Local Grouped Invariant Order Pattern for Grayscale-Inversion and Rotation Invariant Texture Classification
Yankai Huang,
Tiecheng Song,
Shuang Li,
Yuanjing Han

Auto-TLDR; Local grouped invariant order pattern for grayscale-inversion and rotation invariant texture classification
Similar papers
First and Second-Order Sorted Local Binary Pattern Features for Grayscale-Inversion and Rotation Invariant Texture Classification
Tiecheng Song, Yuanjing Han, Jie Feng, Yuanlin Wang, Chenqiang Gao

Auto-TLDR; First- and Secondorder Sorted Local Binary Pattern for texture classification under inverse grayscale changes and image rotation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Color Texture Description Based on Holistic and Hierarchical Order-Encoding Patterns
Tiecheng Song, Jie Feng, Yuanlin Wang, Chenqiang Gao

Auto-TLDR; Holistic and Hierarchical Order-Encoding Patterns for Color Texture Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Local Binary Quaternion Rotation Pattern for Colour Texture Retrieval
Hela Jebali, Noel Richard, Mohamed Naouai
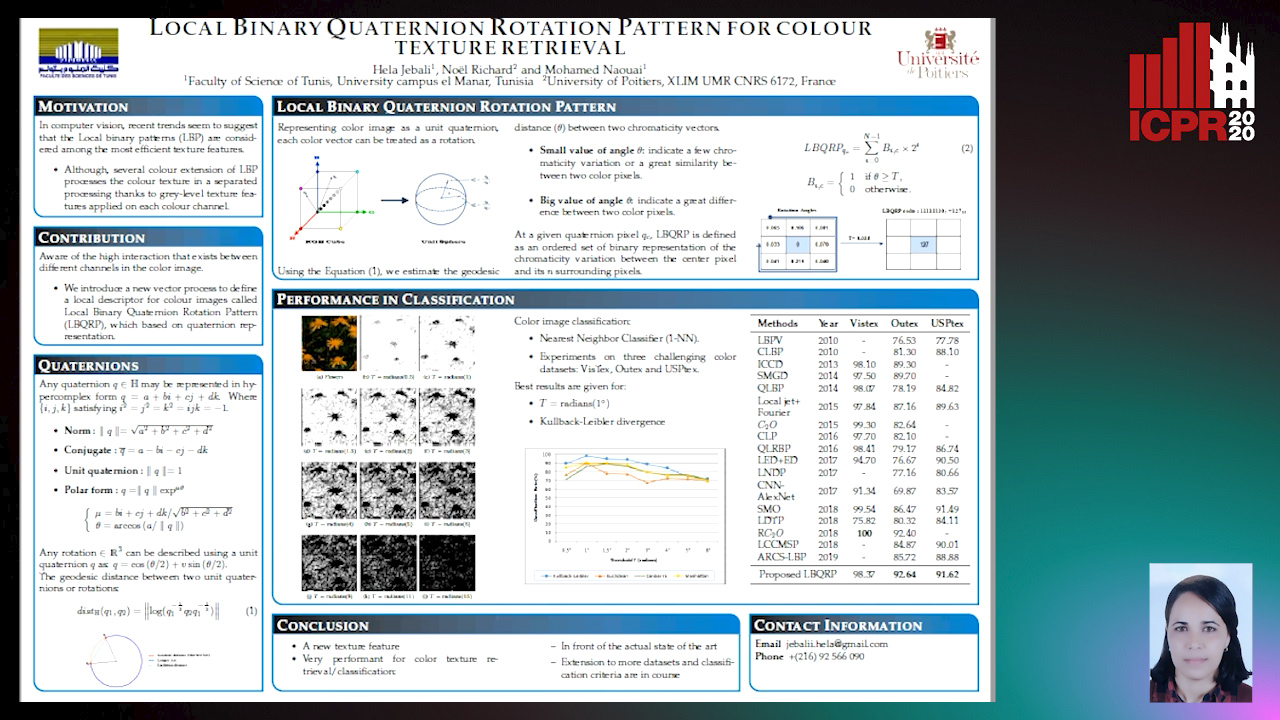
Auto-TLDR; Local Binary Quaternion Rotation Pattern for Color Texture Classification
Joint Learning Multiple Curvature Descriptor for 3D Palmprint Recognition
Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Jie Wen, Chunwei Tian, Peng Liu, Shuping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Joint Feature Learning for 3D palmprint recognition using curvature data vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Dynamic Color Texture Analysis Using Local Directional Number Pattern
Junwei Zhou, Ke Shu, Peng Liu, Jianwen Xiang, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; LDN-TOP Representation followed by ProCRC Classification for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gaussian Convolution Angles: Invariant Vein and Texture Descriptors for Butterfly Species Identification
Xin Chen, Bin Wang, Yongsheng Gao

Auto-TLDR; Gaussian convolution angle for butterfly species classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Distinct Discriminant Canonical Correlation Analysis Network Based Deep Information Quality Representation for Image Classification
Lei Gao, Zheng Guo, Ling Guan Ling Guan
Auto-TLDR; DDCCANet: Deep Information Quality Representation for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Appliance Identification Using a Histogram Post-Processing of 2D Local Binary Patterns for Smart Grid Applications
Yassine Himeur, Abdullah Alsalemi, Faycal Bensaali, Abbes Amira

Auto-TLDR; LBP-BEVM based Local Binary Patterns for Appliances Identification in the Smart Grid
A Local Descriptor with Physiological Characteristic for Finger Vein Recognition
Liping Zhang, Weijun Li, Ning Xin

Auto-TLDR; Finger vein-specific local feature descriptors based physiological characteristic of finger vein patterns
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Merged 1D-2D Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Nerve Detection in Ultrasound Images
Mohammad Alkhatib, Adel Hafiane, Pierre Vieyres

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for Deep Neural Networks to Detect Median Nerve in Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Keypoint Matching

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Scale Keypoint Matching Using Multi-Scale Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Anti-Spoofing Using Spatial Pyramid Pooling
Lei Shi, Zhuo Zhou, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Face Anti-Spoofing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GraphBGS: Background Subtraction Via Recovery of Graph Signals
Jhony Heriberto Giraldo Zuluaga, Thierry Bouwmans
Auto-TLDR; Graph BackGround Subtraction using Graph Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Low-Resolution Image Classification by Super-Resolution with Enhancing High-Frequency Content
Liguo Zhou, Guang Chen, Mingyue Feng, Alois Knoll

Auto-TLDR; Super-resolution for Low-Resolution Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Quality-Based Representation for Unconstrained Face Recognition
Nelson Méndez-Llanes, Katy Castillo-Rosado, Heydi Mendez-Vazquez, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; activation map for face recognition in unconstrained environments
Automatic Tuberculosis Detection Using Chest X-Ray Analysis with Position Enhanced Structural Information
Hermann Jepdjio Nkouanga, Szilard Vajda
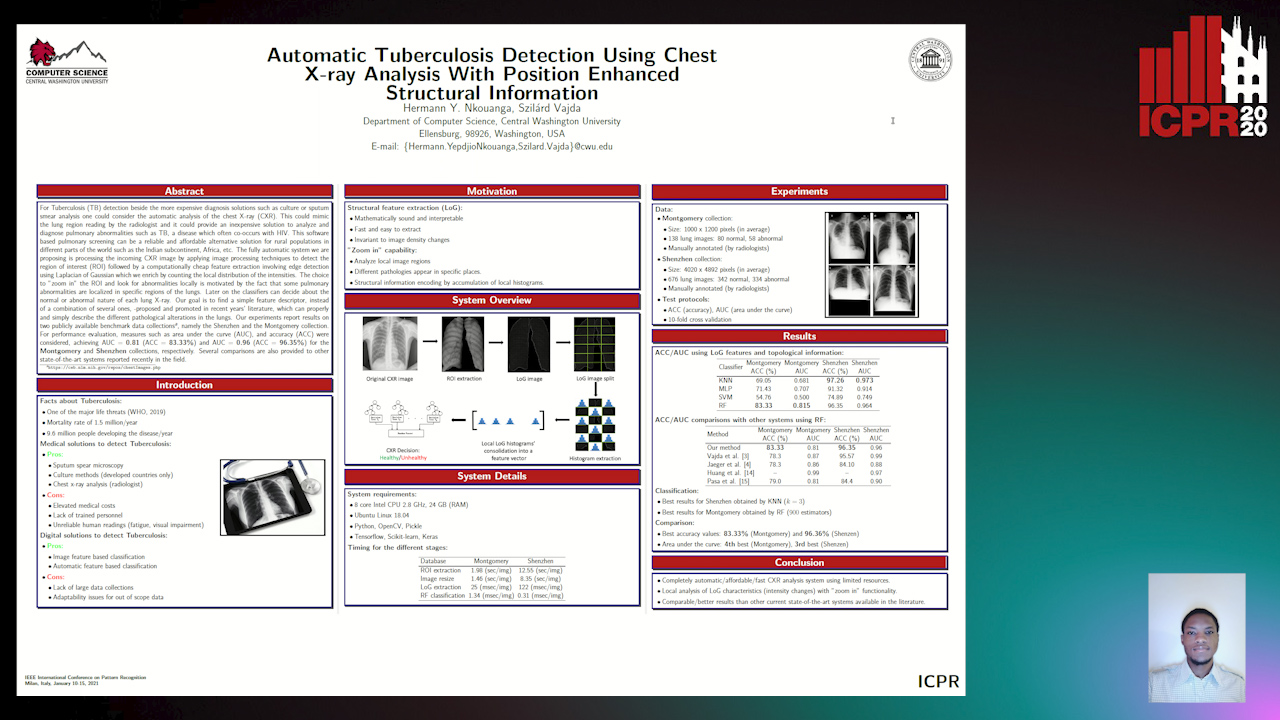
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Chest X-ray Screening for Tuberculosis in Rural Population using Localized Region on Interest
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction by Joint Robust Discriminant Analysis and Inter-Class Sparsity
Auto-TLDR; Robust Discriminant Analysis with Feature Selection and Inter-class Sparsity (RDA_FSIS)
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Region-Adaptive Defogging and Enhancement for Outdoor Images Containing Sky
Zhan Li, Xiaopeng Zheng, Bir Bhanu, Shun Long, Qingfeng Zhang, Zhenghao Huang

Auto-TLDR; Image defogging and enhancement of hazy outdoor scenes using region-adaptive segmentation and region-ratio-based adaptive Gamma correction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Magnifying Spontaneous Facial Micro Expressions for Improved Recognition
Pratikshya Sharma, Sonya Coleman, Pratheepan Yogarajah, Laurence Taggart, Pradeepa Samarasinghe
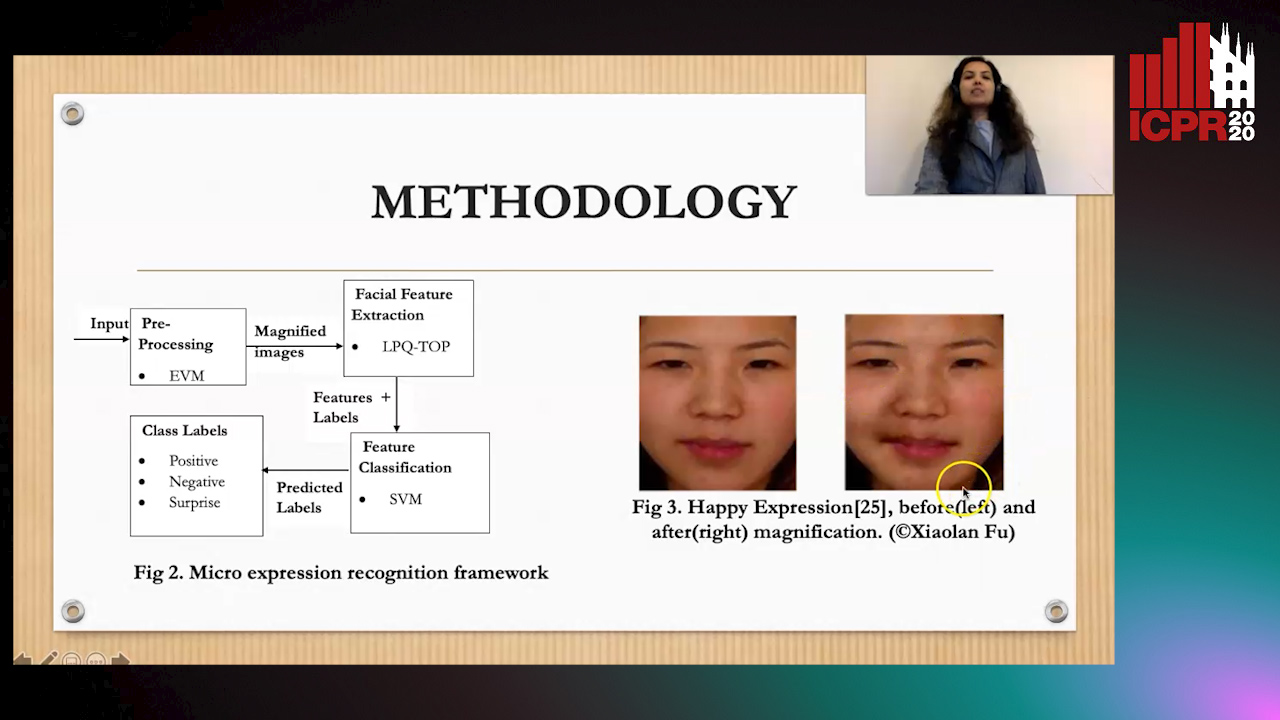
Auto-TLDR; Eulerian Video Magnification for Micro Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scanning Based Recurrent Neural Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Weilian Zhou, Sei-Ichiro Kamata
Auto-TLDR; Spatial-Spectral Unification for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PointSpherical: Deep Shape Context for Point Cloud Learning in Spherical Coordinates
Hua Lin, Bin Fan, Yongcheng Liu, Yirong Yang, Zheng Pan, Jianbo Shi, Chunhong Pan, Huiwen Xie

Auto-TLDR; Spherical Hierarchical Modeling of 3D Point Cloud
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Compressive Autoencoders for Full-Image-To-Image Hiding
Xiyao Liu, Ziping Ma, Xingbei Guo, Jialu Hou, Lei Wang, Gerald Schaefer, Hui Fang

Auto-TLDR; J-CAE: Joint Compressive Autoencoder for Image Hiding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
One Step Clustering Based on A-Contrario Framework for Detection of Alterations in Historical Violins
Alireza Rezaei, Sylvie Le Hégarat-Mascle, Emanuel Aldea, Piercarlo Dondi, Marco Malagodi

Auto-TLDR; A-Contrario Clustering for the Detection of Altered Violins using UVIFL Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Lightening with Dedicated CNN Architecture
Li-Wen Wang, Wan-Chi Siu, Zhi-Song Liu, Chu-Tak Li, P. K. Daniel Lun

Auto-TLDR; VLN: Video Lightening Network for Driving Assistant Systems in Dark Environment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Hybrid Feature Based a Two-Step Fusion for Facial Expression Recognition
Jun Weng, Yang Yang, Zichang Tan, Zhen Lei
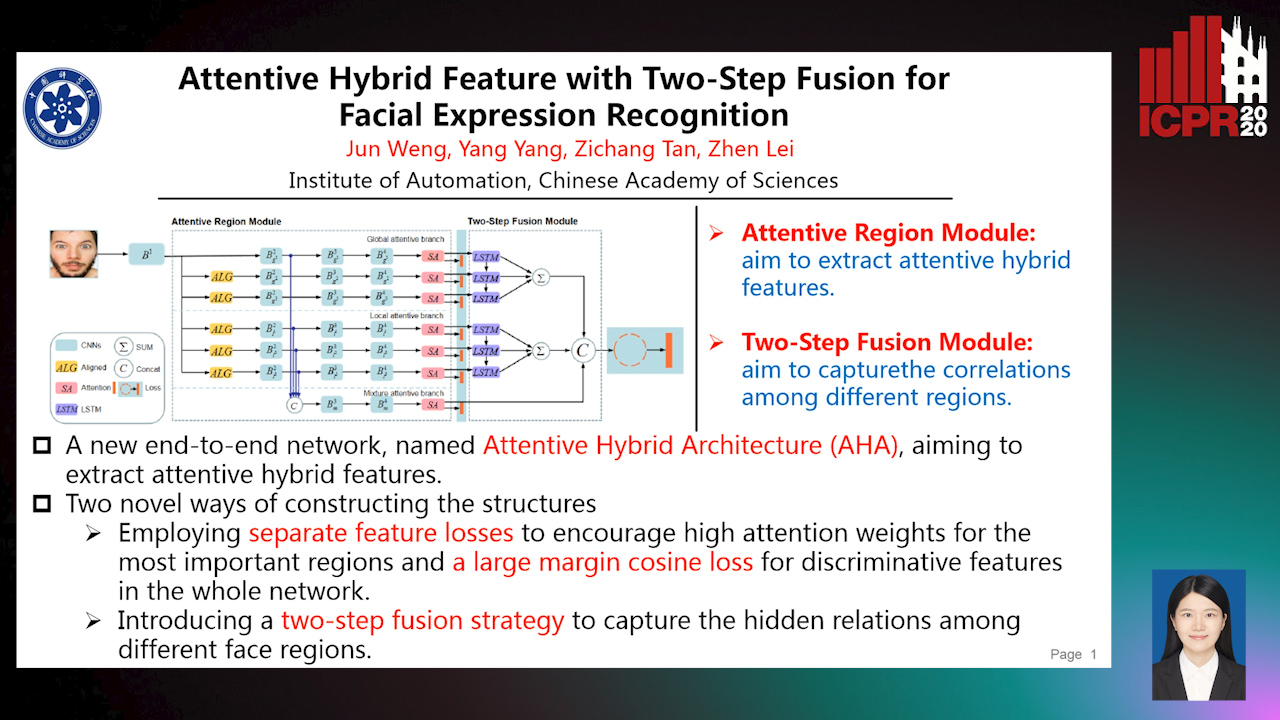
Auto-TLDR; Attentive Hybrid Architecture for Facial Expression Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring the Ability of CNNs to Generalise to Previously Unseen Scales Over Wide Scale Ranges
Auto-TLDR; A theoretical analysis of invariance and covariance properties of scale channel networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction and Selection Via Robust Discriminant Analysis and Class Sparsity

Auto-TLDR; Hybrid Linear Discriminant Embedding for supervised multi-class classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Invariant Aerial Image Retrieval with Group Convolutional Metric Learning
Hyunseung Chung, Woo-Jeoung Nam, Seong-Whan Lee

Auto-TLDR; Robust Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Group Convolution with Attention Mechanism and Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A CNN-RNN Framework for Image Annotation from Visual Cues and Social Network Metadata
Tobia Tesan, Pasquale Coscia, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Image Annotation with Multiple Semantic Embeddings and Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Depth Videos for the Classification of Micro-Expressions
Ankith Jain Rakesh Kumar, Bir Bhanu, Christopher Casey, Sierra Cheung, Aaron Seitz

Auto-TLDR; RGB-D Dataset for the Classification of Facial Micro-expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Extent-Of-Texture Information for Ground Terrain Recognition
Shuvozit Ghose, Pinaki Nath Chowdhury, Partha Pratim Roy, Umapada Pal

Auto-TLDR; Extent-of-Texture Guided Inter-domain Message Passing for Ground Terrain Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Local Indexing and Deep Feature Confidence Scores for Fast Image-To-Video Search
Savas Ozkan, Gözde Bozdağı Akar

Auto-TLDR; Fast and Robust Image-to-Video Retrieval Using Local and Global Descriptors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Force Banner for the Recognition of Spatial Relations
Robin Deléarde, Camille Kurtz, Laurent Wendling, Philippe Dejean

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Relation Recognition using Force Banners
Creating Classifier Ensembles through Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Aerial Scene Classification
Álvaro Roberto Ferreira Jr., Gustavo Gustavo Henrique De Rosa, Joao Paulo Papa, Gustavo Carneiro, Fabio Augusto Faria

Auto-TLDR; Univariate Marginal Distribution Algorithm for Aerial Scene Classification Using Meta-Heuristic Optimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Deep-Learning Pipeline for Light Field Image Based Material Recognition
Yunlong Wang, Kunbo Zhang, Zhenan Sun

Auto-TLDR; Factorize-Connect-Merge Deep Learning Pipeline for Light Field Image Based Material Recognition
A Flatter Loss for Bias Mitigation in Cross-Dataset Facial Age Estimation
Ali Akbari, Muhammad Awais, Zhenhua Feng, Ammarah Farooq, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; Cross-dataset Age Estimation for Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On Morphological Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Caglayan Tuna, Alain Giros, François Merciol, Sébastien Lefèvre

Auto-TLDR; Comparison of Hierarchies for Image Sequences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Deep Hashing for Fast Large Scale Image Retrieval
Yongfei Zhang, Cheng Peng, Zhang Jingtao, Xianglong Liu, Shiliang Pu, Changhuai Chen

Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical indexed deep hashing for fast large scale image retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Surface IR Reflectance Estimation and Material Recognition Using ToF Camera

Auto-TLDR; Material Type Recognition Using IR Reflectance Based Material Type Recognitions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Resource-Aware Corner Detection for Bio-Inspired Vision Sensors
Sherif Abdelmonem Sayed Mohamed, Jawad Yasin, Mohammad-Hashem Haghbayan, Antonio Miele, Jukka Veikko Heikkonen, Hannu Tenhunen, Juha Plosila

Auto-TLDR; Three Layer Filtering-Harris Algorithm for Event-based Cameras in Real-Time
Object Classification of Remote Sensing Images Based on Optimized Projection Supervised Discrete Hashing
Qianqian Zhang, Yazhou Liu, Quansen Sun

Auto-TLDR; Optimized Projection Supervised Discrete Hashing for Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Object Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Based Deep Metric Learning for Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
Kuan-Hsun Wang, Chia Chun Cheng, Yi-Ling Chen, Yale Song, Shang-Hong Lai

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Deep Metric Learning for Near-duplicate Video Retrieval
Documents Counterfeit Detection through a Deep Learning Approach
Darwin Danilo Saire Pilco, Salvatore Tabbone

Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Learning for Counterfeit Documents Detection using Deep Neural Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Writer Identification Using Deep Neural Networks: Impact of Patch Size and Number of Patches
Akshay Punjabi, José Ramón Prieto Fontcuberta, Enrique Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Writer Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks for Handwritten Text Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Single Image Super Resolution

Auto-TLDR; HARTnet: Hierarchically Aggregated Residual Transformation for Multi-Scale Super-resolution
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar