UDBNET: Unsupervised Document Binarization Network Via Adversarial Game
Amandeep Kumar,
Shuvozit Ghose,
Pinaki Nath Chowdhury,
Partha Pratim Roy,
Umapada Pal

Auto-TLDR; Three-player Min-max Adversarial Game for Unsupervised Document Binarization
Similar papers
Efficient Shadow Detection and Removal Using Synthetic Data with Domain Adaptation
Rui Guo, Babajide Ayinde, Hao Sun
Auto-TLDR; Shadow Detection and Removal with Domain Adaptation and Synthetic Image Database
Unsupervised deep learning for text line segmentation
Berat Kurar Barakat, Ahmad Droby, Reem Alaasam, Borak Madi, Irina Rabaev, Raed Shammes, Jihad El-Sana
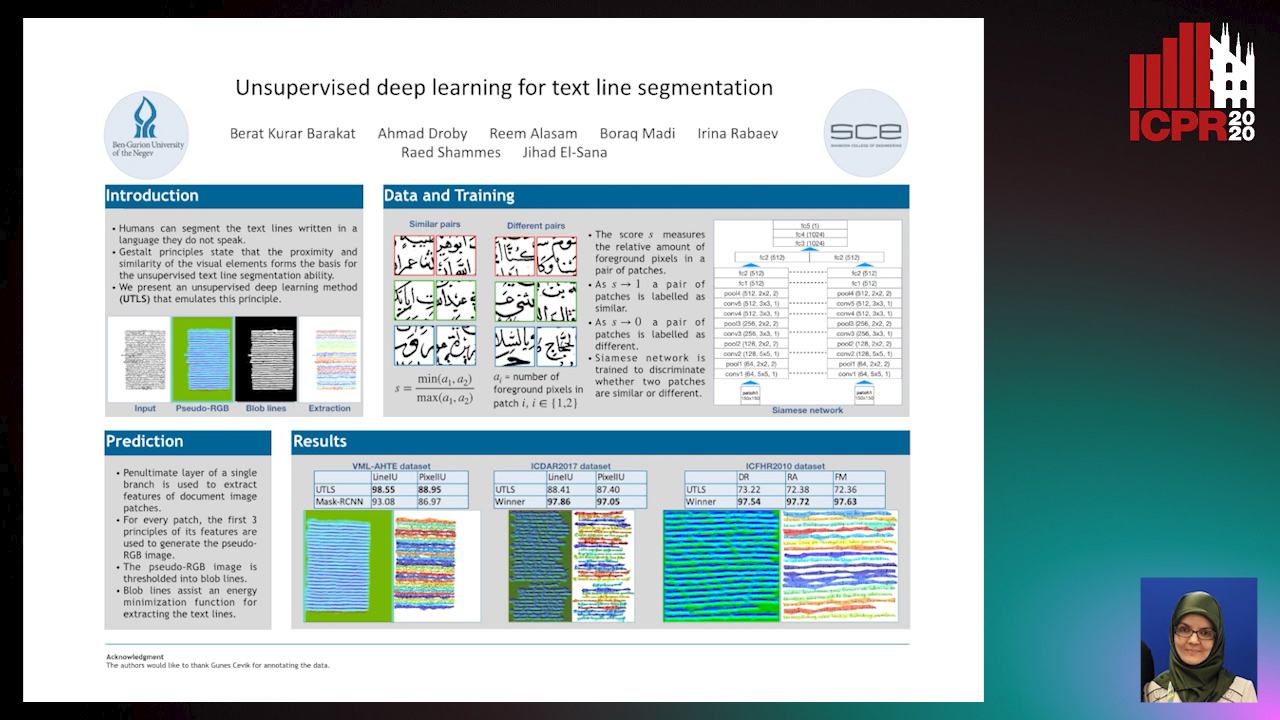
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Deep Learning for Handwritten Text Line Segmentation without Annotation
Ancient Document Layout Analysis: Autoencoders Meet Sparse Coding
Homa Davoudi, Marco Fiorucci, Arianna Traviglia
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Unsupervised Representation Learning for Document Layout Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Boundary Guided Image Translation for Pose Estimation from Ultra-Low Resolution Thermal Sensor
Kohei Kurihara, Tianren Wang, Teng Zhang, Brian Carrington Lovell
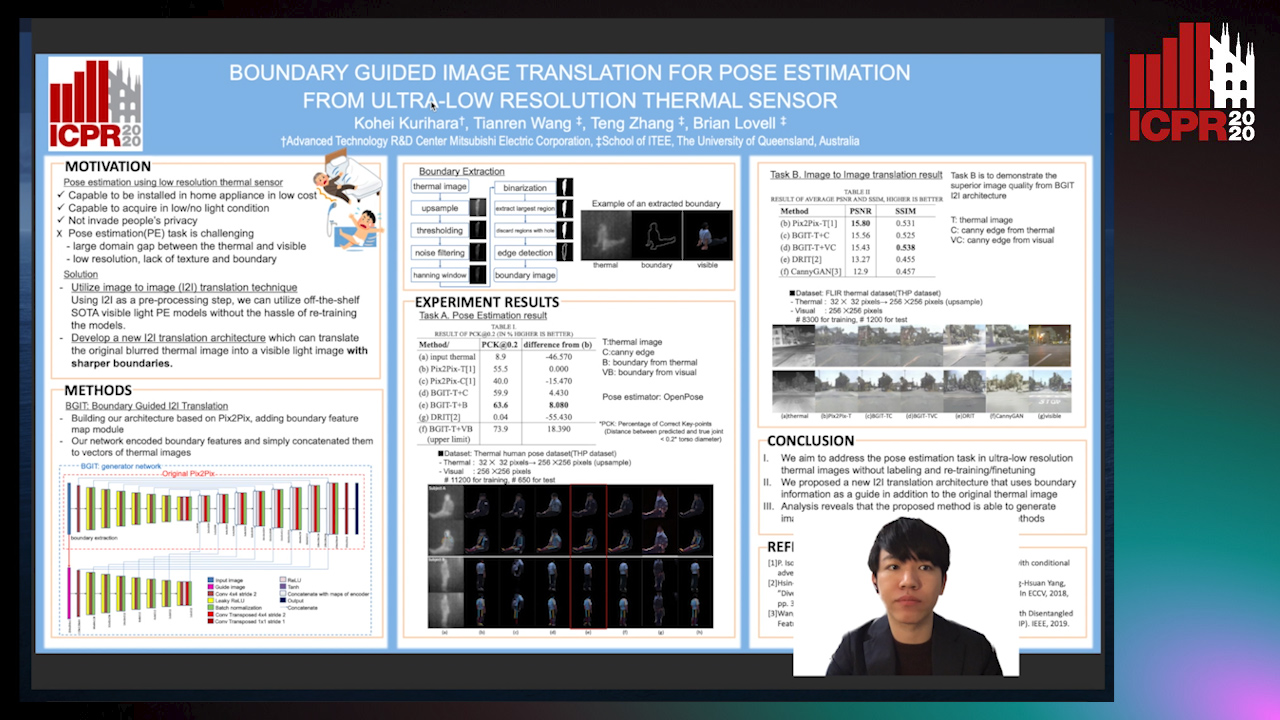
Auto-TLDR; Pose Estimation on Low-Resolution Thermal Images Using Image-to-Image Translation Architecture
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks and Fast Adaptive Bi-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer
Elissavet Batziou, Petros Alvanitopoulos, Konstantinos Ioannidis, Ioannis Patras, Stefanos Vrochidis, Ioannis Kompatsiaris

Auto-TLDR; FABEMD: Fast and Adaptive Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition for Style Transfer on Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Font Generation with Deep Metric Learning
Haruka Aoki, Koki Tsubota, Hikaru Ikuta, Kiyoharu Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; Deep Metric Learning for Japanese Typographic Font Synthesis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Facial Attribute Transfer through Inpainting
Ricard Durall, Franz-Josef Pfreundt, Janis Keuper

Auto-TLDR; Attribute Transfer Inpainting Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SIDGAN: Single Image Dehazing without Paired Supervision
Pan Wei, Xin Wang, Lei Wang, Ji Xiang, Zihan Wang

Auto-TLDR; DehazeGAN: An End-to-End Generative Adversarial Network for Image Dehazing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Galaxy Image Translation with Semi-Supervised Noise-Reconstructed Generative Adversarial Networks
Qiufan Lin, Dominique Fouchez, Jérôme Pasquet
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Image Translation with Generative Adversarial Networks Using Paired and Unpaired Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stylized-Colorization for Line Arts
Tzu-Ting Fang, Minh Duc Vo, Akihiro Sugimoto, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Stylized-colorization using GAN-based End-to-End Model for Anime
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Gated and Bifurcated Stacked U-Net Module for Document Image Dewarping
Hmrishav Bandyopadhyay, Tanmoy Dasgupta, Nibaran Das, Mita Nasipuri
Auto-TLDR; Gated and Bifurcated Stacked U-Net for Dewarping Document Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multiple Domain Discriminators and Adaptive Self-Training
Teo Spadotto, Marco Toldo, Umberto Michieli, Pietro Zanuttigh

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Face Manipulation Via Hallucination
Keerthy Kusumam, Enrique Sanchez, Georgios Tzimiropoulos

Auto-TLDR; Unpaired Face Image Manipulation using Autoencoders
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combining Deep and Ad-Hoc Solutions to Localize Text Lines in Ancient Arabic Document Images
Olfa Mechi, Maroua Mehri, Rolf Ingold, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara

Auto-TLDR; Text Line Localization in Ancient Handwritten Arabic Document Images using U-Net and Topological Structural Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Shape Consistent 2D Keypoint Estimation under Domain Shift
Levi Vasconcelos, Massimiliano Mancini, Davide Boscaini, Barbara Caputo, Elisa Ricci

Auto-TLDR; Deep Adaptation for Keypoint Prediction under Domain Shift
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On-Device Text Image Super Resolution
Dhruval Jain, Arun Prabhu, Gopi Ramena, Manoj Goyal, Debi Mohanty, Naresh Purre, Sukumar Moharana
Auto-TLDR; A Novel Deep Neural Network for Super-Resolution on Low Resolution Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Thermal Image Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Network for Pedestrian Detection
Mohamed Amine Marnissi, Hajer Fradi, Anis Sahbani, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara
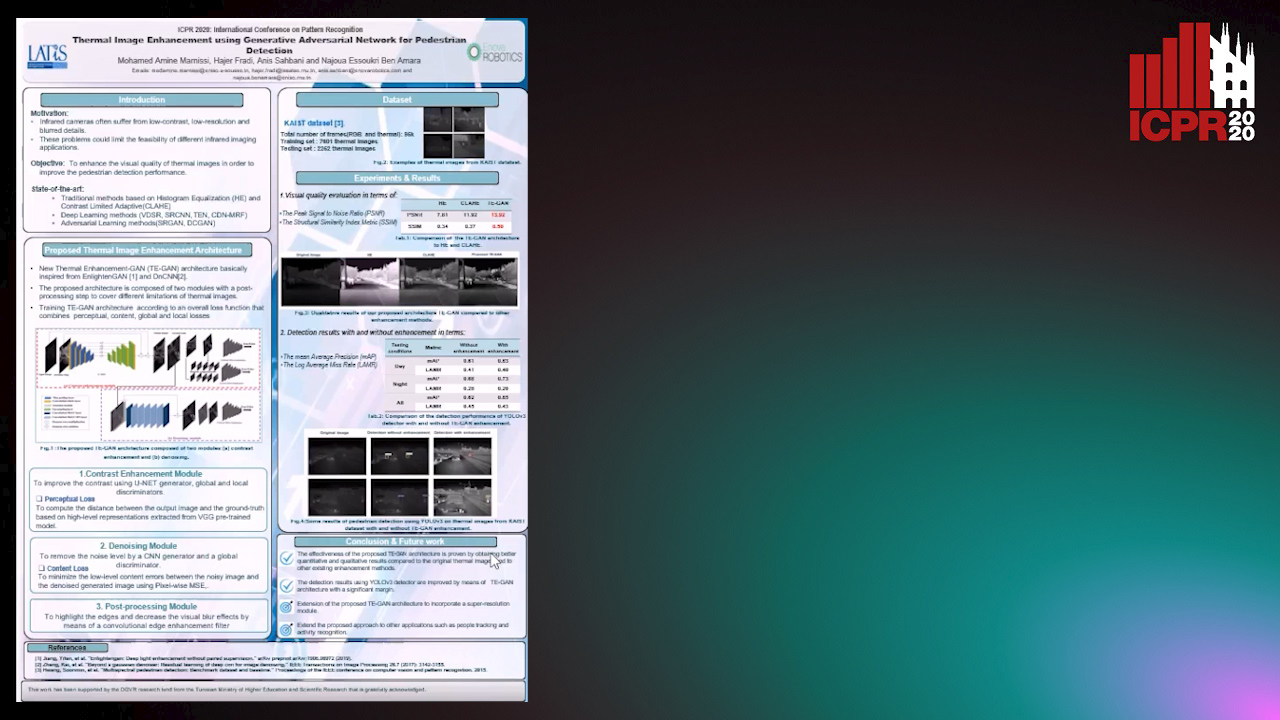
Auto-TLDR; Improving Visual Quality of Infrared Images for Pedestrian Detection Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Role of Cycle Consistency for Generating Better Human Action Videos from a Single Frame

Auto-TLDR; Generating Videos with Human Action Semantics using Cycle Constraints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Domain Image-To-Image Translation with Adaptive Inference Graph
The Phuc Nguyen, Stéphane Lathuiliere, Elisa Ricci
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Graph Structure for Multi-Domain Image-to-Image Translation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Word Recognition Using Multiple Hypotheses and Deep Embeddings
Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; EmbedNet: fuse recognition-based and recognition-free approaches for word recognition using learning-based methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
High Resolution Face Age Editing
Xu Yao, Gilles Puy, Alasdair Newson, Yann Gousseau, Pierre Hellier
Auto-TLDR; An Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Face Age editing on High Resolution Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A GAN-Based Blind Inpainting Method for Masonry Wall Images
Yahya Ibrahim, Balázs Nagy, Csaba Benedek

Auto-TLDR; An End-to-End Blind Inpainting Algorithm for Masonry Wall Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Identity-Preserved Face Beauty Transformation with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks

Auto-TLDR; Identity-preserved face beauty transformation using conditional GANs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Multi-Task Domain Adaptation

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Multi-task Learning for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic-Guided Inpainting Network for Complex Urban Scenes Manipulation
Pierfrancesco Ardino, Yahui Liu, Elisa Ricci, Bruno Lepri, Marco De Nadai

Auto-TLDR; Semantic-Guided Inpainting of Complex Urban Scene Using Semantic Segmentation and Generation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition in Real Scenarios with a Few Labeled Samples
Jinghuang Lin, Cheng Zhanzhan, Fan Bai, Yi Niu, Shiliang Pu, Shuigeng Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Adversarial Sequence Domain Adaptation for Scene Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes Via Multi-Level Feature Alignment
Bin Zhang, Shengjie Zhao, Rongqing Zhang
Auto-TLDR; Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Low-Shot Generative Networks for Cross-Domain Data
Hsuan-Kai Kao, Cheng-Che Lee, Wei-Chen Chiu
Auto-TLDR; Learning Generators for Cross-Domain Data under Low-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enlarging Discriminative Power by Adding an Extra Class in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Hai Tran, Sumyeong Ahn, Taeyoung Lee, Yung Yi

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Domain Adaptation using Artificial Classes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Robust Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Imagery Using Synthesized Images
My Kieu, Lorenzo Berlincioni, Leonardo Galteri, Marco Bertini, Andrew Bagdanov, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Improving Pedestrian Detection in the thermal domain using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Attention Guided Residue Learning GAN for Cross-Modal Translation
Bin Duan, Wei Wang, Hao Tang, Hugo Latapie, Yan Yan

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Attention-Guided Residue GAN for Cross-modal Audio-Visual Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DEN: Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
You-Feng Wu, Vu-Hoang Tran, Ting-Wei Chang, Wei-Chen Chiu, Ching-Chun Huang

Auto-TLDR; Disentangling and Exchanging Network for Depth Completion
Towards Artifacts-Free Image Defogging
Gabriele Graffieti, Davide Maltoni

Auto-TLDR; CurL-Defog: Learning Based Defogging with CycleGAN and HArD
Stratified Multi-Task Learning for Robust Spotting of Scene Texts
Kinjal Dasgupta, Sudip Das, Ujjwal Bhattacharya

Auto-TLDR; Feature Representation Block for Multi-task Learning of Scene Text
Pose Variation Adaptation for Person Re-Identification
Lei Zhang, Na Jiang, Qishuai Diao, Yue Xu, Zhong Zhou, Wei Wu

Auto-TLDR; Pose Transfer Generative Adversarial Network for Person Re-identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Super-Resolution Guided Pore Detection for Fingerprint Recognition
Syeda Nyma Ferdous, Ali Dabouei, Jeremy Dawson, Nasser M. Nasarabadi

Auto-TLDR; Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for Fingerprint Recognition Using Pore Features
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GarmentGAN: Photo-Realistic Adversarial Fashion Transfer
Amir Hossein Raffiee, Michael Sollami

Auto-TLDR; GarmentGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Image-Based Garment Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail Fusion GAN: High-Quality Translation for Unpaired Images with GAN-Based Data Augmentation
Ling Li, Yaochen Li, Chuan Wu, Hang Dong, Peilin Jiang, Fei Wang

Auto-TLDR; Data Augmentation with GAN-based Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DUET: Detection Utilizing Enhancement for Text in Scanned or Captured Documents
Eun-Soo Jung, Hyeonggwan Son, Kyusam Oh, Yongkeun Yun, Soonhwan Kwon, Min Soo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Text Detection for Document Images Using Synthetic and Real Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multimodal Side-Tuning for Document Classification
Stefano Zingaro, Giuseppe Lisanti, Maurizio Gabbrielli

Auto-TLDR; Side-tuning for Multimodal Document Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Data Augmentation Via Mixed Class Interpolation Using Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks Applied to Cross-Domain Imagery
Hiroshi Sasaki, Chris G. Willcocks, Toby Breckon
Auto-TLDR; C2GMA: A Generative Domain Transfer Model for Non-visible Domain Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Position-Aware and Symmetry Enhanced GAN for Radial Distortion Correction
Yongjie Shi, Xin Tong, Jingsi Wen, He Zhao, Xianghua Ying, Jinshi Hongbin Zha

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Radial Distorted Image Correction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detail-Revealing Deep Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Xinchen Ye, Yuyao Xu, Rui Xu, Shoji Kido, Noriyuki Tomiyama

Auto-TLDR; A Dual-branch Aggregation Network for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combining GANs and AutoEncoders for Efficient Anomaly Detection
Fabio Carrara, Giuseppe Amato, Luca Brombin, Fabrizio Falchi, Claudio Gennaro
Auto-TLDR; CBIGAN: Anomaly Detection in Images with Consistency Constrained BiGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Age Gap Reducer-GAN for Recognizing Age-Separated Faces
Daksha Yadav, Naman Kohli, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh, Afzel Noore

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Age-separated Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
UCCTGAN: Unsupervised Clothing Color Transformation Generative Adversarial Network
Shuming Sun, Xiaoqiang Li, Jide Li

Auto-TLDR; An Unsupervised Clothing Color Transformation Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar