Unconstrained Vision Guided UAV Based Safe Helicopter Landing
Arindam Sikdar,
Abhimanyu Sahu,
Debajit Sen,
Rohit Mahajan,
Ananda Chowdhury

Auto-TLDR; Autonomous Helicopter Landing in Hazardous Environments from Unmanned Aerial Images Using Constrained Graph Clustering
Similar papers
Localization of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Corridor Environments Using Deep Learning
Ram Padhy, Shahzad Ahmad, Sachin Verma, Sambit Bakshi, Pankaj Kumar Sa
Auto-TLDR; A monocular vision assisted localization algorithm for indoor corridor environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Total Estimation from RGB Video: On-Line Camera Self-Calibration, Non-Rigid Shape and Motion

Auto-TLDR; Joint Auto-Calibration, Pose and 3D Reconstruction of a Non-rigid Object from an uncalibrated RGB Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RISEdb: A Novel Indoor Localization Dataset
Carlos Sanchez Belenguer, Erik Wolfart, Álvaro Casado Coscollá, Vitor Sequeira

Auto-TLDR; Indoor Localization Using LiDAR SLAM and Smartphones: A Benchmarking Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AV-SLAM: Autonomous Vehicle SLAM with Gravity Direction Initialization
Kaan Yilmaz, Baris Suslu, Sohini Roychowdhury, L. Srikar Muppirisetty

Auto-TLDR; VI-SLAM with AGI: A combination of three SLAM algorithms for autonomous vehicles
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Derivation of Geometrically and Semantically Annotated UAV Datasets at Large Scales from 3D City Models
Sidi Wu, Lukas Liebel, Marco Körner
Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Dataset of Synthetic UAV Imagery for Geometric and Semantic Annotation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Step Approach to Lidar-Camera Calibration
Yingna Su, Yaqing Ding, Jian Yang, Hui Kong

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Lidar-camera System for Ego-motion Estimation and Scene Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Segmentation with Pairwise Matches and Unknown Number of Motions
Federica Arrigoni, Tomas Pajdla, Luca Magri

Auto-TLDR; Motion Segmentation using Multi-Modelfitting andpermutation synchronization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Sketch-Based Community Detection Via Representative Node Sampling
Mahlagha Sedghi, Andre Beckus, George Atia
Auto-TLDR; Sketch-based Clustering of Community Detection Using a Small Sketch
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Plane-Based Approach for Indoor Point Clouds Registration
Ketty Favre, Muriel Pressigout, Luce Morin, Eric Marchand

Auto-TLDR; A plane-based registration approach for indoor environments based on LiDAR data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Map-Based Temporally Consistent Geolocalization through Learning Motion Trajectories

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Motion Trajectories for Geolocalization of Object on Topological Map using Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CARRADA Dataset: Camera and Automotive Radar with Range-Angle-Doppler Annotations
Arthur Ouaknine, Alasdair Newson, Julien Rebut, Florence Tupin, Patrick Pérez
Auto-TLDR; CARRADA: A dataset of synchronized camera and radar recordings with range-angle-Doppler annotations for autonomous driving
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Minimal Solvers for Indoor UAV Positioning
Marcus Valtonen Örnhag, Patrik Persson, Mårten Wadenbäck, Kalle Åström, Anders Heyden

Auto-TLDR; Relative Pose Solvers for Visual Indoor UAV Navigation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
NetCalib: A Novel Approach for LiDAR-Camera Auto-Calibration Based on Deep Learning
Shan Wu, Amnir Hadachi, Damien Vivet, Yadu Prabhakar

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Calibration of LiDAR and Cameras using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Holistic Grid Fusion Based Stop Line Estimation
Runsheng Xu, Faezeh Tafazzoli, Li Zhang, Timo Rehfeld, Gunther Krehl, Arunava Seal

Auto-TLDR; Fused Multi-Sensory Data for Stop Lines Detection in Intersection Scenarios
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Drone Detection and Tracking with Visible, Thermal and Acoustic Sensors
Fredrik Svanström, Cristofer Englund, Fernando Alonso-Fernandez

Auto-TLDR; Automatic multi-sensor drone detection using sensor fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extending Single Beam Lidar to Full Resolution by Fusing with Single Image Depth Estimation
Yawen Lu, Yuxing Wang, Devarth Parikh, Guoyu Lu

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised LIDAR for Low-Cost Depth Estimation
Generic Merging of Structure from Motion Maps with a Low Memory Footprint
Gabrielle Flood, David Gillsjö, Patrik Persson, Anders Heyden, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; A Low-Memory Footprint Representation for Robust Map Merge
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can You Trust Your Pose? Confidence Estimation in Visual Localization
Luca Ferranti, Xiaotian Li, Jani Boutellier, Juho Kannala

Auto-TLDR; Pose Confidence Estimation in Large-Scale Environments: A Light-weight Approach to Improving Pose Estimation Pipeline
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Calibration and Absolute Pose Estimation of Trinocular Linear Camera Array for Smart City Applications
Martin Ahrnbom, Mikael Nilsson, Håkan Ardö, Kalle Åström, Oksana Yastremska-Kravchenko, Aliaksei Laureshyn

Auto-TLDR; Trinocular Linear Camera Array Calibration for Traffic Surveillance Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Camera Calibration Using Parallel Line Segments

Auto-TLDR; Closed-Form Calibration of Surveillance Cameras using Parallel 3D Line Segment Projections
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partially Supervised Multi-Task Network for Single-View Dietary Assessment
Ya Lu, Thomai Stathopoulou, Stavroula Mougiakakou
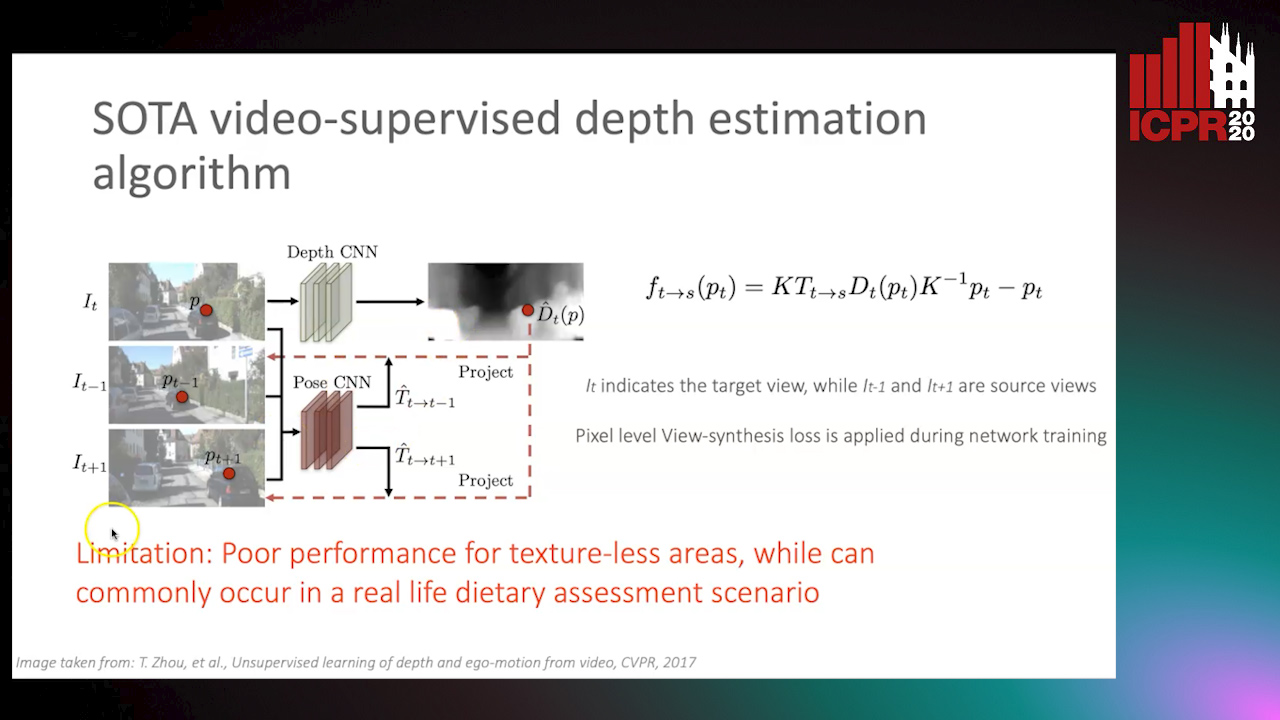
Auto-TLDR; Food Volume Estimation from a Single Food Image via Geometric Understanding and Semantic Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Inner Eye Canthus Localization for Human Body Temperature Screening
Claudio Ferrari, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Marco Bertini, Alberto Del Bimbo
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Localization of the Inner Eye Canthus in Thermal Face Images using 3D Morphable Face Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Knowledge-Rich Sequential Model for Planar Homography Estimation in Aerial Video

Auto-TLDR; Sequential Estimation of Planar Homographic Transformations over Aerial Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Extent-Of-Texture Information for Ground Terrain Recognition
Shuvozit Ghose, Pinaki Nath Chowdhury, Partha Pratim Roy, Umapada Pal

Auto-TLDR; Extent-of-Texture Guided Inter-domain Message Passing for Ground Terrain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vehicle Lane Merge Visual Benchmark
Auto-TLDR; A Benchmark for Automated Cooperative Maneuvering Using Multi-view Video Streams and Ground Truth Vehicle Description
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Facetwise Mesh Refinement for Multi-View Stereo
Andrea Romanoni, Matteo Matteucci

Auto-TLDR; Facetwise Refinement of Multi-View Stereo using Delaunay Triangulations
Object-Oriented Map Exploration and Construction Based on Auxiliary Task Aided DRL
Junzhe Xu, Jianhua Zhang, Shengyong Chen, Honghai Liu

Auto-TLDR; Auxiliary Task Aided Deep Reinforcement Learning for Environment Exploration by Autonomous Robots
Benchmarking Cameras for OpenVSLAM Indoors
Kevin Chappellet, Guillaume Caron, Fumio Kanehiro, Ken Sakurada, Abderrahmane Kheddar

Auto-TLDR; OpenVSLAM: Benchmarking Camera Types for Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Saliency Oriented Vehicle Scale Estimation
Qixin Chen, Tie Liu, Jiali Ding, Zejian Yuan, Yuanyuan Shang

Auto-TLDR; Regularized Intensity Matching for Vehicle Scale Estimation with salient object detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Two-Stage Adaptive Object Scene Flow Using Hybrid CNN-CRF Model
Congcong Li, Haoyu Ma, Qingmin Liao

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive object scene flow estimation using a hybrid CNN-CRF model and adaptive iteration
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A New Geodesic-Based Feature for Characterization of 3D Shapes: Application to Soft Tissue Organ Temporal Deformations
Karim Makki, Amine Bohi, Augustin Ogier, Marc-Emmanuel Bellemare

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature Descriptors for 3D Shape Characterization from Point Clouds
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Approach for 3D Head Reconstruction: Using Neural Networks and Visual Geometry
Oussema Bouafif, Bogdan Khomutenko, Mohammed Daoudi
Auto-TLDR; Recovering 3D Head Geometry from a Single Image using Deep Learning and Geometric Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Resource-Aware Corner Detection for Bio-Inspired Vision Sensors
Sherif Abdelmonem Sayed Mohamed, Jawad Yasin, Mohammad-Hashem Haghbayan, Antonio Miele, Jukka Veikko Heikkonen, Hannu Tenhunen, Juha Plosila

Auto-TLDR; Three Layer Filtering-Harris Algorithm for Event-based Cameras in Real-Time
Approach for Document Detection by Contours and Contrasts
Daniil Tropin, Sergey Ilyuhin, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov
Auto-TLDR; A countor-based method for arbitrary document detection on a mobile device
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Pots Configuration System by Optimizing Over Geometric Constraints
Jae Eun Kim, Muhammad Zeeshan Arshad, Seong Jong Yoo, Je Hyeong Hong, Jinwook Kim, Young Min Kim

Auto-TLDR; Optimizing 3D Configurations for Stable Pottery Restoration from irregular and noisy evidence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Find Good Correspondences of Multiple Objects
Youye Xie, Yingheng Tang, Gongguo Tang, William Hoff

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Object Inliers and Outliers for Perspective-n-Point and Object Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cluster-Size Constrained Network Partitioning
Maksim Mironov, Konstantin Avrachenkov
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Graph Clustering with Stochastic Block Model
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Non-Rigid Surface Reconstruction from Spatio-Temporal Image Patches
Matteo Pedone, Abdelrahman Mostafa, Janne Heikkilä

Auto-TLDR; Dense Spatio-Temporal Depth Maps of Deformable Objects from Video Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time End-To-End Lane ID Estimation Using Recurrent Networks
Ibrahim Halfaoui, Fahd Bouzaraa, Onay Urfalioglu

Auto-TLDR; Real-Time, Vision-Only Lane Identification Using Monocular Camera
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty Guided Recognition of Tiny Craters on the Moon
Thorsten Wilhelm, Christian Wöhler
Auto-TLDR; Accurately Detecting Tiny Craters in Remote Sensed Images Using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weakly Supervised Geodesic Segmentation of Egyptian Mummy CT Scans
Avik Hati, Matteo Bustreo, Diego Sona, Vittorio Murino, Alessio Del Bue

Auto-TLDR; A Weakly Supervised and Efficient Interactive Segmentation of Ancient Egyptian Mummies CT Scans Using Geodesic Distance Measure and GrabCut
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mobile Augmented Reality: Fast, Precise, and Smooth Planar Object Tracking
Dmitrii Matveichev, Daw-Tung Lin
Auto-TLDR; Planar Object Tracking with Sparse Optical Flow Tracking and Descriptor Matching
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Future Prediction Leveraging Synthetic Trajectories
Lorenzo Berlincioni, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Synthetic Trajectory Prediction using Markov Chains
Abstract Slides Poster Similar