Dependently Coupled Principal Component Analysis for Bivariate Inversion Problems
Navdeep Dahiya,
Yifei Fan,
Samuel Bignardi,
Tony Yezzi,
Romeil Sandhu

Auto-TLDR; Asymmetric Principal Component Analysis between Paired Data in an Asymmetric manner
Similar papers
Directionally Paired Principal Component Analysis for Bivariate Estimation Problems
Navdeep Dahiya, Yifei Fan, Samuel Bignardi, Tony Yezzi, Romeil Sandhu

Auto-TLDR; Asymmetrically-Paired Principal Component Analysis for Linear Dimension-Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AdaFilter: Adaptive Filter Design with Local Image Basis Decomposition for Optimizing Image Recognition Preprocessing
Aiga Suzuki, Keiichi Ito, Takahide Ibe, Nobuyuki Otsu
Auto-TLDR; Optimal Preprocessing Filtering for Pattern Recognition Using Higher-Order Local Auto-Correlation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Embedding Shared Low-Rank and Feature Correlation for Multi-View Data Analysis
Zhan Wang, Lizhi Wang, Hua Huang

Auto-TLDR; embedding shared low-rank and feature correlation for multi-view data analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction by Joint Robust Discriminant Analysis and Inter-Class Sparsity
Auto-TLDR; Robust Discriminant Analysis with Feature Selection and Inter-class Sparsity (RDA_FSIS)
Detecting Rare Cell Populations in Flow Cytometry Data Using UMAP
Lisa Weijler, Markus Diem, Michael Reiter

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Manifold Approximation and Projection for Small Cell Population Detection in Flow cytometry Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling the Distribution of Normal Data in Pre-Trained Deep Features for Anomaly Detection
Oliver Rippel, Patrick Mertens, Dorit Merhof

Auto-TLDR; Deep Feature Representations for Anomaly Detection in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FOANet: A Focus of Attention Network with Application to Myocardium Segmentation
Zhou Zhao, Elodie Puybareau, Nicolas Boutry, Thierry Geraud

Auto-TLDR; FOANet: A Hybrid Loss Function for Myocardium Segmentation of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Supervised Feature Embedding for Classification by Learning Rank-Based Neighborhoods
Ghazaal Sheikhi, Hakan Altincay

Auto-TLDR; Supervised Feature Embedding with Representation Learning of Rank-based Neighborhoods
Bayesian Active Learning for Maximal Information Gain on Model Parameters
Kasra Arnavaz, Aasa Feragen, Oswin Krause, Marco Loog

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian assumptions for Bayesian classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Segment Clustered Amoeboid Cells from Brightfield Microscopy Via Multi-Task Learning with Adaptive Weight Selection
Rituparna Sarkar, Suvadip Mukherjee, Elisabeth Labruyere, Jean-Christophe Olivo-Marin
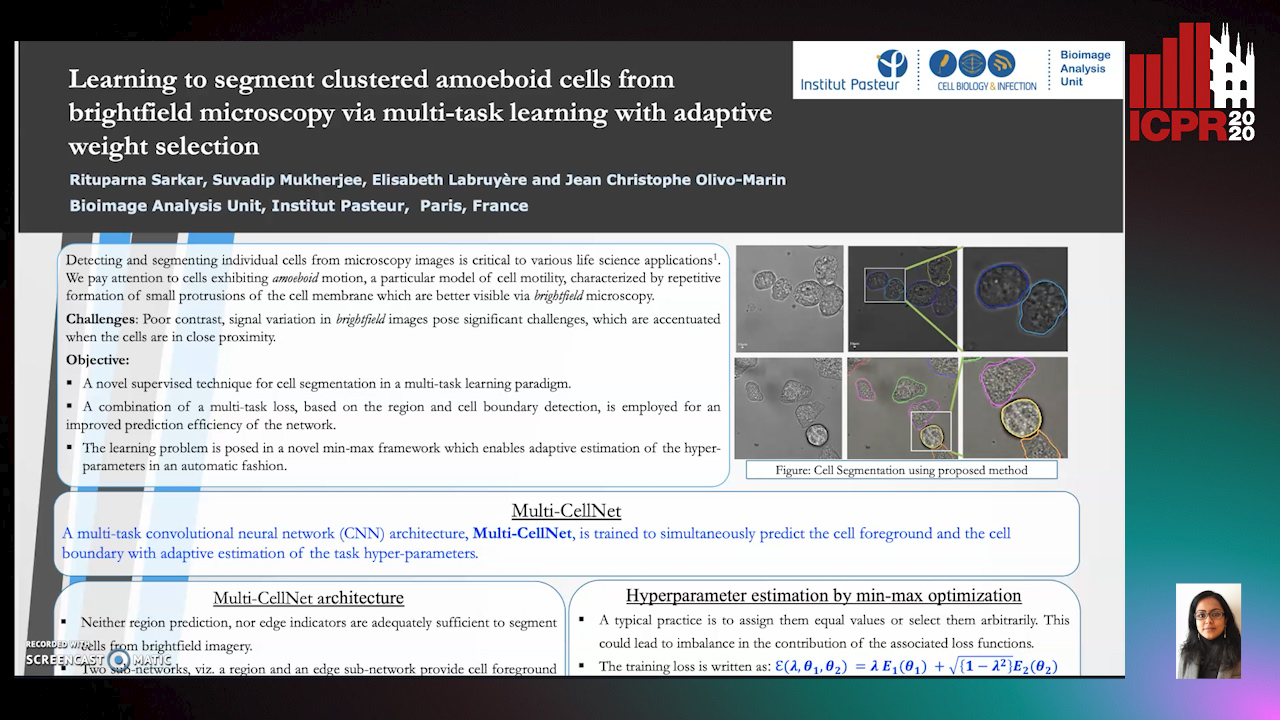
Auto-TLDR; Supervised Cell Segmentation from Microscopy Images using Multi-task Learning in a Multi-Task Learning Paradigm
A New Geodesic-Based Feature for Characterization of 3D Shapes: Application to Soft Tissue Organ Temporal Deformations
Karim Makki, Amine Bohi, Augustin Ogier, Marc-Emmanuel Bellemare

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature Descriptors for 3D Shape Characterization from Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Surprising Effectiveness of Linear Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation

Auto-TLDR; linear encoder-decoder architectures for unsupervised image-to-image translation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
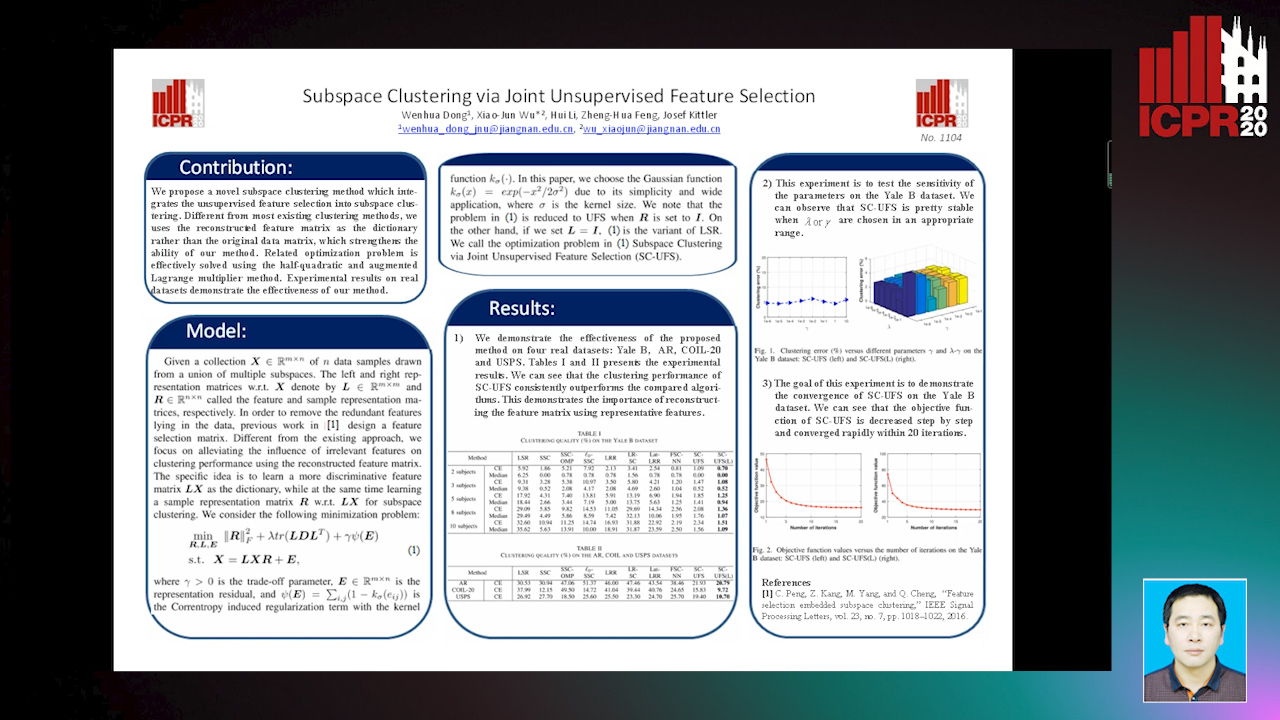
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering
Temporal Pattern Detection in Time-Varying Graphical Models
Federico Tomasi, Veronica Tozzo, Annalisa Barla

Auto-TLDR; A dynamical network inference model that leverages on kernels to consider general temporal patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
How to Define a Rejection Class Based on Model Learning?
Sarah Laroui, Xavier Descombes, Aurelia Vernay, Florent Villiers, Francois Villalba, Eric Debreuve

Auto-TLDR; An innovative learning strategy for supervised classification that is able, by design, to reject a sample as not belonging to any of the known classes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Q-SNE: Visualizing Data Using Q-Gaussian Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding
Motoshi Abe, Junichi Miyao, Takio Kurita
Auto-TLDR; Q-Gaussian distributed stochastic neighbor embedding for 2-dimensional mapping and classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Soft Label and Discriminant Embedding Estimation for Semi-Supervised Classification
Fadi Dornaika, Abdullah Baradaaji, Youssof El Traboulsi
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Semi-Supervised Learning for Linear Feature Extraction and Label Propagation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantifying Model Uncertainty in Inverse Problems Via Bayesian Deep Gradient Descent
Riccardo Barbano, Chen Zhang, Simon Arridge, Bangti Jin

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Neural Networks for Inverse Reconstruction via Bayesian Knowledge-Aided Computation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Random Forest Dissimilarity Measure for Multi-View Learning
Hongliu Cao, Simon Bernard, Robert Sabourin, Laurent Heutte
Auto-TLDR; Multi-view Learning with Random Forest Relation Measure and Instance Hardness
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MedZip: 3D Medical Images Lossless Compressor Using Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM)
Omniah Nagoor, Joss Whittle, Jingjing Deng, Benjamin Mora, Mark W. Jones

Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Neural Network for Lossless Medical Image Compression using Long Short-Term Memory
Feature Extraction and Selection Via Robust Discriminant Analysis and Class Sparsity

Auto-TLDR; Hybrid Linear Discriminant Embedding for supervised multi-class classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Factor Screening Using Bayesian Active Learning and Gaussian Process Meta-Modelling
Cheng Li, Santu Rana, Andrew William Gill, Dang Nguyen, Sunil Kumar Gupta, Svetha Venkatesh

Auto-TLDR; Data-Efficient Bayesian Active Learning for Factor Screening in Combat Simulations
Weakly Supervised Geodesic Segmentation of Egyptian Mummy CT Scans
Avik Hati, Matteo Bustreo, Diego Sona, Vittorio Murino, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; A Weakly Supervised and Efficient Interactive Segmentation of Ancient Egyptian Mummies CT Scans Using Geodesic Distance Measure and GrabCut
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dimensionality Reduction for Data Visualization and Linear Classification, and the Trade-Off between Robustness and Classification Accuracy
Martin Becker, Jens Lippel, Thomas Zielke

Auto-TLDR; Robustness Assessment of Deep Autoencoder for Data Visualization using Scatter Plots
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
Inferring Functional Properties from Fluid Dynamics Features
Andrea Schillaci, Maurizio Quadrio, Carlotta Pipolo, Marcello Restelli, Giacomo Boracchi

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Convective Properties of Computational Fluid Dynamics for Medical Diagnosis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Nonlinear Ranking Loss on Riemannian Potato Embedding
Byung Hyung Kim, Yoonje Suh, Honggu Lee, Sungho Jo

Auto-TLDR; Riemannian Potato for Rank-based Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Computing Stable Resultant-Based Minimal Solvers by Hiding a Variable
Snehal Bhayani, Zuzana Kukelova, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Permian-Based Method for Solving Minimal Systems of Polynomial Equations
Interactive Style Space of Deep Features and Style Innovation

Auto-TLDR; Interactive Style Space of Convolutional Neural Network Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classification and Feature Selection Using a Primal-Dual Method and Projections on Structured Constraints
Michel Barlaud, Antonin Chambolle, Jean_Baptiste Caillau

Auto-TLDR; A Constrained Primal-dual Method for Structured Feature Selection on High Dimensional Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Total Estimation from RGB Video: On-Line Camera Self-Calibration, Non-Rigid Shape and Motion

Auto-TLDR; Joint Auto-Calibration, Pose and 3D Reconstruction of a Non-rigid Object from an uncalibrated RGB Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Digit Recognition Applied to Reconstructed Audio Signals Using Deep Learning
Anastasia-Sotiria Toufa, Constantine Kotropoulos
Auto-TLDR; Compressed Sensing for Digit Recognition in Audio Reconstruction
Unveiling Groups of Related Tasks in Multi-Task Learning
Jordan Frecon, Saverio Salzo, Massimiliano Pontil

Auto-TLDR; Continuous Bilevel Optimization for Multi-Task Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Naturally Constrained Online Expectation Maximization
Daniela Pamplona, Antoine Manzanera
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Online Expectation-Maximization for Probabilistic Principal Components Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Pots Configuration System by Optimizing Over Geometric Constraints
Jae Eun Kim, Muhammad Zeeshan Arshad, Seong Jong Yoo, Je Hyeong Hong, Jinwook Kim, Young Min Kim

Auto-TLDR; Optimizing 3D Configurations for Stable Pottery Restoration from irregular and noisy evidence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved Time-Series Clustering with UMAP Dimension Reduction Method
Clément Pealat, Vincent Cheutet, Guillaume Bouleux

Auto-TLDR; Time Series Clustering with UMAP as a Pre-processing Step
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Spectral Feature Learning for Mixed Data of Categorical and Numerical Type
Saswata Sahoo, Souradip Chakraborty

Auto-TLDR; Feature Learning in Mixed Type of Variable by an undirected graph
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Riemannian Framework for Detecting Stimulus-Relevant Fiber Pathways
Jingyong Su, Linlin Tang, Zhipeng Yang, Mengmeng Guo

Auto-TLDR; Clustering Task-Specific Fiber Pathways in Functional MRI using BOLD Signals
2D Discrete Mirror Transform for Image Non-Linear Approximation
Alessandro Gnutti, Fabrizio Guerrini, Riccardo Leonardi

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Mirror Transform (DMT)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Scalable Direction-Search-Based Approach to Subspace Clustering

Auto-TLDR; Fast Direction-Search-Based Subspace Clustering
Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering
Shuai Yang, Wenqi Zhu, Yuesheng Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Sparse-Dense Subspace Clustering with Piecewise Correlation Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Dependent Gaussian Experts in Local Approximation

Auto-TLDR; A novel approach for aggregating the Gaussian experts by detecting strong violations of conditional independence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Silhouette Body Measurement Benchmarks
Song Yan, Johan Wirta, Joni-Kristian Kamarainen

Auto-TLDR; BODY-fit: A Realistic 3D Body Measurement Dataset for Anthropometric Measurement
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-annotator Probabilistic Active Learning
Marek Herde, Daniel Kottke, Denis Huseljic, Bernhard Sick

Auto-TLDR; MaPAL: Multi-annotator Probabilistic Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Relative Feature Importance
Gunnar König, Christoph Molnar, Bernd Bischl, Moritz Grosse-Wentrup

Auto-TLDR; Relative Feature Importance for Interpretable Machine Learning