3D Dental Biometrics: Automatic Pose-Invariant Dental Arch Extraction and Matching

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Dental Arch Extraction and Matching for 3D Dental Identification using Laser-Scanned Plasters
Similar papers
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Pots Configuration System by Optimizing Over Geometric Constraints
Jae Eun Kim, Muhammad Zeeshan Arshad, Seong Jong Yoo, Je Hyeong Hong, Jinwook Kim, Young Min Kim

Auto-TLDR; Optimizing 3D Configurations for Stable Pottery Restoration from irregular and noisy evidence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Learning Multiple Curvature Descriptor for 3D Palmprint Recognition
Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Jie Wen, Chunwei Tian, Peng Liu, Shuping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Joint Feature Learning for 3D palmprint recognition using curvature data vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Lookalike Disambiguation: Improving Face Identification Performance at Top Ranks

Auto-TLDR; Lookalike Face Identification Using a Disambiguator for Lookalike Images
Inner Eye Canthus Localization for Human Body Temperature Screening
Claudio Ferrari, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Localization of the Inner Eye Canthus in Thermal Face Images using 3D Morphable Face Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking ReID:Multi-Feature Fusion Person Re-Identification Based on Orientation Constraints
Mingjing Ai, Guozhi Shan, Bo Liu, Tianyang Liu
Auto-TLDR; Person Re-identification with Orientation Constrained Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Detection in Finger Vein Biometrics Using CNNs
Bernhard Prommegger, Georg Wimmer, Andreas Uhl
Auto-TLDR; A CNN based rotation detector for finger vein recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A New Geodesic-Based Feature for Characterization of 3D Shapes: Application to Soft Tissue Organ Temporal Deformations
Karim Makki, Amine Bohi, Augustin Ogier, Marc-Emmanuel Bellemare

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature Descriptors for 3D Shape Characterization from Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Calibration and Absolute Pose Estimation of Trinocular Linear Camera Array for Smart City Applications
Martin Ahrnbom, Mikael Nilsson, Håkan Ardö, Kalle Åström, Oksana Yastremska-Kravchenko, Aliaksei Laureshyn

Auto-TLDR; Trinocular Linear Camera Array Calibration for Traffic Surveillance Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Level Three Synthetic Fingerprint Generation
Andre Wyzykowski, Mauricio Pamplona Segundo, Rubisley Lemes

Auto-TLDR; Synthesis of High-Resolution Fingerprints with Pore Detection Using CycleGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Document Image Dewarping by Probabilistic Discretization of Vanishing Points
Gilles Simon, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Robust Document Dewarping using vanishing points
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Finger Vein Recognition and Intra-Subject Similarity Evaluation of Finger Veins Using the CNN Triplet Loss
Georg Wimmer, Bernhard Prommegger, Andreas Uhl

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein recognition using CNNs and hard triplet online selection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Three-Dimensional Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition
Jianrong Wang, Tong Wu, Shanyu Wang, Mei Yu, Qiang Fang, Ju Zhang, Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Lip Motion Network for Text-Independent and Text-Dependent Speaker Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gaussian Convolution Angles: Invariant Vein and Texture Descriptors for Butterfly Species Identification
Xin Chen, Bin Wang, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian convolution angle for butterfly species classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Unique Is a Face: An Investigative Study
Michal Balazia, S L Happy, Francois Bremond, Antitza Dantcheva

Auto-TLDR; Uniqueness of Face Recognition: Exploring the Impact of Factors such as image resolution, feature representation, database size, age and gender
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recovery of 2D and 3D Layout Information through an Advanced Image Stitching Algorithm Using Scanning Electron Microscope Images
Aayush Singla, Bernhard Lippmann, Helmut Graeb

Auto-TLDR; Image Stitching for True Geometrical Layout Recovery in Nanoscale Dimension
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One-Shot Representational Learning for Joint Biometric and Device Authentication

Auto-TLDR; Joint Biometric and Device Recognition from a Single Biometric Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fingerprints, Forever Young?
Roman Kessler, Olaf Henniger, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; Mated Similarity Scores for Fingerprint Recognition: A Hierarchical Linear Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Walk the Lines: Object Contour Tracing CNN for Contour Completion of Ships

Auto-TLDR; Walk the Lines: A Convolutional Neural Network trained to follow object contours
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Step Approach to Lidar-Camera Calibration
Yingna Su, Yaqing Ding, Jian Yang, Hui Kong

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Lidar-camera System for Ego-motion Estimation and Scene Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
User-Independent Gaze Estimation by Extracting Pupil Parameter and Its Mapping to the Gaze Angle

Auto-TLDR; Gaze Point Estimation using Pupil Shape for Generalization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
BiLuNet: A Multi-Path Network for Semantic Segmentation on X-Ray Images
Van Luan Tran, Huei-Yung Lin, Rachel Liu, Chun-Han Tseng, Chun-Han Tseng
Auto-TLDR; BiLuNet: Multi-path Convolutional Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar vertebrae, sacrum,
Wireless Localisation in WiFi Using Novel Deep Architectures
Peizheng Li, Han Cui, Aftab Khan, Usman Raza, Robert Piechocki, Angela Doufexi, Tim Farnham
Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Indoor Localisation of WiFi Devices in Indoor Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Are Spoofs from Latent Fingerprints a Real Threat for the Best State-Of-Art Liveness Detectors?
Roberto Casula, Giulia Orrù, Daniele Angioni, Xiaoyi Feng, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; ScreenSpoof: Attacks using latent fingerprints against state-of-art fingerprint liveness detectors and verification systems
A Local Descriptor with Physiological Characteristic for Finger Vein Recognition
Liping Zhang, Weijun Li, Ning Xin

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein-specific local feature descriptors based physiological characteristic of finger vein patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Implicitly Represent 3D Human Body from Multi-Scale Features and Multi-View Images
Zhongguo Li, Magnus Oskarsson, Anders Heyden
Auto-TLDR; Reconstruction of 3D human bodies from multi-view images using multi-stage end-to-end neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-View Object Detection Using Epipolar Constraints within Cluttered X-Ray Security Imagery
Brian Kostadinov Shalon Isaac-Medina, Chris G. Willcocks, Toby Breckon
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Epipolar Constraints for Multi-View Object Detection in X-ray Security Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Photometric Stereo with Twin-Fisheye Cameras
Jordan Caracotte, Fabio Morbidi, El Mustapha Mouaddib

Auto-TLDR; Photometric stereo problem for low-cost 360-degree cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
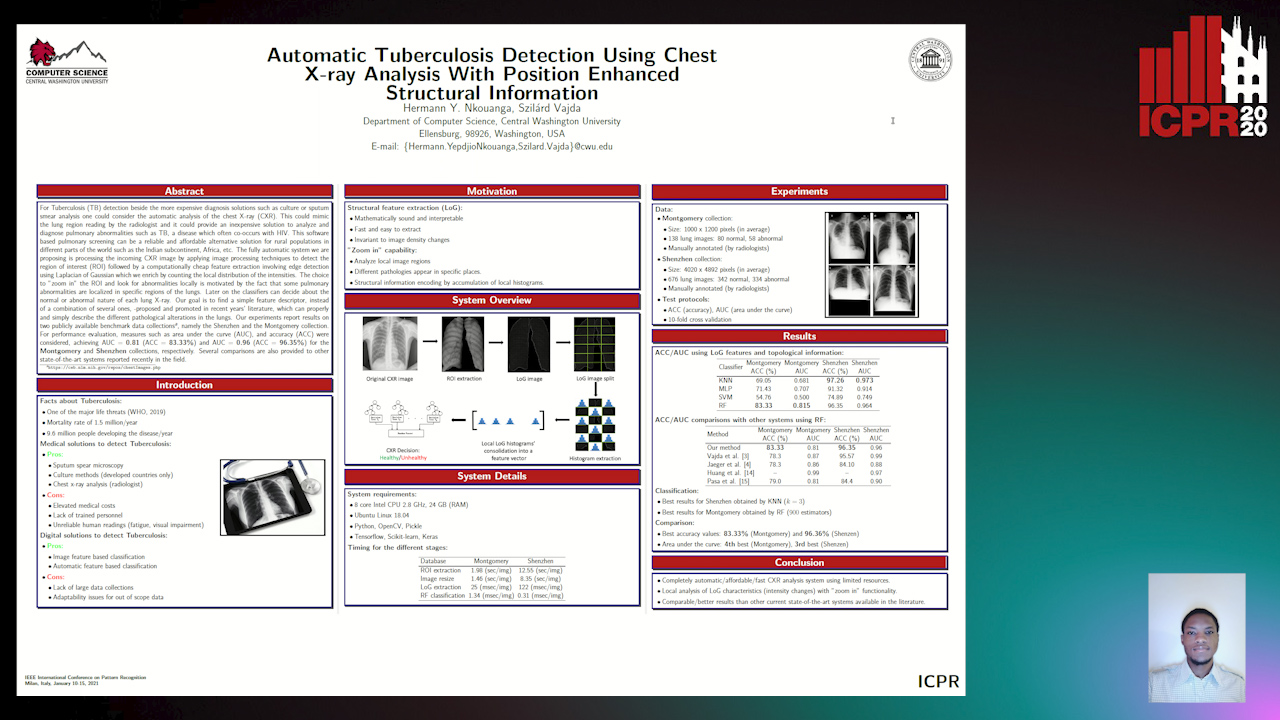
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Seismocardiogram Biometrics with Wavelet Transform
Po-Ya Hsu, Po-Han Hsu, Hsin-Li Liu

Auto-TLDR; Seismocardiogram Biometric Matching Using Wavelet Transform and Deep Learning Models
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotational Adjoint Methods for Learning-Free 3D Human Pose Estimation from IMU Data
Caterina Emilia Agelide Buizza, Yiannis Demiris
Auto-TLDR; Learning-free 3D Human Pose Estimation from Inertial Measurement Unit Data
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
To Honor Our Heroes: Analysis of the Obituaries of Australians Killed in Action in WWI and WWII

Auto-TLDR; Obituaries of World War I and World War II: A Map of Values and Virtues attributed to Australian Military Personnel
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Semantic Labeling of Photogrammetry Meshes Based on Active Learning
Mengqi Rong, Shuhan Shen, Zhanyi Hu

Auto-TLDR; 3D Semantic Expression of Urban Scenes Based on Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Important Are Faces for Person Re-Identification?
Julia Dietlmeier, Joseph Antony, Kevin Mcguinness, Noel E O'Connor

Auto-TLDR; Anonymization of Person Re-identification Datasets with Face Detection and Blurring
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Skeletonization for Plant Root Structure Reconstruction from MRI

Auto-TLDR; Structural reconstruction of plant roots from MRI using semantic root vs shoot segmentation and 3D skeletonization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detection of Makeup Presentation Attacks Based on Deep Face Representations
Christian Rathgeb, Pawel Drozdowski, Christoph Busch

Auto-TLDR; An Attack Detection Scheme for Face Recognition Using Makeup Presentation Attacks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RISEdb: A Novel Indoor Localization Dataset
Carlos Sanchez Belenguer, Erik Wolfart, Álvaro Casado Coscollá, Vitor Sequeira

Auto-TLDR; Indoor Localization Using LiDAR SLAM and Smartphones: A Benchmarking Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu, Amnir Hadachi, Damien Vivet, Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Gait Relative Attribute Using a Signed Quadratic Contrastive Loss
Yuta Hayashi, Shehata Allam, Yasushi Makihara, Daigo Muramatsu, Yasushi Yagi

Auto-TLDR; Signal-Contrastive Loss for Gait Attributes Estimation
A Globally Optimal Method for the PnP Problem with MRP Rotation Parameterization
Manolis Lourakis, George Terzakis
Auto-TLDR; A Direct least squares, algebraic PnP solver with modified Rodrigues parameters
Dependently Coupled Principal Component Analysis for Bivariate Inversion Problems
Navdeep Dahiya, Yifei Fan, Samuel Bignardi, Tony Yezzi, Romeil Sandhu

Auto-TLDR; Asymmetric Principal Component Analysis between Paired Data in an Asymmetric manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attack-Agnostic Adversarial Detection on Medical Data Using Explainable Machine Learning
Matthew Watson, Noura Al Moubayed

Auto-TLDR; Explainability-based Detection of Adversarial Samples on EHR and Chest X-Ray Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Total Estimation from RGB Video: On-Line Camera Self-Calibration, Non-Rigid Shape and Motion

Auto-TLDR; Joint Auto-Calibration, Pose and 3D Reconstruction of a Non-rigid Object from an uncalibrated RGB Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantization in Relative Gradient Angle Domain for Building Polygon Estimation
Yuhao Chen, Yifan Wu, Linlin Xu, Alexander Wong

Auto-TLDR; Relative Gradient Angle Transform for Building Footprint Extraction from Remote Sensing Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar