Fast Blending of Planar Shapes Based on Invariant Invertible and Stable Descriptors
Emna Ghorbel,
Faouzi Ghorbel,
Ines Sakly,
Slim Mhiri

Auto-TLDR; Fined-Fourier-based Invariant Descriptor for Planar Shape Blending
Similar papers
2D Discrete Mirror Transform for Image Non-Linear Approximation
Alessandro Gnutti, Fabrizio Guerrini, Riccardo Leonardi

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Mirror Transform (DMT)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A New Geodesic-Based Feature for Characterization of 3D Shapes: Application to Soft Tissue Organ Temporal Deformations
Karim Makki, Amine Bohi, Augustin Ogier, Marc-Emmanuel Bellemare

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature Descriptors for 3D Shape Characterization from Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combined Invariants to Gaussian Blur and Affine Transformation
Jitka Kostkova, Jan Flusser, Matteo Pedone

Auto-TLDR; A new theory of combined moment invariants to Gaussian blur and spatial affine transformation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Force Banner for the Recognition of Spatial Relations
Robin Deléarde, Camille Kurtz, Laurent Wendling, Philippe Dejean

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Relation Recognition using Force Banners
A Plane-Based Approach for Indoor Point Clouds Registration
Ketty Favre, Muriel Pressigout, Luce Morin, Eric Marchand

Auto-TLDR; A plane-based registration approach for indoor environments based on LiDAR data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Walk the Lines: Object Contour Tracing CNN for Contour Completion of Ships

Auto-TLDR; Walk the Lines: A Convolutional Neural Network trained to follow object contours
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stabilized Calculation of Gaussian Smoothing and Its Differentials Using Attenuated Sliding Fourier Transform
Yukihiko Yamashita, Toru Wakahara

Auto-TLDR; An attenuated SFT for Gaussian smoothing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Signal Active Contours

Auto-TLDR; Adaptation of Active Contour Without Edges for Graph Signal Processing
Generalized Shortest Path-Based Superpixels for Accurate Segmentation of Spherical Images
Rémi Giraud, Rodrigo Borba Pinheiro, Yannick Berthoumieu

Auto-TLDR; SPS: Spherical Shortest Path-based Superpixels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Conics: Properties and Applications
Aysylu Gabdulkhakova, Walter Kropatsch
Auto-TLDR; A Generalized Conic Representation for Distance Fields
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Document Image Dewarping by Probabilistic Discretization of Vanishing Points
Gilles Simon, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; Robust Document Dewarping using vanishing points
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Non-Rigid Surface Reconstruction from Spatio-Temporal Image Patches
Matteo Pedone, Abdelrahman Mostafa, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Dense Spatio-Temporal Depth Maps of Deformable Objects from Video Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Signature Features with the Visibility Transformation
Yue Wu, Hao Ni, Terry Lyons, Robin Hudson

Auto-TLDR; The Visibility Transformation for Pattern Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Computing Stable Resultant-Based Minimal Solvers by Hiding a Variable
Snehal Bhayani, Zuzana Kukelova, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Sparse Permian-Based Method for Solving Minimal Systems of Polynomial Equations
Multi-Scale Keypoint Matching

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Scale Keypoint Matching Using Multi-Scale Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DCT/IDCT Filter Design for Ultrasound Image Filtering
Barmak Honarvar Shakibaei Asli, Jan Flusser, Yifan Zhao, John Ahmet Erkoyuncu, Rajkumar Roy

Auto-TLDR; Finite impulse response digital filter using DCT-II and inverse DCT
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Distinctive 3D Local Deep Descriptors

Auto-TLDR; DIPs: Local Deep Descriptors for Point Cloud Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Learning Multiple Curvature Descriptor for 3D Palmprint Recognition
Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Jie Wen, Chunwei Tian, Peng Liu, Shuping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Joint Feature Learning for 3D palmprint recognition using curvature data vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Understanding When Spatial Transformer Networks Do Not Support Invariance, and What to Do about It
Lukas Finnveden, Ylva Jansson, Tony Lindeberg

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Transformer Networks are unable to support invariance when transforming CNN feature maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Minimal Solvers for Indoor UAV Positioning
Marcus Valtonen Örnhag, Patrik Persson, Mårten Wadenbäck, Kalle Åström, Anders Heyden

Auto-TLDR; Relative Pose Solvers for Visual Indoor UAV Navigation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Point Cloud Registration Based on Cascaded Mutual Information Attention Network

Auto-TLDR; Cascaded Mutual Information Attention Network for 3D Point Cloud Registration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for Power Line Outage Identification
Auto-TLDR; Graph Convolutional Networks for Power Line Outage Identification
Appliance Identification Using a Histogram Post-Processing of 2D Local Binary Patterns for Smart Grid Applications
Yassine Himeur, Abdullah Alsalemi, Faycal Bensaali, Abbes Amira

Auto-TLDR; LBP-BEVM based Local Binary Patterns for Appliances Identification in the Smart Grid
Sketch-Based Community Detection Via Representative Node Sampling
Mahlagha Sedghi, Andre Beckus, George Atia
Auto-TLDR; Sketch-based Clustering of Community Detection Using a Small Sketch
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Hierarchical Framework for Leaf Instance Segmentation: Application to Plant Phenotyping
Swati Bhugra, Kanish Garg, Santanu Chaudhury, Brejesh Lall

Auto-TLDR; Under-segmentation of plant image using a graph based formulation to extract leaf shape knowledge for the task of leaf instance segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unconstrained Vision Guided UAV Based Safe Helicopter Landing
Arindam Sikdar, Abhimanyu Sahu, Debajit Sen, Rohit Mahajan, Ananda Chowdhury

Auto-TLDR; Autonomous Helicopter Landing in Hazardous Environments from Unmanned Aerial Images Using Constrained Graph Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Approach for Document Detection by Contours and Contrasts
Daniil Tropin, Sergey Ilyuhin, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov
Auto-TLDR; A countor-based method for arbitrary document detection on a mobile device
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cluster-Size Constrained Network Partitioning
Maksim Mironov, Konstantin Avrachenkov
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Graph Clustering with Stochastic Block Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FourierNet: Compact Mask Representation for Instance Segmentation Using Differentiable Shape Decoders
Hamd Ul Moqeet Riaz, Nuri Benbarka, Andreas Zell

Auto-TLDR; FourierNet: A Single shot, anchor-free, fully convolutional instance segmentation method that predicts a shape vector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Morphological Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Caglayan Tuna, Alain Giros, François Merciol, Sébastien Lefèvre

Auto-TLDR; Comparison of Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quantization in Relative Gradient Angle Domain for Building Polygon Estimation
Yuhao Chen, Yifan Wu, Linlin Xu, Alexander Wong

Auto-TLDR; Relative Gradient Angle Transform for Building Footprint Extraction from Remote Sensing Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Invariance-Guided Stability Criterion for Time Series Clustering Validation
Florent Forest, Alex Mourer, Mustapha Lebbah, Hanane Azzag, Jérôme Lacaille

Auto-TLDR; An invariance-guided method for clustering model selection in time series data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dependently Coupled Principal Component Analysis for Bivariate Inversion Problems
Navdeep Dahiya, Yifei Fan, Samuel Bignardi, Tony Yezzi, Romeil Sandhu

Auto-TLDR; Asymmetric Principal Component Analysis between Paired Data in an Asymmetric manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gaussian Convolution Angles: Invariant Vein and Texture Descriptors for Butterfly Species Identification
Xin Chen, Bin Wang, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian convolution angle for butterfly species classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Riemannian Framework for Detecting Stimulus-Relevant Fiber Pathways
Jingyong Su, Linlin Tang, Zhipeng Yang, Mengmeng Guo

Auto-TLDR; Clustering Task-Specific Fiber Pathways in Functional MRI using BOLD Signals
A Hybrid Metric Based on Persistent Homology and Its Application to Signal Classification
Austin Lawson, Yu-Min Chung, William Cruse

Auto-TLDR; Topological Data Analysis with Persistence Curves
Graph Approximations to Geodesics on Metric Graphs
Robin Vandaele, Yvan Saeys, Tijl De Bie

Auto-TLDR; Topological Pattern Recognition of Metric Graphs Using Proximity Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Pots Configuration System by Optimizing Over Geometric Constraints
Jae Eun Kim, Muhammad Zeeshan Arshad, Seong Jong Yoo, Je Hyeong Hong, Jinwook Kim, Young Min Kim

Auto-TLDR; Optimizing 3D Configurations for Stable Pottery Restoration from irregular and noisy evidence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sequential Non-Rigid Factorisation for Head Pose Estimation
Stefania Cristina, Kenneth Patrick Camilleri

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Shape-and-Motion Factorisation for Head Pose Estimation in Eye-Gaze Tracking
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probabilistic Word Embeddings in Kinematic Space
Adarsh Jamadandi, Rishabh Tigadoli, Ramesh Ashok Tabib, Uma Mudenagudi

Auto-TLDR; Kinematic Space for Hierarchical Representation Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Binary Quaternion Rotation Pattern for Colour Texture Retrieval
Hela Jebali, Noel Richard, Mohamed Naouai
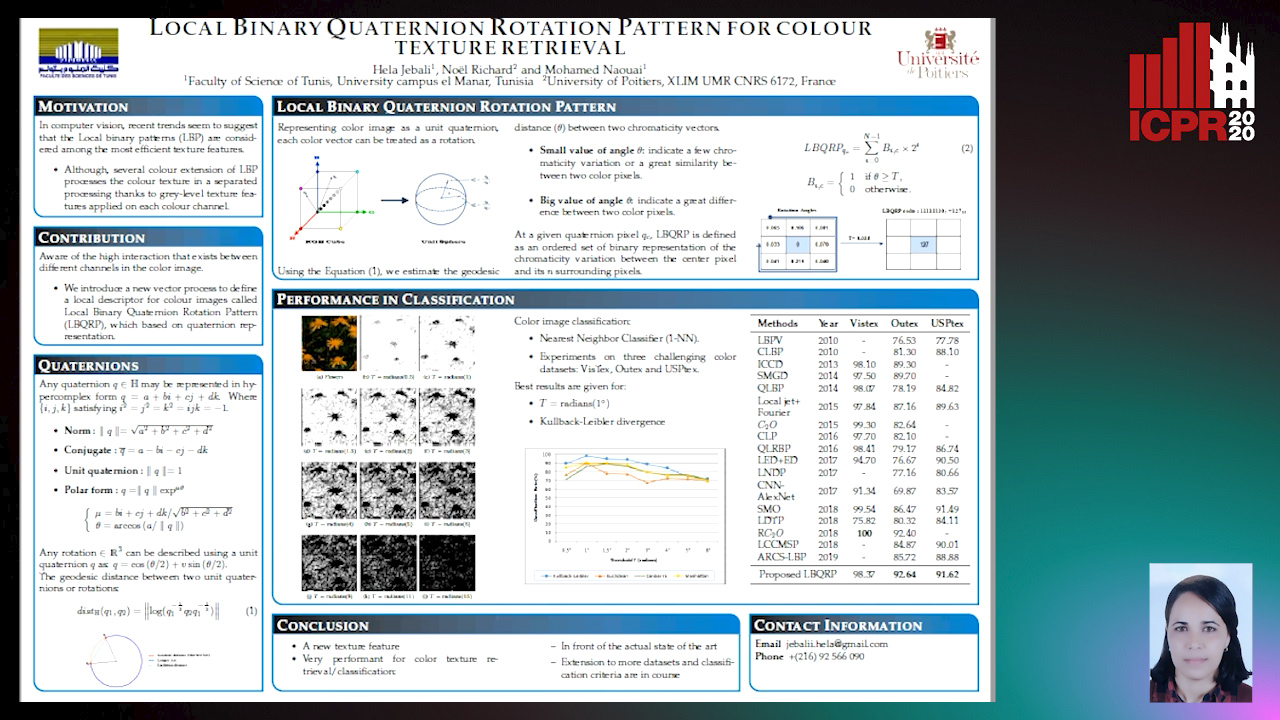
Auto-TLDR; Local Binary Quaternion Rotation Pattern for Color Texture Classification
3D Facial Matching by Spiral Convolutional Metric Learning and a Biometric Fusion-Net of Demographic Properties
Soha Sadat Mahdi, Nele Nauwelaers, Philip Joris, Giorgos Bouritsas, Imperial London, Sergiy Bokhnyak, Susan Walsh, Mark Shriver, Michael Bronstein, Peter Claes

Auto-TLDR; Multi-biometric Fusion for Biometric Verification using 3D Facial Mesures
PIF: Anomaly detection via preference embedding
Filippo Leveni, Luca Magri, Giacomo Boracchi, Cesare Alippi

Auto-TLDR; PIF: Anomaly Detection with Preference Embedding for Structured Patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Quantitative Evaluation Framework of Video De-Identification Methods
Sathya Bursic, Alessandro D'Amelio, Marco Granato, Giuliano Grossi, Raffaella Lanzarotti

Auto-TLDR; Face de-identification using photo-reality and facial expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar