Signature Features with the Visibility Transformation
Yue Wu,
Hao Ni,
Terry Lyons,
Robin Hudson

Auto-TLDR; The Visibility Transformation for Pattern Recognition
Similar papers
Kernel-based Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Spatial Graph Convolutional Networks in Recurrent Kernel Hilbert Space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Recurrent High-Order Statistics for Skeleton-Based Hand Gesture Recognition
Xuan Son Nguyen, Luc Brun, Olivier Lezoray, Sébastien Bougleux
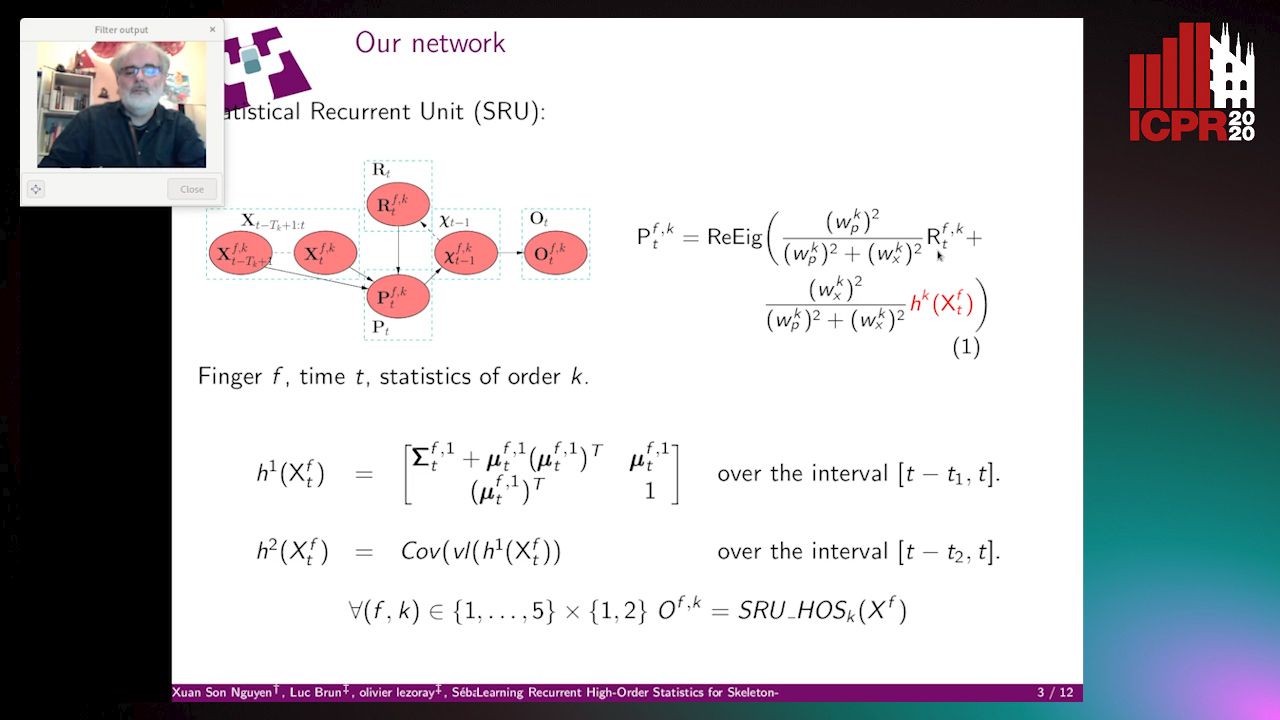
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting High-Order Statistics in Recurrent Neural Networks for Hand Gesture Recog-nition
Subspace Clustering for Action Recognition with Covariance Representations and Temporal Pruning
Giancarlo Paoletti, Jacopo Cavazza, Cigdem Beyan, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Learning for Human Action Recognition from Skeletal Data
Vision-Based Multi-Modal Framework for Action Recognition
Djamila Romaissa Beddiar, Mourad Oussalah, Brahim Nini

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Framework for Human Activity Recognition Using RGB, Depth and Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Hybrid Metric Based on Persistent Homology and Its Application to Signal Classification
Austin Lawson, Yu-Min Chung, William Cruse

Auto-TLDR; Topological Data Analysis with Persistence Curves
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Attention-Augmented Graph Convolutional Network for Efficient Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition
Negar Heidari, Alexandros Iosifidis

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Attention Module for Efficient Graph Convolutional Network-based Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vertex Feature Encoding and Hierarchical Temporal Modeling in a Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Action Recognition
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Enjie Ghorbel, Djamila Aouada, Bjorn Ottersten

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Switching Dynamical Systems with Deep Neural Networks
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev, Ramses J. Sanchez

Auto-TLDR; Variational RNN for Switching Dynamics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SL-DML: Signal Level Deep Metric Learning for Multimodal One-Shot Action Recognition
Raphael Memmesheimer, Nick Theisen, Dietrich Paulus

Auto-TLDR; One-Shot Action Recognition using Metric Learning
JT-MGCN: Joint-Temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Joint-temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition
Cross-People Mobile-Phone Based Airwriting Character Recognition
Yunzhe Li, Hui Zheng, He Zhu, Haojun Ai, Xiaowei Dong

Auto-TLDR; Cross-People Airwriting Recognition via Motion Sensor Signal via Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Networks for Trajectory Forecasting
Francesco Giuliari, Hasan Irtiza, Marco Cristani, Fabio Galasso

Auto-TLDR; TransformerNetworks for Trajectory Prediction of People Interactions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Connectivity with Graph Convolutional Networks
Auto-TLDR; Learning Graph Convolutional Networks Using Topological Properties of Graphs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D Deep Video Capsule Network with Temporal Shift for Action Recognition
Théo Voillemin, Hazem Wannous, Jean-Philippe Vandeborre

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Shift Module over Capsule Network for Action Recognition in Continuous Videos
DeepPear: Deep Pose Estimation and Action Recognition
Wen-Jiin Tsai, You-Ying Jhuang

Auto-TLDR; Human Action Recognition Using RGB Video Using 3D Human Pose and Appearance Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Air-Writing with Sparse Network of Radars Using Spatio-Temporal Learning
Muhammad Arsalan, Avik Santra, Kay Bierzynski, Vadim Issakov

Auto-TLDR; An Air-writing System for Sparse Radars using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Auto Encoding Explanatory Examples with Stochastic Paths
Cesar Ali Ojeda Marin, Ramses J. Sanchez, Kostadin Cvejoski, Bogdan Georgiev

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Stochastic Path: Explaining a Classifier's Decision Making Process using latent codes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Channel-Wise Dense Connection Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Michael Lao Banteng, Zhiyong Wu

Auto-TLDR; Two-stream channel-wise dense connection GCN for human action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpolation in Auto Encoders with Bridge Processes
Carl Ringqvist, Henrik Hult, Judith Butepage, Hedvig Kjellstrom
Auto-TLDR; Stochastic interpolations from auto encoders trained on flattened sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Joint Encoding of Motion and Appearance for First Person Action Recognition
Mirco Planamente, Andrea Bottino, Barbara Caputo

Auto-TLDR; A Single Stream Architecture for Egocentric Action Recognition from the First-Person Point of View
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DCT/IDCT Filter Design for Ultrasound Image Filtering
Barmak Honarvar Shakibaei Asli, Jan Flusser, Yifan Zhao, John Ahmet Erkoyuncu, Rajkumar Roy

Auto-TLDR; Finite impulse response digital filter using DCT-II and inverse DCT
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Randomized Algorithm for Sparse Recovery
Huiyuan Yu, Maggie Cheng, Yingdong Lu

Auto-TLDR; A Constrained Graph Optimization Algorithm for Sparse Signal Recovery
A Prototype-Based Generalized Zero-Shot Learning Framework for Hand Gesture Recognition
Jinting Wu, Yujia Zhang, Xiao-Guang Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Zero-Shot Learning for Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inferring Functional Properties from Fluid Dynamics Features
Andrea Schillaci, Maurizio Quadrio, Carlotta Pipolo, Marcello Restelli, Giacomo Boracchi

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Convective Properties of Computational Fluid Dynamics for Medical Diagnosis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Classification of Spatially Enriched Pixel Time Series with Convolutional Neural Networks
Mohamed Chelali, Camille Kurtz, Anne Puissant, Nicole Vincent
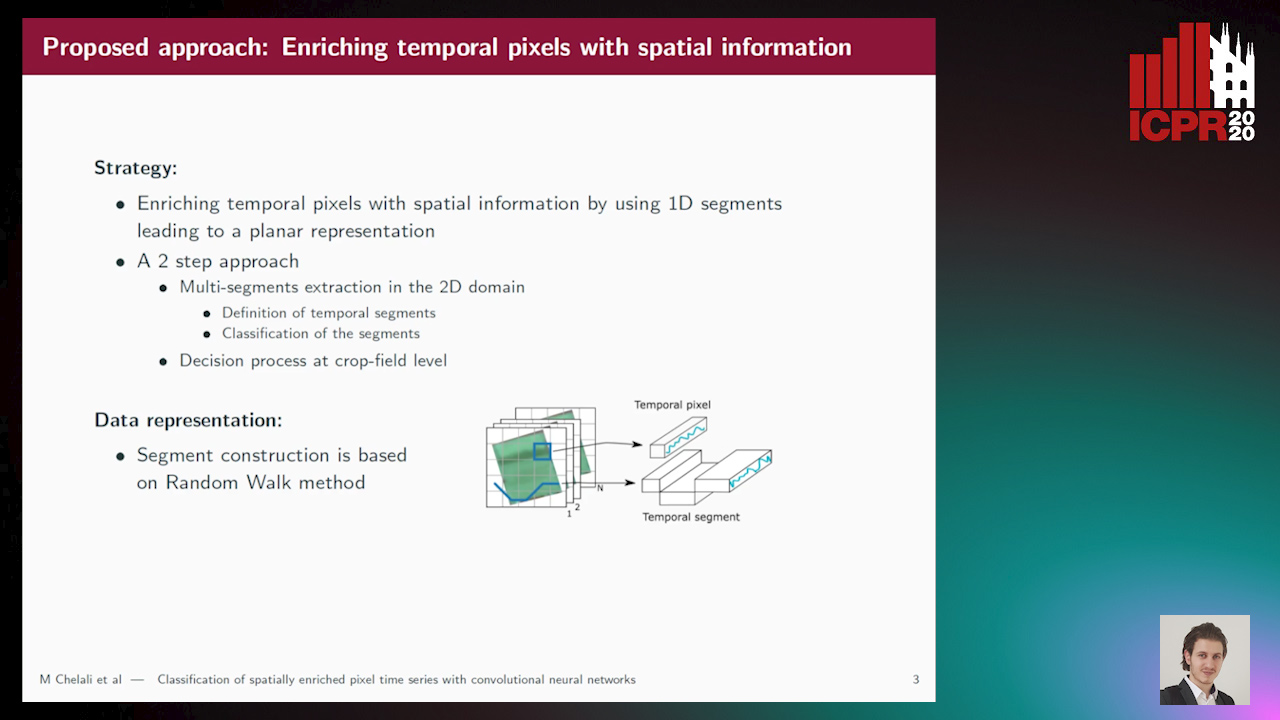
Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Features Extraction from Satellite Image Time Series Using Random Walk
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Oriented Action Recognition for Real-Time Human-Robot Interaction
Ziyang Song, Ziyi Yin, Zejian Yuan, Chong Zhang, Wanchao Chi, Yonggen Ling, Shenghao Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-Oriented Multi-Level Network for Action Recognition in Interaction Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cut and Compare: End-To-End Offline Signature Verification Network

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Cut-and-Compare Network for Offline Signature Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Non-Rigid Surface Reconstruction from Spatio-Temporal Image Patches
Matteo Pedone, Abdelrahman Mostafa, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Dense Spatio-Temporal Depth Maps of Deformable Objects from Video Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Map-Based Temporally Consistent Geolocalization through Learning Motion Trajectories

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Motion Trajectories for Geolocalization of Object on Topological Map using Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human or Machine? It Is Not What You Write, but How You Write It
Luis Leiva, Moises Diaz, M.A. Ferrer, Réjean Plamondon

Auto-TLDR; Behavioral Biometrics via Handwritten Symbols for Identification and Verification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context Matters: Self-Attention for Sign Language Recognition
Fares Ben Slimane, Mohamed Bouguessa

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Network for Continuous Sign Language Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recurrent Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Guangming Zhu, Lu Yang, Liang Zhang, Peiyi Shen, Juan Song
Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Graph Convolutional Network for Human Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Extension Module for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Extended Temporal Graph for Action Recognition with Kinetics-Skeleton
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partial Monotone Dependence
Denis Khryashchev, Huy Vo, Robert Haralick

Auto-TLDR; Partially Monotone Autoregressive Correlation for Time Series Forecasting
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3CS Algorithm for Efficient Gaussian Process Model Retrieval
Fabian Berns, Kjeld Schmidt, Ingolf Bracht, Christian Beecks

Auto-TLDR; Efficient retrieval of Gaussian Process Models for large-scale data using divide-&-conquer-based approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring the Ability of CNNs to Generalise to Previously Unseen Scales Over Wide Scale Ranges
Auto-TLDR; A theoretical analysis of invariance and covariance properties of scale channel networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar