with Two-Stream Residual Convolutional Networks
Ning Zhang, Jingen Liu, Ke Wang, Dan Zeng, Tao Mei

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Residual Convolutional Network for Visual Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSDM: Tracking by SiamRPN++ with a Depth-Refiner and a Mask-Generator
Pengyao Zhao, Quanli Liu, Wei Wang, Qiang Guo

Auto-TLDR; TSDM: A Depth-D Tracker for 3D Object Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Domain Siamese CNNs for Sparse Multispectral Disparity Estimation
David-Alexandre Beaupre, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau

Auto-TLDR; Multispectral Disparity Estimation between Thermal and Visible Images using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EAGLE: Large-Scale Vehicle Detection Dataset in Real-World Scenarios Using Aerial Imagery
Seyed Majid Azimi, Reza Bahmanyar, Corentin Henry, Kurz Franz

Auto-TLDR; EAGLE: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multi-class Vehicle Detection with Object Orientation Information in Airborne Imagery
Loop-closure detection by LiDAR scan re-identification
Jukka Peltomäki, Xingyang Ni, Jussi Puura, Joni-Kristian Kamarainen, Heikki Juhani Huttunen

Auto-TLDR; Loop-Closing Detection from LiDAR Scans Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vehicle Lane Merge Visual Benchmark
Auto-TLDR; A Benchmark for Automated Cooperative Maneuvering Using Multi-view Video Streams and Ground Truth Vehicle Description
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota, Alexander Stone, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
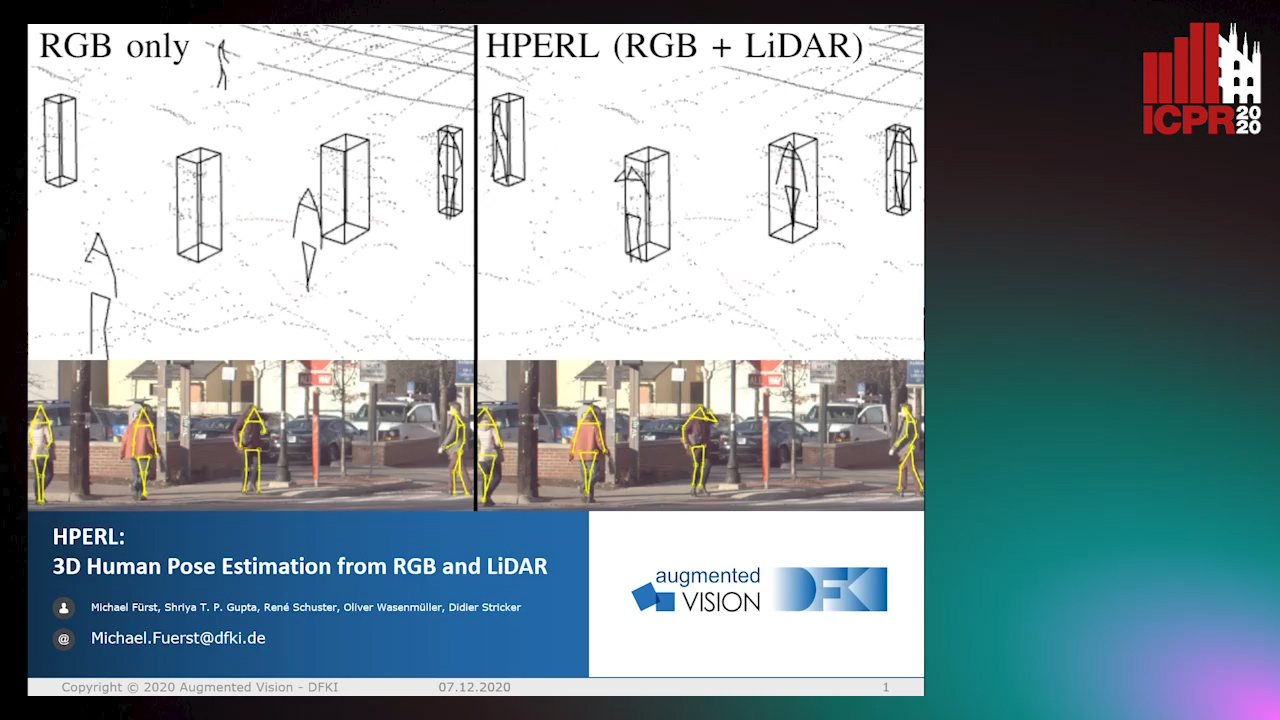
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VTT: Long-Term Visual Tracking with Transformers
Tianling Bian, Yang Hua, Tao Song, Zhengui Xue, Ruhui Ma, Neil Robertson, Haibing Guan

Auto-TLDR; Visual Tracking Transformer with transformers for long-term visual tracking
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Anomalies from Video-Sequences: A Novel Descriptor
Giulia Orrù, Davide Ghiani, Maura Pintor, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Trit-based Measurement of Group Dynamics for Crowd Behavior Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
Multi-Scale Keypoint Matching

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Scale Keypoint Matching Using Multi-Scale Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tackling Occlusion in Siamese Tracking with Structured Dropouts
Deepak Gupta, Efstratios Gavves, Arnold Smeulders
Auto-TLDR; Structured Dropout for Occlusion in latent space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SIMCO: SIMilarity-Based Object COunting
Marco Godi, Christian Joppi, Andrea Giachetti, Marco Cristani

Auto-TLDR; SIMCO: An Unsupervised Multi-class Object Counting Approach on InShape
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RSINet: Rotation-Scale Invariant Network for Online Visual Tracking
Yang Fang, Geunsik Jo, Chang-Hee Lee

Auto-TLDR; RSINet: Rotation-Scale Invariant Network for Adaptive Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Utilising Visual Attention Cues for Vehicle Detection and Tracking
Feiyan Hu, Venkatesh Gurram Munirathnam, Noel E O'Connor, Alan Smeaton, Suzanne Little
Auto-TLDR; Visual Attention for Object Detection and Tracking in Driver-Assistance Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Object Detection Using Object's Motion Context and Spatio-Temporal Feature Aggregation
Jaekyum Kim, Junho Koh, Byeongwon Lee, Seungji Yang, Jun Won Choi

Auto-TLDR; Video Object Detection Using Spatio-Temporal Aggregated Features and Gated Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Effective Deployment of CNNs for 3DoF Pose Estimation and Grasping in Industrial Settings
Daniele De Gregorio, Riccardo Zanella, Gianluca Palli, Luigi Di Stefano
Auto-TLDR; Automated Deep Learning for Robotic Grasping Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFST: Multi-Features Siamese Tracker
Zhenxi Li, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Wassim Bouachir

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Features Siamese Tracker for Robust Deep Similarity Tracking
Visual Object Tracking in Drone Images with Deep Reinforcement Learning

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Reinforcement Learning based Single Object Tracker for Drone Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Model Decay in Long-Term Tracking
Efstratios Gavves, Ran Tao, Deepak Gupta, Arnold Smeulders
Auto-TLDR; Model Bias in Long-Term Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPN Hand: A Video Dataset and Benchmark for Real-Time Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jesus Olivares-Mercado, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai

Auto-TLDR; IPN Hand: A Benchmark Dataset for Continuous Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Visual Voice Activity Detection with an Automatically Annotated Dataset
Stéphane Lathuiliere, Pablo Mesejo, Radu Horaud

Auto-TLDR; Deep Visual Voice Activity Detection with Optical Flow
Attention-Based Model with Attribute Classification for Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification
Simin Xu, Lingkun Luo, Shiqiang Hu

Auto-TLDR; An attention-based model with attribute classification for cross-domain person re-identification