RSINet: Rotation-Scale Invariant Network for Online Visual Tracking
Yang Fang,
Geunsik Jo,
Chang-Hee Lee

Auto-TLDR; RSINet: Rotation-Scale Invariant Network for Adaptive Tracking
Similar papers
DAL: A Deep Depth-Aware Long-Term Tracker
Yanlin Qian, Song Yan, Alan Lukežič, Matej Kristan, Joni-Kristian Kamarainen, Jiri Matas
Auto-TLDR; Deep Depth-Aware Long-Term RGBD Tracking with Deep Discriminative Correlation Filter
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TSDM: Tracking by SiamRPN++ with a Depth-Refiner and a Mask-Generator
Pengyao Zhao, Quanli Liu, Wei Wang, Qiang Guo

Auto-TLDR; TSDM: A Depth-D Tracker for 3D Object Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Model Decay in Long-Term Tracking
Efstratios Gavves, Ran Tao, Deepak Gupta, Arnold Smeulders
Auto-TLDR; Model Bias in Long-Term Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Visual Object Tracking with Two-Stream Residual Convolutional Networks
Ning Zhang, Jingen Liu, Ke Wang, Dan Zeng, Tao Mei

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Residual Convolutional Network for Visual Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Distilled Learning for Deep Siamese Tracking
Chengxin Liu, Zhiguo Cao, Wei Li, Yang Xiao, Shuaiyuan Du, Angfan Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Distilled Learning Framework for Siamese Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VTT: Long-Term Visual Tracking with Transformers
Tianling Bian, Yang Hua, Tao Song, Zhengui Xue, Ruhui Ma, Neil Robertson, Haibing Guan

Auto-TLDR; Visual Tracking Transformer with transformers for long-term visual tracking
Efficient Correlation Filter Tracking with Adaptive Training Sample Update Scheme
Shan Jiang, Shuxiao Li, Chengfei Zhu, Nan Yan

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Training Sample Update Scheme of Correlation Filter Based Trackers for Visual Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tackling Occlusion in Siamese Tracking with Structured Dropouts
Deepak Gupta, Efstratios Gavves, Arnold Smeulders
Auto-TLDR; Structured Dropout for Occlusion in latent space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MFST: Multi-Features Siamese Tracker
Zhenxi Li, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Wassim Bouachir

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Features Siamese Tracker for Robust Deep Similarity Tracking
Adaptive Context-Aware Discriminative Correlation Filters for Robust Visual Object Tracking
Tianyang Xu, Zhenhua Feng, Xiaojun Wu, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; ACA-DCF: Adaptive Context-Aware Discriminative Correlation Filter with complementary attention mechanisms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Object Tracking in Drone Images with Deep Reinforcement Learning

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Reinforcement Learning based Single Object Tracker for Drone Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation Network for Fast Video Object Segmentation
Dexiang Hong, Guorong Li, Kai Xu, Li Su, Qingming Huang

Auto-TLDR; Siamese Dynamic Mask Estimation for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese Fully Convolutional Tracker with Motion Correction
Mathew Francis, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; A Siamese Ensemble for Visual Tracking with Appearance and Motion Components
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SiamMT: Real-Time Arbitrary Multi-Object Tracking
Lorenzo Vaquero, Manuel Mucientes, Victor Brea

Auto-TLDR; SiamMT: A Deep-Learning-based Arbitrary Multi-Object Tracking System for Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Compact and Discriminative Multi-Object Tracking with Siamese CNNs
Claire Labit-Bonis, Jérôme Thomas, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fast, Light-Weight and All-in-One Single Object Tracking for Multi-Target Management
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Reducing False Positives in Object Tracking with Siamese Network
Takuya Ogawa, Takashi Shibata, Shoji Yachida, Toshinori Hosoi

Auto-TLDR; Robust Long-Term Object Tracking with Adaptive Search based on Motion Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SynDHN: Multi-Object Fish Tracker Trained on Synthetic Underwater Videos
Mygel Andrei Martija, Prospero Naval

Auto-TLDR; Underwater Multi-Object Tracking in the Wild with Deep Hungarian Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scene Text Detection with Selected Anchors
Anna Zhu, Hang Du, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; AS-RPN: Anchor Selection-based Region Proposal Network for Scene Text Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Object Deformation and Motion Adaption for Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
Xiaoyang Zheng, Xin Tan, Jianming Guo, Lizhuang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Video Object Segmentation with Mask-propagation-based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AerialMPTNet: Multi-Pedestrian Tracking in Aerial Imagery Using Temporal and Graphical Features
Maximilian Kraus, Seyed Majid Azimi, Emec Ercelik, Reza Bahmanyar, Peter Reinartz, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; AerialMPTNet: A novel approach for multi-pedestrian tracking in geo-referenced aerial imagery by fusing appearance features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CenterRepp: Predict Central Representative Point Set's Distribution for Detection
Yulin He, Limeng Zhang, Wei Chen, Xin Luo, Chen Li, Xiaogang Jia

Auto-TLDR; CRPDet: CenterRepp Detector for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Saliency Oriented Vehicle Scale Estimation
Qixin Chen, Tie Liu, Jiali Ding, Zejian Yuan, Yuanyuan Shang

Auto-TLDR; Regularized Intensity Matching for Vehicle Scale Estimation with salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Utilising Visual Attention Cues for Vehicle Detection and Tracking
Feiyan Hu, Venkatesh Gurram Munirathnam, Noel E O'Connor, Alan Smeaton, Suzanne Little
Auto-TLDR; Visual Attention for Object Detection and Tracking in Driver-Assistance Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Auto-TLDR; A Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Correlation-Based ConvNet for Small Object Detection in Videos
Brais Bosquet, Manuel Mucientes, Victor Brea

Auto-TLDR; STDnet-ST: An End-to-End Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Network for Small Object Detection in Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FourierNet: Compact Mask Representation for Instance Segmentation Using Differentiable Shape Decoders
Hamd Ul Moqeet Riaz, Nuri Benbarka, Andreas Zell

Auto-TLDR; FourierNet: A Single shot, anchor-free, fully convolutional instance segmentation method that predicts a shape vector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Augmented Reality: Fast, Precise, and Smooth Planar Object Tracking
Dmitrii Matveichev, Daw-Tung Lin
Auto-TLDR; Planar Object Tracking with Sparse Optical Flow Tracking and Descriptor Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Multi-View Representation Learning
Akrem Sellami, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Deep Multi-view Representation Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
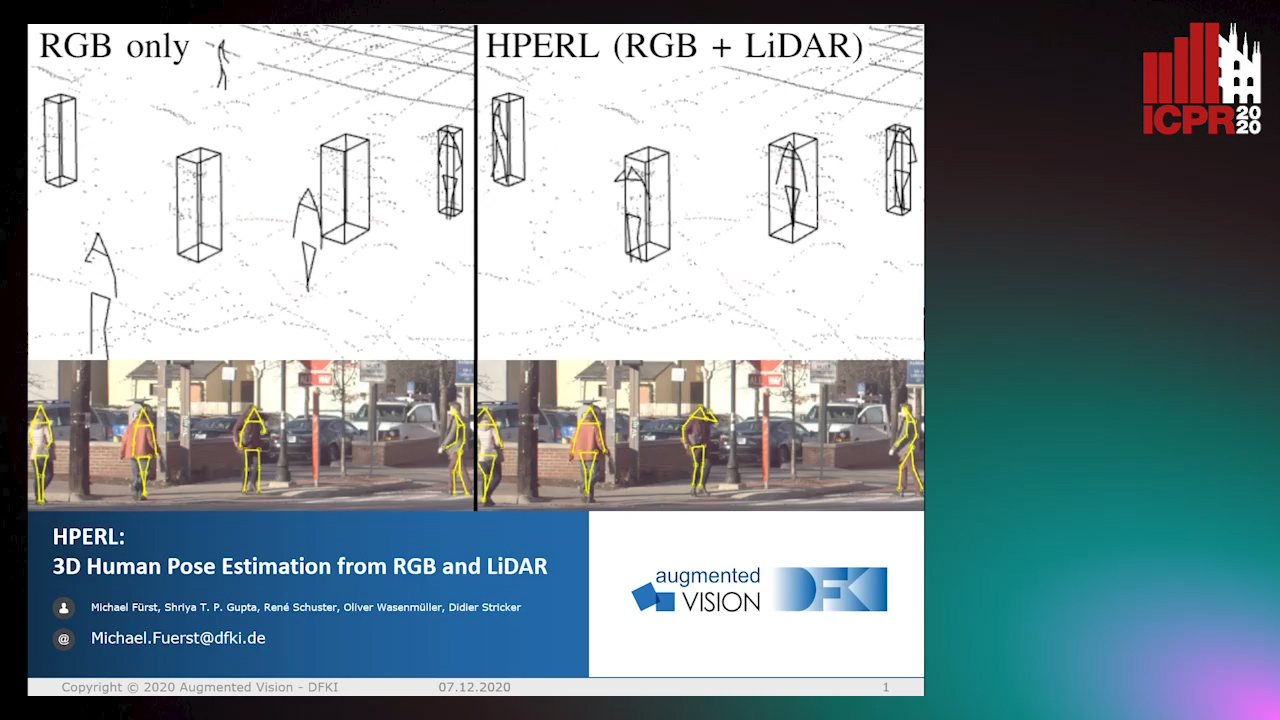
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Adaptive Fusion Model Based on Kalman Filtering and LSTM for Fast Tracking of Road Signs
Chengliang Wang, Xin Xie, Chao Liao

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of ThunderNet and Region Growing Detector for Road Sign Detection and Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detective: An Attentive Recurrent Model for Sparse Object Detection
Amine Kechaou, Manuel Martinez, Monica Haurilet, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Detective: An attentive object detector that identifies objects in images in a sequential manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stratified Multi-Task Learning for Robust Spotting of Scene Texts
Kinjal Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; Feature Representation Block for Multi-task Learning of Scene Text
Augmented Bi-Path Network for Few-Shot Learning
Baoming Yan, Chen Zhou, Bo Zhao, Kan Guo, Yang Jiang, Xiaobo Li, Zhang Ming, Yizhou Wang

Auto-TLDR; Augmented Bi-path Network for Few-shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PRF-Ped: Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detector with Prior-Based Receptive Field
Yuzhi Tan, Hongxun Yao, Haoran Li, Xiusheng Lu, Haozhe Xie

Auto-TLDR; Bidirectional Feature Enhancement Module for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Sequence-To-Sequence Video Object Segmentation with Multi-Task Loss and Skip-Memory
Fatemeh Azimi, Benjamin Bischke, Sebastian Palacio, Federico Raue, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for Video Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Coarse to Fine: Progressive and Multi-Task Learning for Salient Object Detection
Dong-Goo Kang, Sangwoo Park, Joonki Paik
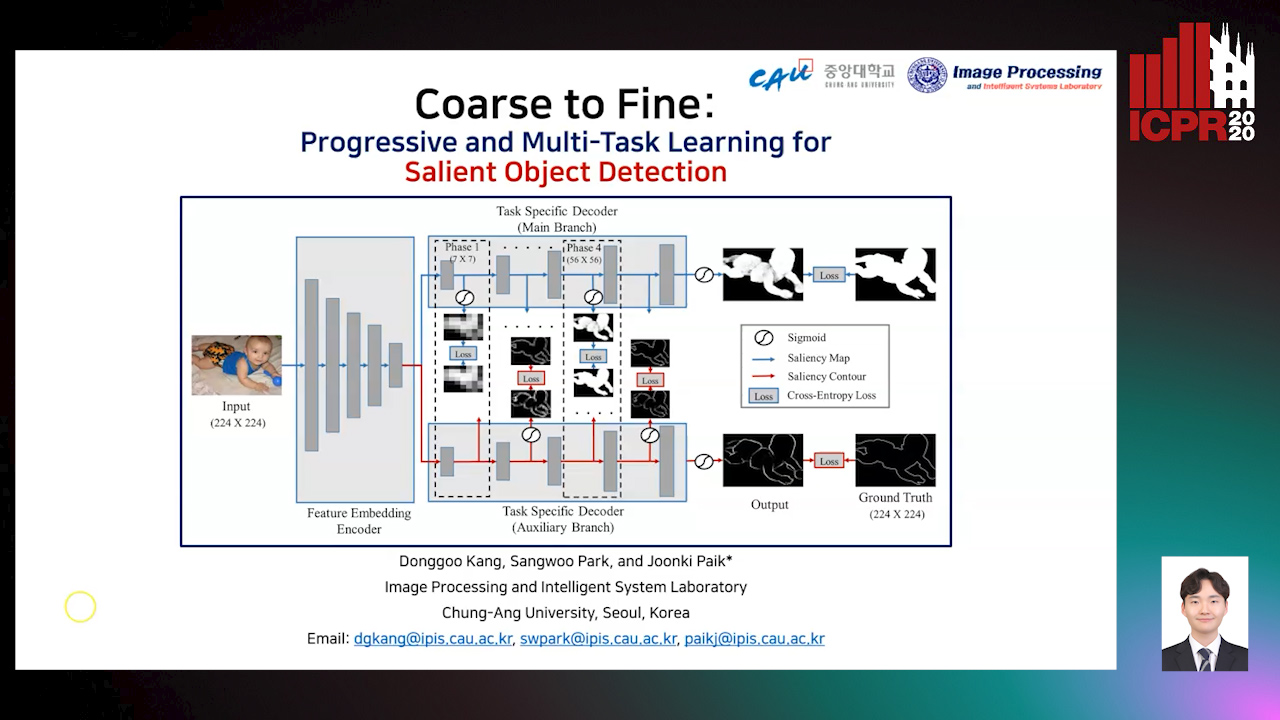
Auto-TLDR; Progressive and mutl-task learning scheme for salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EAGLE: Large-Scale Vehicle Detection Dataset in Real-World Scenarios Using Aerial Imagery
Seyed Majid Azimi, Reza Bahmanyar, Corentin Henry, Kurz Franz

Auto-TLDR; EAGLE: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multi-class Vehicle Detection with Object Orientation Information in Airborne Imagery
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection Based on Improved Faster R-CNN
Tao Wang, Can Zhang, Runwei Ding, Ge Yang

Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for Mobile Phone Surface Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar