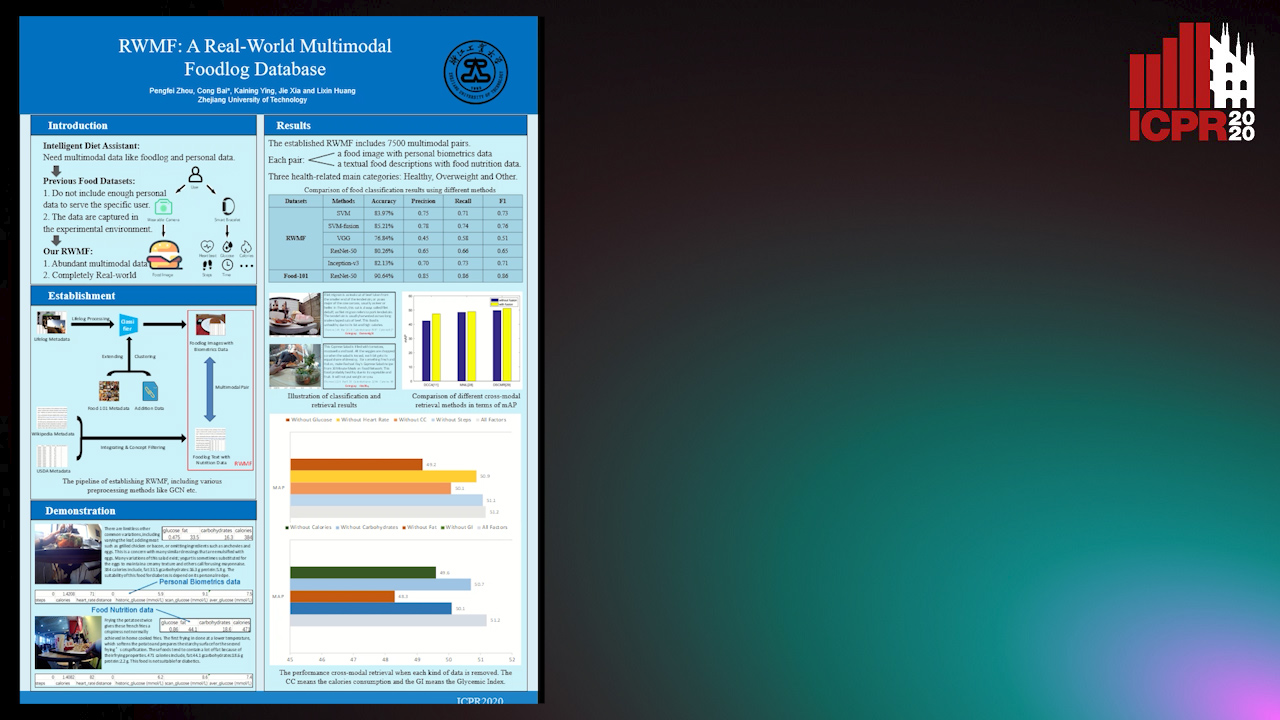
RWMF: A Real-World Multimodal Foodlog Database
Pengfei Zhou,
Cong Bai,
Kaining Ying,
Jie Xia,
Lixin Huang
Auto-TLDR; Real-World Multimodal Foodlog: A Real-World Foodlog Database for Diet Assistant
Similar papers
Picture-To-Amount (PITA): Predicting Relative Ingredient Amounts from Food Images
Jiatong Li, Fangda Han, Ricardo Guerrero, Vladimir Pavlovic

Auto-TLDR; PITA: A Deep Learning Architecture for Predicting the Relative Amount of Ingredients from Food Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Task Learning for Calorie Prediction on a Novel Large-Scale Recipe Dataset Enriched with Nutritional Information
Robin Ruede, Verena Heusser, Lukas Frank, Monica Haurilet, Alina Roitberg, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Pic2kcal: Learning Food Recipes from Images for Calorie Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partially Supervised Multi-Task Network for Single-View Dietary Assessment
Ya Lu, Thomai Stathopoulou, Stavroula Mougiakakou
Auto-TLDR; Food Volume Estimation from a Single Food Image via Geometric Understanding and Semantic Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty-Aware Data Augmentation for Food Recognition
Eduardo Aguilar, Bhalaji Nagarajan, Rupali Khatun, Marc Bolaños, Petia Radeva

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation for Food Recognition Using Epistemic Uncertainty
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching and Retrieval
Nicola Messina, Fabrizio Falchi, Andrea Esuli, Giuseppe Amato

Auto-TLDR; A Transformer Encoder Reasoning Network for Image-Text Matching in Large-Scale Information Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Webly Supervised Image-Text Embedding with Noisy Tag Refinement
Niluthpol Mithun, Ravdeep Pasricha, Evangelos Papalexakis, Amit Roy-Chowdhury
Auto-TLDR; Robust Joint Embedding for Image-Text Retrieval Using Web Images
Zero-Shot Text Classification with Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network
Tengfei Liu, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network for Zero-shot Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Price Suggestion for Online Second-Hand Items
Liang Han, Zhaozheng Yin, Zhurong Xia, Li Guo, Mingqian Tang, Rong Jin
Auto-TLDR; An Intelligent Price Suggestion System for Online Second-hand Items
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A CNN-RNN Framework for Image Annotation from Visual Cues and Social Network Metadata
Tobia Tesan, Pasquale Coscia, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Image Annotation with Multiple Semantic Embeddings and Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Media Hash Retrieval Using Multi-head Attention Network
Zhixin Li, Feng Ling, Chuansheng Xu, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Cross-Media Hash Retrieval Using Multi-Head Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Classification of Human Granulosa Cells in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Vibrational Spectroscopy Imaging
Marina Paolanti, Emanuele Frontoni, Giorgia Gioacchini, Giorgini Elisabetta, Notarstefano Valentina, Zacà Carlotta, Carnevali Oliana, Andrea Borini, Marco Mameli

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Oocyte Quality in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Integrating Historical States and Co-Attention Mechanism for Visual Dialog
Tianling Jiang, Yi Ji, Chunping Liu
Auto-TLDR; Integrating Historical States and Co-attention for Visual Dialog
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MEG: Multi-Evidence GNN for Multimodal Semantic Forensics
Ekraam Sabir, Ayush Jaiswal, Wael Abdalmageed, Prem Natarajan
Auto-TLDR; Scalable Image Repurposing Detection with Graph Neural Network Based Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Assessing the Severity of Health States Based on Social Media Posts
Shweta Yadav, Joy Prakash Sain, Amit Sheth, Asif Ekbal, Sriparna Saha, Pushpak Bhattacharyya

Auto-TLDR; A Multiview Learning Framework for Assessment of Health State in Online Health Communities
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Beyond the Deep Metric Learning: Enhance the Cross-Modal Matching with Adversarial Discriminative Domain Regularization
Li Ren, Kai Li, Liqiang Wang, Kien Hua

Auto-TLDR; Adversarial Discriminative Domain Regularization for Efficient Cross-Modal Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSR++: Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Hui Yuan, Yan Huang, Dongbo Zhang, Zerui Chen, Wenlong Cheng, Liang Wang

Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Semantic Reasoning for Fine-Grained Image-Text Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Decomposition Convolution Neural Network and Vocabulary Forest for Image Retrieval
Djenouri Youcef, Jon Hjelmervik
Auto-TLDR; DCNN-vForest: Convolutional Neural Network and Vocabulary Forest for Efficient Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BAT Optimized CNN Model Identifies Water Stress in Chickpea Plant Shoot Images
Shiva Azimi, Taranjit Kaur, Tapan Gandhi

Auto-TLDR; BAT Optimized ResNet-18 for Stress Classification of chickpea shoot images under water deficiency
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Discrete Semantic Matrix Factorization Hashing for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Jianyang Qin, Lunke Fei, Shaohua Teng, Wei Zhang, Genping Zhao, Haoliang Yuan

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Semantic Matrix Factorization Hashing for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Identification of State-Sponsored Propaganda on Social Media

Auto-TLDR; A balanced dataset for detecting state-sponsored Internet propaganda
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Label or Message: A Large-Scale Experimental Survey of Texts and Objects Co-Occurrence
Koki Takeshita, Juntaro Shioyama, Seiichi Uchida

Auto-TLDR; Large-scale Survey of Co-occurrence between Objects and Scene Text with a State-of-the-art Scene Text detector and Recognizer
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Annotation of Corpora for Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions Analysis
Alex Mircoli, Claudia Diamantini, Domenico Potena, Emanuele Storti

Auto-TLDR; Automatic annotation of video subtitles on the basis of facial expressions using machine learning algorithms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JECL: Joint Embedding and Cluster Learning for Image-Text Pairs
Sean Yang, Kuan-Hao Huang, Bill Howe
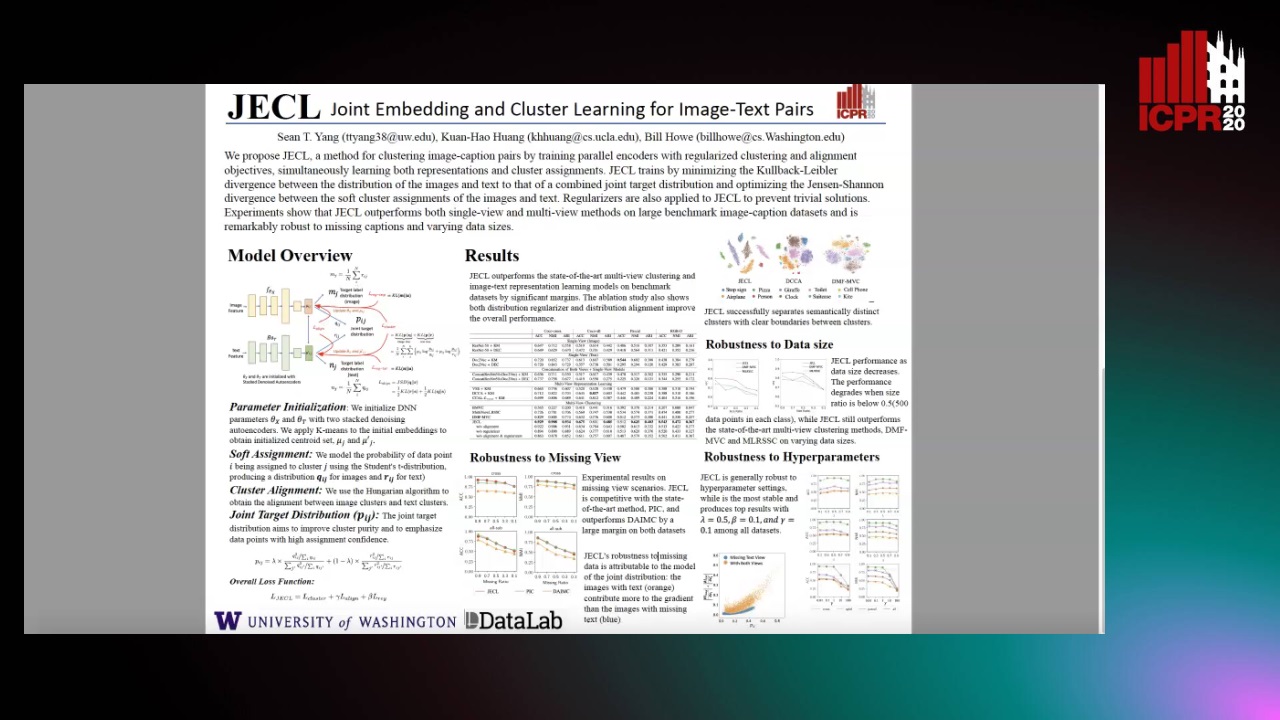
Auto-TLDR; JECL: Clustering Image-Caption Pairs with Parallel Encoders and Regularized Clusters
Information Graphic Summarization Using a Collection of Multimodal Deep Neural Networks
Edward Kim, Connor Onweller, Kathleen F. Mccoy
Auto-TLDR; A multimodal deep learning framework that can generate summarization text supporting the main idea of an information graphic for presentation to blind or visually impaired
RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification Via Image Modality Conversion
Huangpeng Dai, Qing Xie, Yanchun Ma, Yongjian Liu, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; CE2L: A Novel Network for Cross-Modality Re-identification with Feature Alignment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSB^2-Net: Visual-Semantic Bi-Branch Network for Zero-Shot Hashing
Xin Li, Xiangfeng Wang, Bo Jin, Wenjie Zhang, Jun Wang, Hongyuan Zha
Auto-TLDR; VSB^2-Net: inductive zero-shot hashing for image retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Discrete Cross-Modal Hashing Based on Label Relaxation and Matrix Factorization
Donglin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Zhen Liu, Jun Yu, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; LRMF: Label Relaxation and Discrete Matrix Factorization for Cross-Modal Retrieval
To Honor Our Heroes: Analysis of the Obituaries of Australians Killed in Action in WWI and WWII

Auto-TLDR; Obituaries of World War I and World War II: A Map of Values and Virtues attributed to Australian Military Personnel
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Identification and Retrieval of Near-Duplicate Biological Images: A New Dataset and Protocol
Thomas E. Koker, Sai Spandana Chintapalli, San Wang, Blake A. Talbot, Daniel Wainstock, Marcelo Cicconet, Mary C. Walsh
Auto-TLDR; BINDER: Bio-Image Near-Duplicate Examples Repository for Image Identification and Retrieval
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Learning with Graph Neural Networks for Region of Interest Retrieval in Histopathology
Yigit Ozen, Selim Aksoy, Kemal Kosemehmetoglu, Sevgen Onder, Aysegul Uner

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Contrastive Learning for Deep Representation Learning of Histopathology Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Jianrong Wang, Tong Wu, Shanyu Wang, Mei Yu, Qiang Fang, Ju Zhang, Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent and Text-Dependent Speaker Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Person Recognition with HGR Maximal Correlation on Multimodal Data
Yihua Liang, Fei Ma, Yang Li, Shao-Lun Huang
Auto-TLDR; A correlation-based multimodal person recognition framework that learns discriminative embeddings of persons by joint learning visual features and audio features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Systematic Investigation on End-To-End Deep Recognition of Grocery Products in the Wild
Marco Leo, Pierluigi Carcagni, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Recognition of Products on grocery shelf images using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
Prior Knowledge about Attributes: Learning a More Effective Potential Space for Zero-Shot Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Correlation Potential Space Generation for Zero-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Graph Convolutional Network for Relationship-Driven Stock Movement Prediction
Jiexia Ye, Juanjuan Zhao, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; Multi-GCGRU: A Deep Learning Framework for Stock Price Prediction with Cross Effect
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Open Set Domain Recognition Via Attention-Based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization
Xinxing He, Yuan Yuan, Zhiyu Jiang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based GCN and Semantic Matching Optimization for Open Set Domain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Making Every Label Count: Handling Semantic Imprecision by Integrating Domain Knowledge
Clemens-Alexander Brust, Björn Barz, Joachim Denzler

Auto-TLDR; Class Hierarchies for Imprecise Label Learning and Annotation eXtrapolation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fusion of Global-Local Features for Image Quality Inspection of Shipping Label
Sungho Suh, Paul Lukowicz, Yong Oh Lee

Auto-TLDR; Input Image Quality Verification for Automated Shipping Address Recognition and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Systematic Investigation on Deep Architectures for Automatic Skin Lesions Classification
Pierluigi Carcagni, Marco Leo, Andrea Cuna, Giuseppe Celeste, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; RegNet: Deep Investigation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Classification of Skin Lesions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Neural Textual Representations for Citation Recommendation
Thanh Binh Kieu, Inigo Jauregi Unanue, Son Bao Pham, Xuan-Hieu Phan, M. Piccardi

Auto-TLDR; Sentence-BERT cascaded with Siamese and triplet networks for citation recommendation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar