2D Discrete Mirror Transform for Image Non-Linear Approximation
Alessandro Gnutti,
Fabrizio Guerrini,
Riccardo Leonardi

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Mirror Transform (DMT)
Similar papers
Fast Blending of Planar Shapes Based on Invariant Invertible and Stable Descriptors
Emna Ghorbel, Faouzi Ghorbel, Ines Sakly, Slim Mhiri

Auto-TLDR; Fined-Fourier-based Invariant Descriptor for Planar Shape Blending
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DCT/IDCT Filter Design for Ultrasound Image Filtering
Barmak Honarvar Shakibaei Asli, Jan Flusser, Yifan Zhao, John Ahmet Erkoyuncu, Rajkumar Roy

Auto-TLDR; Finite impulse response digital filter using DCT-II and inverse DCT
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for Power Line Outage Identification
Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Networks for Power Line Outage Identification
A Randomized Algorithm for Sparse Recovery
Huiyuan Yu, Maggie Cheng, Yingdong Lu

Auto-TLDR; A Constrained Graph Optimization Algorithm for Sparse Signal Recovery
Computational Data Analysis for First Quantization Estimation on JPEG Double Compressed Images
Sebastiano Battiato, Oliver Giudice, Francesco Guarnera, Giovanni Puglisi

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Discrete Cosine Transform Coefficients for Multimedia Forensics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Morphological Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Caglayan Tuna, Alain Giros, François Merciol, Sébastien Lefèvre

Auto-TLDR; Comparison of Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stabilized Calculation of Gaussian Smoothing and Its Differentials Using Attenuated Sliding Fourier Transform
Yukihiko Yamashita, Toru Wakahara

Auto-TLDR; An attenuated SFT for Gaussian smoothing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sketch-Based Community Detection Via Representative Node Sampling
Mahlagha Sedghi, Andre Beckus, George Atia
Auto-TLDR; Sketch-based Clustering of Community Detection Using a Small Sketch
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Heuristic-Based Decision Tree for Connected Components Labeling of 3D Volumes
Maximilian Söchting, Stefano Allegretti, Federico Bolelli, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; Entropy Partitioning Decision Tree for Connected Components Labeling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GraphBGS: Background Subtraction Via Recovery of Graph Signals
Jhony Heriberto Giraldo Zuluaga, Thierry Bouwmans
Auto-TLDR; Graph BackGround Subtraction using Graph Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extended Depth of Field Preserving Color Fidelity for Automated Digital Cytology
Alexandre Bouyssoux, Riadh Fezzani, Jean-Christophe Olivo-Marin
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Channel Extended Depth of Field for Digital cytology based on the stationary wavelet transform
Generic Document Image Dewarping by Probabilistic Discretization of Vanishing Points
Gilles Simon, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Robust Document Dewarping using vanishing points
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cluster-Size Constrained Network Partitioning
Maksim Mironov, Konstantin Avrachenkov
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Graph Clustering with Stochastic Block Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting Graph Neural Networks: Graph Filtering Perspective
Hoang Nguyen-Thai, Takanori Maehara, Tsuyoshi Murata
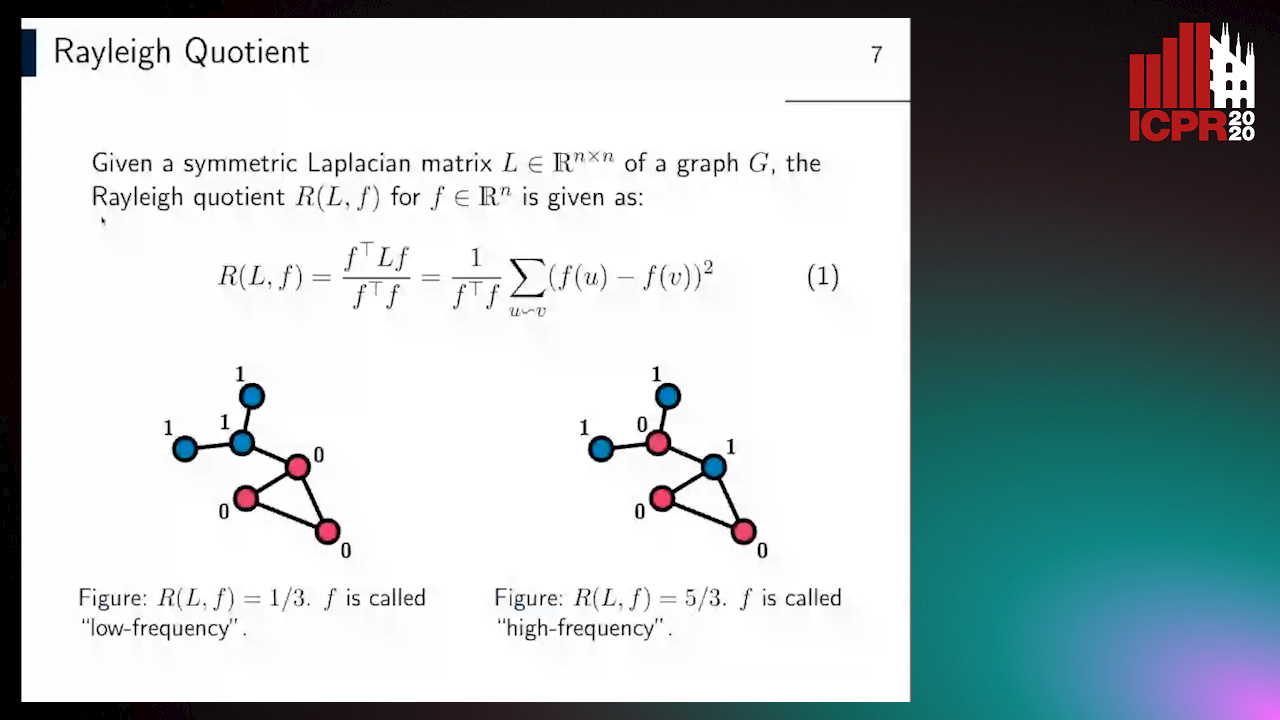
Auto-TLDR; Two-Layers Graph Convolutional Network with Graph Filters Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Use of Benford's Law to Detect GAN-Generated Images
Nicolo Bonettini, Paolo Bestagini, Simone Milani, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Using Benford's Law to Detect GAN-generated Images from Natural Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Compression Strategies and Space-Conscious Representations for Deep Neural Networks
Giosuè Marinò, Gregorio Ghidoli, Marco Frasca, Dario Malchiodi

Auto-TLDR; Compression of Large Convolutional Neural Networks by Weight Pruning and Quantization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dependently Coupled Principal Component Analysis for Bivariate Inversion Problems
Navdeep Dahiya, Yifei Fan, Samuel Bignardi, Tony Yezzi, Romeil Sandhu

Auto-TLDR; Asymmetric Principal Component Analysis between Paired Data in an Asymmetric manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Computing Stable Resultant-Based Minimal Solvers by Hiding a Variable
Snehal Bhayani, Zuzana Kukelova, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Permian-Based Method for Solving Minimal Systems of Polynomial Equations
Generation of Hypergraphs from the N-Best Parsing of 2D-Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Noya Ernesto, Joan Andreu Sánchez, Jose Miguel Benedi

Auto-TLDR; Hypergraphs: A Compact Representation of the N-best parse trees from 2D-PCFGs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Defocus Analysis for Finger Detection on a Virtual Keyboard
Miwa Michio, Honda Kenji, Sato Makoto
Auto-TLDR; Analysis of defocus information when a finger touching a virtual keyboard by using DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficient without detecting 3D position
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Signal Active Contours

Auto-TLDR; Adaptation of Active Contour Without Edges for Graph Signal Processing
PIF: Anomaly detection via preference embedding
Filippo Leveni, Luca Magri, Giacomo Boracchi, Cesare Alippi

Auto-TLDR; PIF: Anomaly Detection with Preference Embedding for Structured Patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Are Multiple Cross-Correlation Identities Better Than Just Two? Improving the Estimate of Time Differences-Of-Arrivals from Blind Audio Signals
Danilo Greco, Jacopo Cavazza, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; Improving Blind Channel Identification Using Cross-Correlation Identity for Time Differences-of-Arrivals Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Connectivity with Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Learning Graph Convolutional Networks Using Topological Properties of Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Conics: Properties and Applications
Aysylu Gabdulkhakova, Walter Kropatsch
Auto-TLDR; A Generalized Conic Representation for Distance Fields
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Force Banner for the Recognition of Spatial Relations
Robin Deléarde, Camille Kurtz, Laurent Wendling, Philippe Dejean

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Relation Recognition using Force Banners
Automatically Mining Relevant Variable Interactions Via Sparse Bayesian Learning
Ryoichiro Yafune, Daisuke Sakuma, Yasuo Tabei, Noritaka Saito, Hiroto Saigo

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Bayes for Interpretable Non-linear Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Magnifying Spontaneous Facial Micro Expressions for Improved Recognition
Pratikshya Sharma, Sonya Coleman, Pratheepan Yogarajah, Laurence Taggart, Pradeepa Samarasinghe
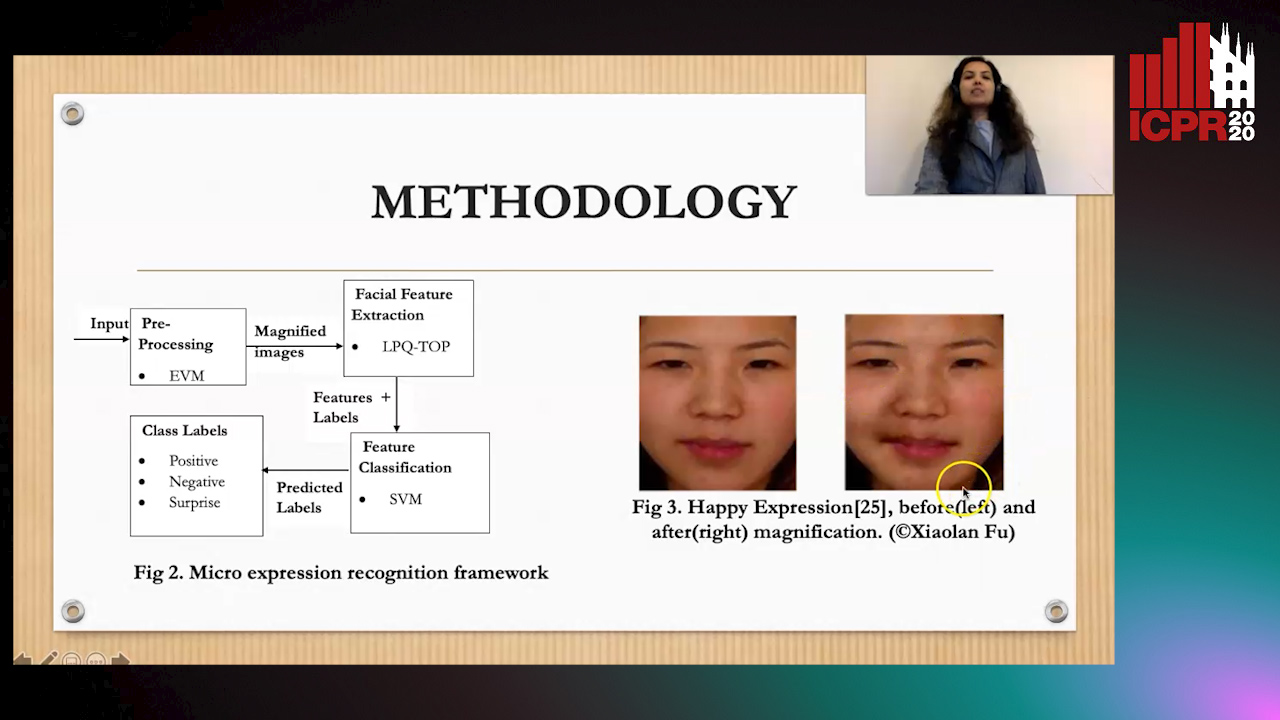
Auto-TLDR; Eulerian Video Magnification for Micro Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction by Joint Robust Discriminant Analysis and Inter-Class Sparsity
Auto-TLDR; Robust Discriminant Analysis with Feature Selection and Inter-class Sparsity (RDA_FSIS)
3D Pots Configuration System by Optimizing Over Geometric Constraints
Jae Eun Kim, Muhammad Zeeshan Arshad, Seong Jong Yoo, Je Hyeong Hong, Jinwook Kim, Young Min Kim

Auto-TLDR; Optimizing 3D Configurations for Stable Pottery Restoration from irregular and noisy evidence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combined Invariants to Gaussian Blur and Affine Transformation
Jitka Kostkova, Jan Flusser, Matteo Pedone

Auto-TLDR; A new theory of combined moment invariants to Gaussian blur and spatial affine transformation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
T-SVD Based Non-Convex Tensor Completion and Robust Principal Component Analysis

Auto-TLDR; Non-Convex tensor rank surrogate function and non-convex sparsity measure for tensor recovery
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Kernel-based Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Graph Convolutional Networks in Recurrent Kernel Hilbert Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Digit Recognition Applied to Reconstructed Audio Signals Using Deep Learning
Anastasia-Sotiria Toufa, Constantine Kotropoulos
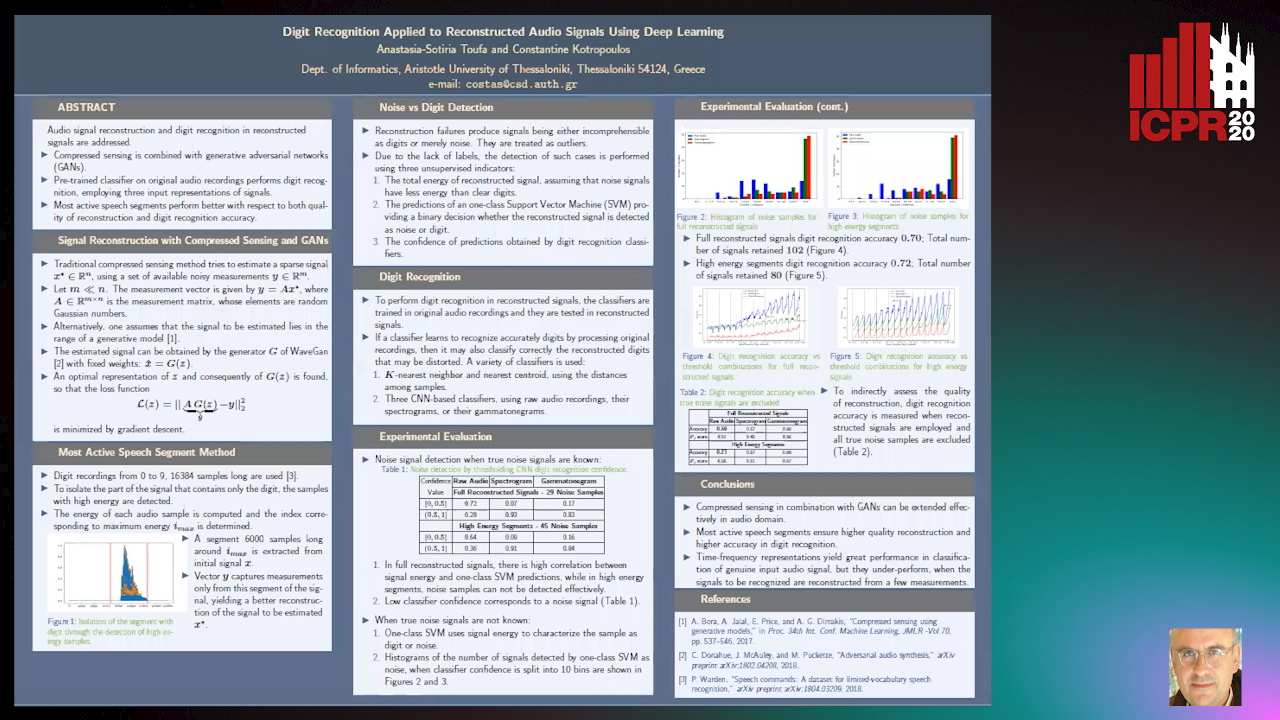
Auto-TLDR; Compressed Sensing for Digit Recognition in Audio Reconstruction
Appliance Identification Using a Histogram Post-Processing of 2D Local Binary Patterns for Smart Grid Applications
Yassine Himeur, Abdullah Alsalemi, Faycal Bensaali, Abbes Amira

Auto-TLDR; LBP-BEVM based Local Binary Patterns for Appliances Identification in the Smart Grid
A Multi-Focus Image Fusion Method Based on Fractal Dimension and Guided Filtering
Nikoo Dehghani, Ehsanollah Kabir
Auto-TLDR; Fractal Dimension-based Multi-focus Image Fusion with Guide Filtering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Engineering and Stacked Echo State Networks for Musical Onset Detection
Peter Steiner, Azarakhsh Jalalvand, Simon Stone, Peter Birkholz

Auto-TLDR; Echo State Networks for Onset Detection in Music Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AdaFilter: Adaptive Filter Design with Local Image Basis Decomposition for Optimizing Image Recognition Preprocessing
Aiga Suzuki, Keiichi Ito, Takahide Ibe, Nobuyuki Otsu
Auto-TLDR; Optimal Preprocessing Filtering for Pattern Recognition Using Higher-Order Local Auto-Correlation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Approximations to Geodesics on Metric Graphs
Robin Vandaele, Yvan Saeys, Tijl De Bie

Auto-TLDR; Topological Pattern Recognition of Metric Graphs Using Proximity Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Image Coding on Synthetic DNA: Reducing Sequencing Noise with Inpainting
Eva Gil San Antonio, Mattia Piretti, Melpomeni Dimopoulou, Marc Antonini

Auto-TLDR; Noise Resilience for DNA Storage
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Near-Infrared Depth-Independent Image Dehazing using Haar Wavelets
Sumit Laha, Ankit Sharma, Shengnan Hu, Hassan Foroosh
Auto-TLDR; A fusion algorithm for haze removal using Haar wavelets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Random Forest Dissimilarity Measure for Multi-View Learning
Hongliu Cao, Simon Bernard, Robert Sabourin, Laurent Heutte
Auto-TLDR; Multi-view Learning with Random Forest Relation Measure and Instance Hardness
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Naturally Constrained Online Expectation Maximization
Daniela Pamplona, Antoine Manzanera
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Online Expectation-Maximization for Probabilistic Principal Components Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TreeRNN: Topology-Preserving Deep Graph Embedding and Learning
Yecheng Lyu, Ming Li, Xinming Huang, Ulkuhan Guler, Patrick Schaumont, Ziming Zhang

Auto-TLDR; TreeRNN: Recurrent Neural Network for General Graph Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts
Wenbo Zhao, Yang Gao, Shahan Ali Memon, Bhiksha Raj, Rita Singh

Auto-TLDR; A Binary Tree-structured Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts for Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Learning Random Forests for Random Forest Clustering
Manuele Bicego, Francisco Escolano

Auto-TLDR; Learning Random Forests for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar