Ancient Document Layout Analysis: Autoencoders Meet Sparse Coding
Homa Davoudi,
Marco Fiorucci,
Arianna Traviglia
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Unsupervised Representation Learning for Document Layout Analysis
Similar papers
Unsupervised deep learning for text line segmentation
Berat Kurar Barakat, Ahmad Droby, Reem Alaasam, Borak Madi, Irina Rabaev, Raed Shammes, Jihad El-Sana
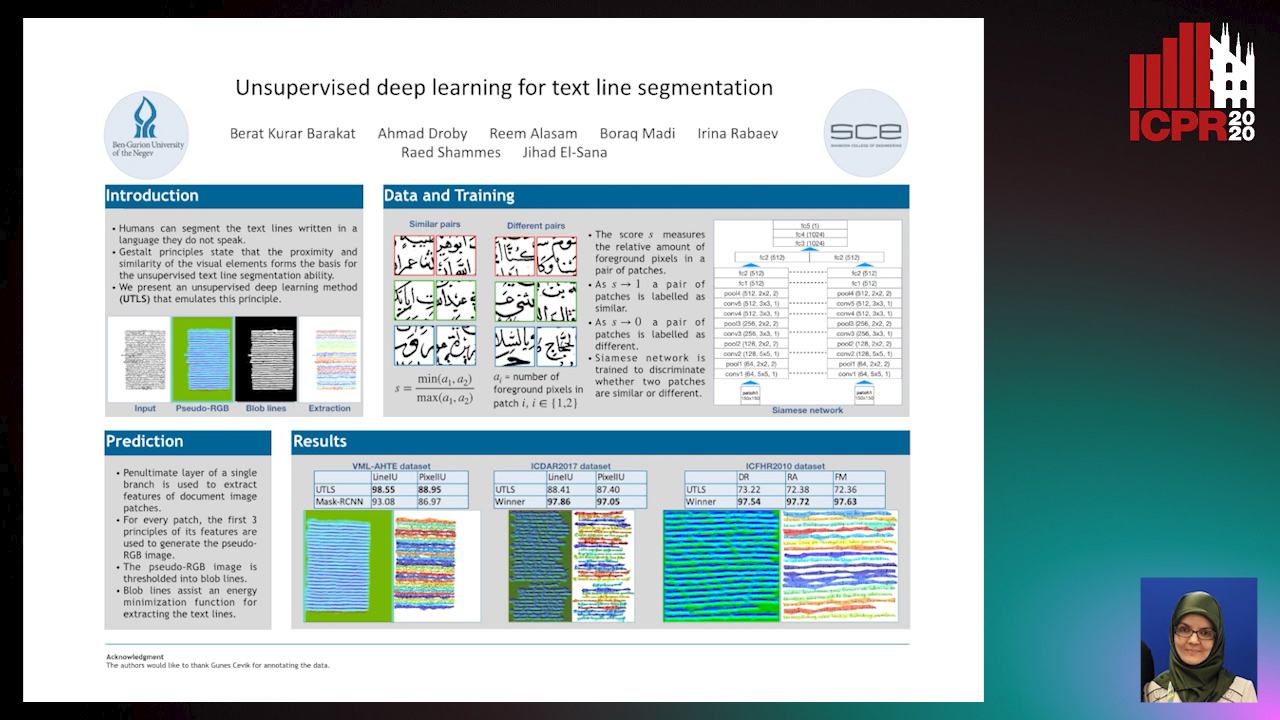
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Deep Learning for Handwritten Text Line Segmentation without Annotation
Text Baseline Recognition Using a Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network
Matthias Wödlinger, Robert Sablatnig

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Baseline Detection of Handwritten Text Using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Writer Identification Using Deep Neural Networks: Impact of Patch Size and Number of Patches
Akshay Punjabi, José Ramón Prieto Fontcuberta, Enrique Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Writer Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The HisClima Database: Historical Weather Logs for Automatic Transcription and Information Extraction
Verónica Romero, Joan Andreu Sánchez

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Handwritten Text Recognition and Information Extraction from Historical Weather Logs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multiple Document Datasets Pre-Training Improves Text Line Detection with Deep Neural Networks
Mélodie Boillet, Christopher Kermorvant, Thierry Paquet

Auto-TLDR; A fully convolutional network for document layout analysis
Watch Your Strokes: Improving Handwritten Text Recognition with Deformable Convolutions
Iulian Cojocaru, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Massimiliano Corsini, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Deformable Convolutional Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Layout Detection from Scientific Literature Using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Scientific Literature Layout Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multimodal Side-Tuning for Document Classification
Stefano Zingaro, Giuseppe Lisanti, Maurizio Gabbrielli

Auto-TLDR; Side-tuning for Multimodal Document Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
UDBNET: Unsupervised Document Binarization Network Via Adversarial Game
Amandeep Kumar, Shuvozit Ghose, Pinaki Nath Chowdhury, Partha Pratim Roy, Umapada Pal

Auto-TLDR; Three-player Min-max Adversarial Game for Unsupervised Document Binarization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Combining Deep and Ad-Hoc Solutions to Localize Text Lines in Ancient Arabic Document Images
Olfa Mechi, Maroua Mehri, Rolf Ingold, Najoua Essoukri Ben Amara

Auto-TLDR; Text Line Localization in Ancient Handwritten Arabic Document Images using U-Net and Topological Structural Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Textual-Content Based Classification of Bundles of Untranscribed of Manuscript Images
José Ramón Prieto Fontcuberta, Enrique Vidal, Vicente Bosch, Carlos Alonso, Carmen Orcero, Lourdes Márquez

Auto-TLDR; Probabilistic Indexing for Text-based Classification of Manuscripts
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ConvMath : A Convolutional Sequence Network for Mathematical Expression Recognition
Zuoyu Yan, Xiaode Zhang, Liangcai Gao, Ke Yuan, Zhi Tang
Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Sequence Modeling for Mathematical Expressions Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning to Sort Handwritten Text Lines in Reading Order through Estimated Binary Order Relations

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Reading Order of Text Lines in Handwritten Text Documents
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LODENet: A Holistic Approach to Offline Handwritten Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Huu Tin Hoang, Chun-Jen Peng, Hung Tran, Hung Le, Huy Hoang Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Logographic DEComposition Encoding for Chinese and Japanese Text Line Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Few-Shot Learning Approach for Historical Ciphered Manuscript Recognition
Mohamed Ali Souibgui, Alicia Fornés, Yousri Kessentini, Crina Tudor

Auto-TLDR; Handwritten Ciphers Recognition Using Few-Shot Object Detection
Multi-Task Learning Based Traditional Mongolian Words Recognition
Hongxi Wei, Hui Zhang, Jing Zhang, Kexin Liu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Learning for Mongolian Words Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Gated and Bifurcated Stacked U-Net Module for Document Image Dewarping
Hmrishav Bandyopadhyay, Tanmoy Dasgupta, Nibaran Das, Mita Nasipuri
Auto-TLDR; Gated and Bifurcated Stacked U-Net for Dewarping Document Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Capsule Encoder
Harish Raviprakash, Syed Anwar, Ulas Bagci

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Capsule Networks for Representation Learning in latent space
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recursive Recognition of Offline Handwritten Mathematical Expressions
Marco Cotogni, Claudio Cusano, Antonino Nocera

Auto-TLDR; Online Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition with Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Evaluation of DNN Architectures for Page Segmentation of Historical Newspapers
Manuel Burghardt, Bernhard Liebl

Auto-TLDR; Evaluation of Backbone Architectures for Optical Character Segmentation of Historical Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Aware Unsupervised Learning with Joint Variational Attention and Automatic Clustering
Wang Ru, Lin Li, Peipei Wang, Liu Peiyu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Variational Attention Encoder-Decoder for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Deep Embedding Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information Maximization
Qiang Ji, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Clustering by Augmented Mutual Information maximization for Deep Embedding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sparse Deep Neural Networks Using Efficient Structured Projections on Convex Constraints for Green AI
Michel Barlaud, Frederic Guyard

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Deep Neural Network with Constrained Splitting Projection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised Feature Learning for Event Data: Direct vs Inverse Problem Formulation
Dimche Kostadinov, Davide Scarammuza

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Representation Learning from Local Event Data for Pattern Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Iterative Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-Resolution
Rao Muhammad Umer, Gian Luca Foresti, Christian Micheloni

Auto-TLDR; ISRResCNet: Deep Iterative Super-Resolution Residual Convolutional Network for Single Image Super-resolution
Explainable Feature Embedding Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Pathological Image Analysis
Kazuki Uehara, Masahiro Murakawa, Hirokazu Nosato, Hidenori Sakanashi
Auto-TLDR; Explainable Diagnosis Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Pathological Image Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PICK: Processing Key Information Extraction from Documents Using Improved Graph Learning-Convolutional Networks
Wenwen Yu, Ning Lu, Xianbiao Qi, Ping Gong, Rong Xiao

Auto-TLDR; PICK: A Graph Learning Framework for Key Information Extraction from Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Online Trajectory Recovery from Offline Handwritten Japanese Kanji Characters of Multiple Strokes
Hung Tuan Nguyen, Tsubasa Nakamura, Cuong Tuan Nguyen, Masaki Nakagawa

Auto-TLDR; Recovering Dynamic Online Trajectories from Offline Japanese Kanji Character Images for Handwritten Character Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-Class Recognition
Pramuditha Perera, Vishal Patel
Auto-TLDR; Combining Generative Features and One-Class Classification for Effective One-class Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Word Recognition Using Multiple Hypotheses and Deep Embeddings
Siddhant Bansal, Praveen Krishnan, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; EmbedNet: fuse recognition-based and recognition-free approaches for word recognition using learning-based methods
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction with Graph Neural Networks in Semi Structured Documents
Manuel Carbonell, Pau Riba, Mauricio Villegas, Alicia Fornés, Josep Llados

Auto-TLDR; Graph Neural Network for Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction in Semi-Structured Documents
Automated Whiteboard Lecture Video Summarization by Content Region Detection and Representation
Bhargava Urala Kota, Alexander Stone, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; A Framework for Summarizing Whiteboard Lecture Videos Using Feature Representations of Handwritten Content Regions
Combining GANs and AutoEncoders for Efficient Anomaly Detection
Fabio Carrara, Giuseppe Amato, Luca Brombin, Fabrizio Falchi, Claudio Gennaro
Auto-TLDR; CBIGAN: Anomaly Detection in Images with Consistency Constrained BiGAN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Hierarchical Relation Extraction for Generic Form Understanding
Tuan Anh Nguyen Dang, Duc-Thanh Hoang, Quang Bach Tran, Chih-Wei Pan, Thanh-Dat Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Joint Entity Labeling and Link Prediction for Form Understanding in Noisy Scanned Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
N2D: (Not Too) Deep Clustering Via Clustering the Local Manifold of an Autoencoded Embedding
Ryan Mcconville, Raul Santos-Rodriguez, Robert Piechocki, Ian Craddock

Auto-TLDR; Local Manifold Learning for Deep Clustering on Autoencoded Embeddings
Approach for Document Detection by Contours and Contrasts
Daniil Tropin, Sergey Ilyuhin, Dmitry Nikolaev, Vladimir V. Arlazarov
Auto-TLDR; A countor-based method for arbitrary document detection on a mobile device
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Variational Information Bottleneck Model for Accurate Indoor Position Recognition
Auto-TLDR; Variational Information Bottleneck for Indoor Positioning with WiFi Fingerprints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Handwritten Digit String Recognition Using Deep Autoencoder Based Segmentation and ResNet Based Recognition Approach
Anuran Chakraborty, Rajonya De, Samir Malakar, Friedhelm Schwenker, Ram Sarkar

Auto-TLDR; Handwritten Digit Strings Recognition Using Residual Network and Deep Autoencoder Based Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Deep Clustering: Unsupervised Partitioning of Images

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Modal Deep Clustering for Unlabeled Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization When Learning from Small Sample
Auto-TLDR; GLICO: Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization for Small Sample Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On-Device Text Image Super Resolution
Dhruval Jain, Arun Prabhu, Gopi Ramena, Manoj Goyal, Debi Mohanty, Naresh Purre, Sukumar Moharana
Auto-TLDR; A Novel Deep Neural Network for Super-Resolution on Low Resolution Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Superpixel Cut for Unsupervised Image Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Deep Superpixel Cut for Deep Unsupervised Image Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Phase Retrieval Using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Tobias Uelwer, Alexander Oberstraß, Stefan Harmeling

Auto-TLDR; Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks for Phase Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar