Object Classification of Remote Sensing Images Based on Optimized Projection Supervised Discrete Hashing
Qianqian Zhang,
Yazhou Liu,
Quansen Sun

Auto-TLDR; Optimized Projection Supervised Discrete Hashing for Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Object Classification
Similar papers
Label Self-Adaption Hashing for Image Retrieval
Jianglin Lu, Zhihui Lai, Hailing Wang, Jie Zhou

Auto-TLDR; Label Self-Adaption Hashing for Large-Scale Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Discrete Semantic Matrix Factorization Hashing for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Jianyang Qin, Lunke Fei, Shaohua Teng, Wei Zhang, Genping Zhao, Haoliang Yuan

Auto-TLDR; Discrete Semantic Matrix Factorization Hashing for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Deep Hashing for Fast Large Scale Image Retrieval
Yongfei Zhang, Cheng Peng, Zhang Jingtao, Xianglong Liu, Shiliang Pu, Changhuai Chen

Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical indexed deep hashing for fast large scale image retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
VSB^2-Net: Visual-Semantic Bi-Branch Network for Zero-Shot Hashing
Xin Li, Xiangfeng Wang, Bo Jin, Wenjie Zhang, Jun Wang, Hongyuan Zha
Auto-TLDR; VSB^2-Net: inductive zero-shot hashing for image retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Discrete Cross-Modal Hashing Based on Label Relaxation and Matrix Factorization
Donglin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Zhen Liu, Jun Yu, Josef Kittler

Auto-TLDR; LRMF: Label Relaxation and Discrete Matrix Factorization for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Improved Deep Classwise Hashing with Centers Similarity Learning for Image Retrieval

Auto-TLDR; Deep Classwise Hashing for Image Retrieval Using Center Similarity Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Media Hash Retrieval Using Multi-head Attention Network
Zhixin Li, Feng Ling, Chuansheng Xu, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Cross-Media Hash Retrieval Using Multi-Head Attention Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DFH-GAN: A Deep Face Hashing with Generative Adversarial Network
Bo Xiao, Lanxiang Zhou, Yifei Wang, Qiangfang Xu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Face Hashing with GAN for Face Image Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Leveraging Quadratic Spherical Mutual Information Hashing for Fast Image Retrieval
Nikolaos Passalis, Anastasios Tefas

Auto-TLDR; Quadratic Mutual Information for Large-Scale Hashing and Information Retrieval
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-spectrum Face Recognition Using Subspace Projection Hashing
Hanrui Wang, Xingbo Dong, Jin Zhe, Jean-Luc Dugelay, Massimo Tistarelli

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Projection Hashing for Cross-Spectrum Face Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Joint Learning Multiple Curvature Descriptor for 3D Palmprint Recognition
Lunke Fei, Bob Zhang, Jie Wen, Chunwei Tian, Peng Liu, Shuping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Joint Feature Learning for 3D palmprint recognition using curvature data vectors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Local Indexing and Deep Feature Confidence Scores for Fast Image-To-Video Search
Savas Ozkan, Gözde Bozdağı Akar

Auto-TLDR; Fast and Robust Image-to-Video Retrieval Using Local and Global Descriptors
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Embedding Shared Low-Rank and Feature Correlation for Multi-View Data Analysis
Zhan Wang, Lizhi Wang, Hua Huang

Auto-TLDR; embedding shared low-rank and feature correlation for multi-view data analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Soft Label and Discriminant Embedding Estimation for Semi-Supervised Classification
Fadi Dornaika, Abdullah Baradaaji, Youssof El Traboulsi
Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Semi-Supervised Learning for Linear Feature Extraction and Label Propagation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction by Joint Robust Discriminant Analysis and Inter-Class Sparsity
Auto-TLDR; Robust Discriminant Analysis with Feature Selection and Inter-class Sparsity (RDA_FSIS)
Supporting Skin Lesion Diagnosis with Content-Based Image Retrieval
Stefano Allegretti, Federico Bolelli, Federico Pollastri, Sabrina Longhitano, Giovanni Pellacani, Costantino Grana

Auto-TLDR; Skin Images Retrieval Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Skin Lesion Classification and Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Subspace Clustering Via Joint Unsupervised Feature Selection
Wenhua Dong, Xiaojun Wu, Hui Li, Zhenhua Feng, Josef Kittler
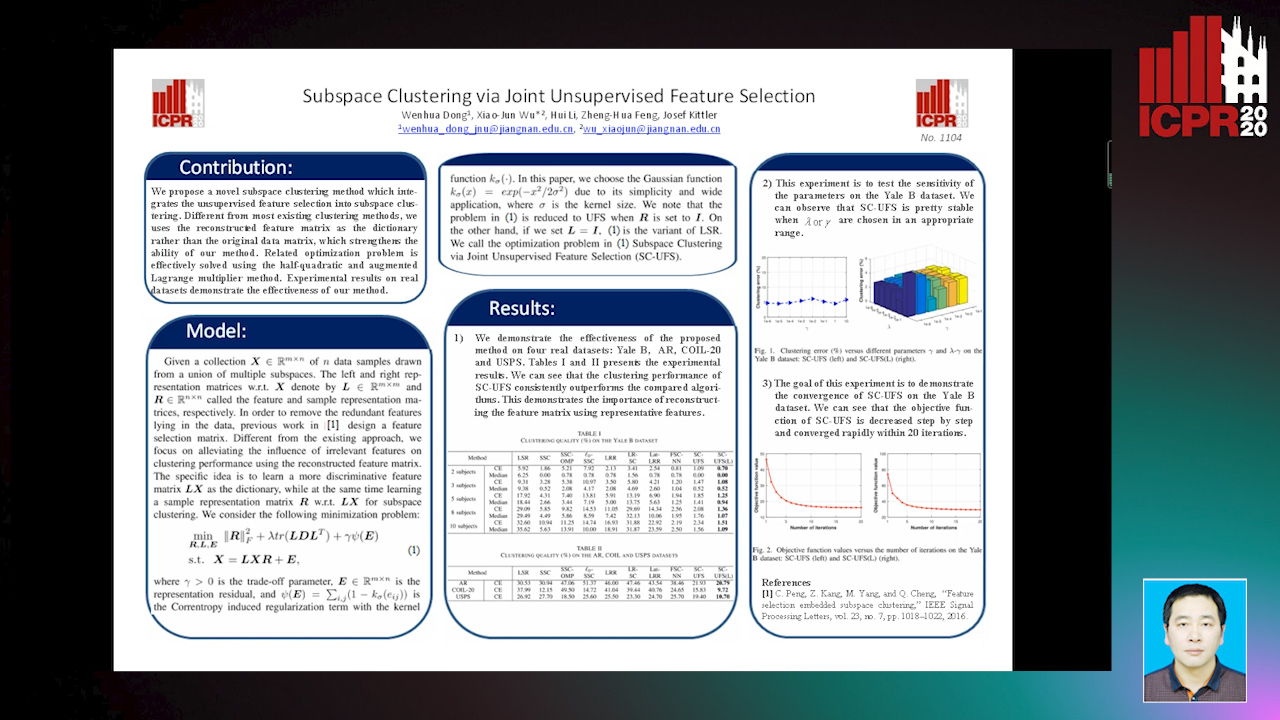
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Feature Selection for Subspace Clustering
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
Tensorized Feature Spaces for Feature Explosion
Ravdeep Pasricha, Pravallika Devineni, Evangelos Papalexakis, Ramakrishnan Kannan
Auto-TLDR; Tensor Rank Decomposition for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Composer: A Hash-Based Duplicative Neural Network for Generating Multi-Instrument Songs
Jacob Galajda, Brandon Royal, Kien Hua

Auto-TLDR; Deep Composer for Intelligence Duplication
Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Ratio of Edge-User Estimation in Mobile Networks
Jiehui Deng, Sheng Wan, Xiang Wang, Enmei Tu, Xiaolin Huang, Jie Yang, Chen Gong

Auto-TLDR; EAGAT: Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Automatic REU Estimation in Mobile Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Creating Classifier Ensembles through Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Aerial Scene Classification
Álvaro Roberto Ferreira Jr., Gustavo Gustavo Henrique De Rosa, Joao Paulo Papa, Gustavo Carneiro, Fabio Augusto Faria

Auto-TLDR; Univariate Marginal Distribution Algorithm for Aerial Scene Classification Using Meta-Heuristic Optimization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Carlos Roig Mari, David Varas, Issey Masuda, Juan Carlos Riveiro, Elisenda Bou-Balust

Auto-TLDR; Generalized Local Attention Pooling for Deep Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Extraction and Selection Via Robust Discriminant Analysis and Class Sparsity

Auto-TLDR; Hybrid Linear Discriminant Embedding for supervised multi-class classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Color Out of Space: Learning Self-Supervised Representations for Earth Observation Imagery
Stefano Vincenzi, Angelo Porrello, Pietro Buzzega, Marco Cipriano, Pietro Fronte, Roberto Cuccu, Carla Ippoliti, Annamaria Conte, Simone Calderara

Auto-TLDR; Satellite Image Representation Learning for Remote Sensing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RGB-Infrared Person Re-Identification Via Image Modality Conversion
Huangpeng Dai, Qing Xie, Yanchun Ma, Yongjian Liu, Shengwu Xiong

Auto-TLDR; CE2L: A Novel Network for Cross-Modality Re-identification with Feature Alignment
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semantic Bilinear Pooling for Fine-Grained Recognition
Xinjie Li, Chun Yang, Song-Lu Chen, Chao Zhu, Xu-Cheng Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantic bilinear pooling for fine-grained recognition with hierarchical label tree
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature-Aware Unsupervised Learning with Joint Variational Attention and Automatic Clustering
Wang Ru, Lin Li, Peipei Wang, Liu Peiyu

Auto-TLDR; Deep Variational Attention Encoder-Decoder for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotation Invariant Aerial Image Retrieval with Group Convolutional Metric Learning
Hyunseung Chung, Woo-Jeoung Nam, Seong-Whan Lee

Auto-TLDR; Robust Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Group Convolution with Attention Mechanism and Metric Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
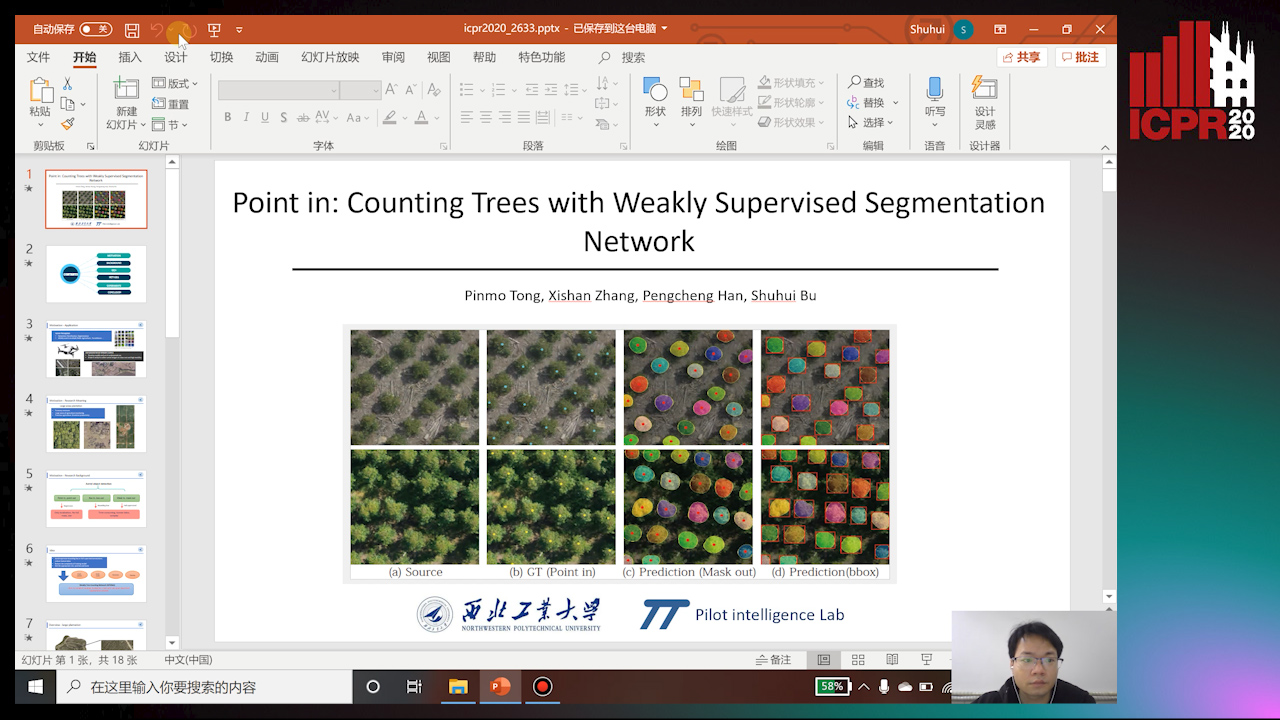
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sign-Constrained Support Vector Machines
Kenya Tajima, Kouhei Tsuchida, Esmeraldo Ronnie Rey Zara, Naoya Ohta, Tsuyoshi Kato
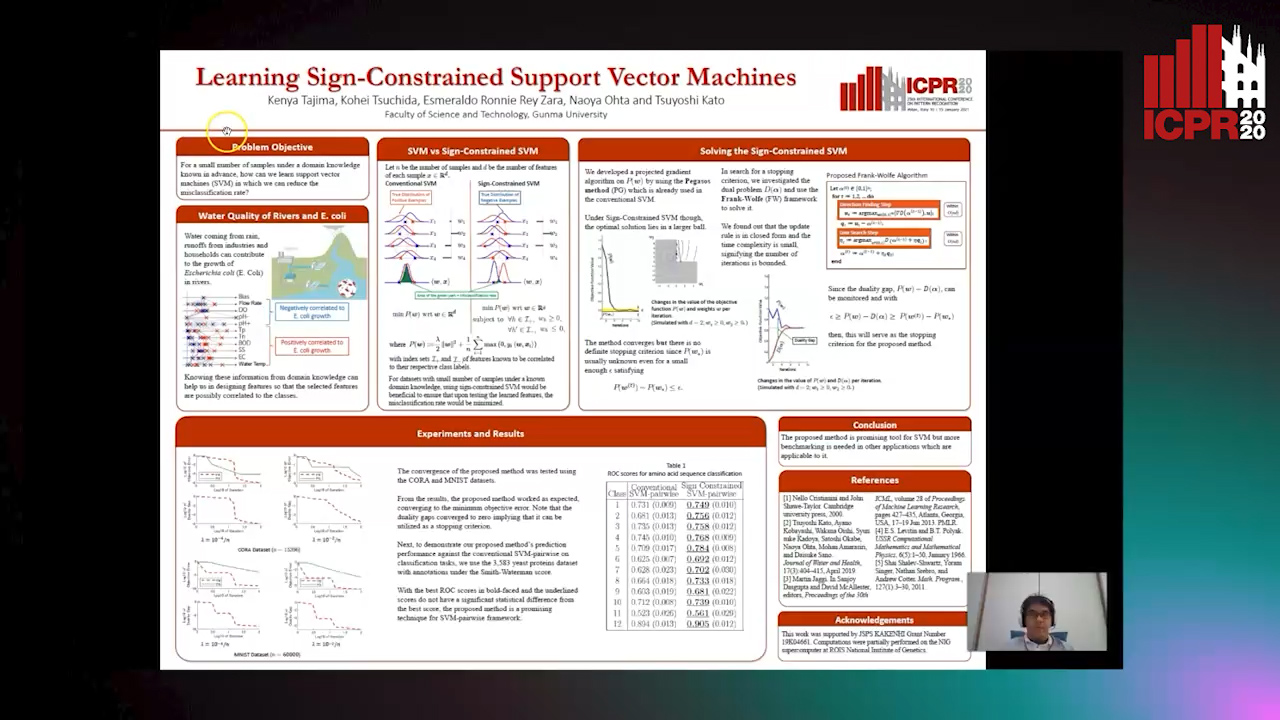
Auto-TLDR; Constrained Sign Constraints for Learning Linear Support Vector Machine
A Spectral Clustering on Grassmann Manifold Via Double Low Rank Constraint
Xinglin Piao, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Xin Yang, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Double Low Rank Representation for High-Dimensional Data Clustering on Grassmann Manifold
Classification and Feature Selection Using a Primal-Dual Method and Projections on Structured Constraints
Michel Barlaud, Antonin Chambolle, Jean_Baptiste Caillau

Auto-TLDR; A Constrained Primal-dual Method for Structured Feature Selection on High Dimensional Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constrained Spectral Clustering Network with Self-Training
Xinyue Liu, Shichong Yang, Linlin Zong

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Spectral Clustering Network: A Constrained Deep spectral clustering network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fast Subspace Clustering Based on the Kronecker Product
Lei Zhou, Xiao Bai, Liang Zhang, Jun Zhou, Edwin Hancock

Auto-TLDR; Subspace Clustering with Kronecker Product for Large Scale Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Label Contrastive Focal Loss for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Xiaoqiang Zheng, Zhenxia Yu, Lin Chen, Fan Zhu, Shilong Wang

Auto-TLDR; Multi-label Contrastive Focal Loss for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Level Deep Learning Vehicle Re-Identification Using Ranked-Based Loss Functions
Eleni Kamenou, Jesus Martinez-Del-Rincon, Paul Miller, Patricia Devlin - Hill
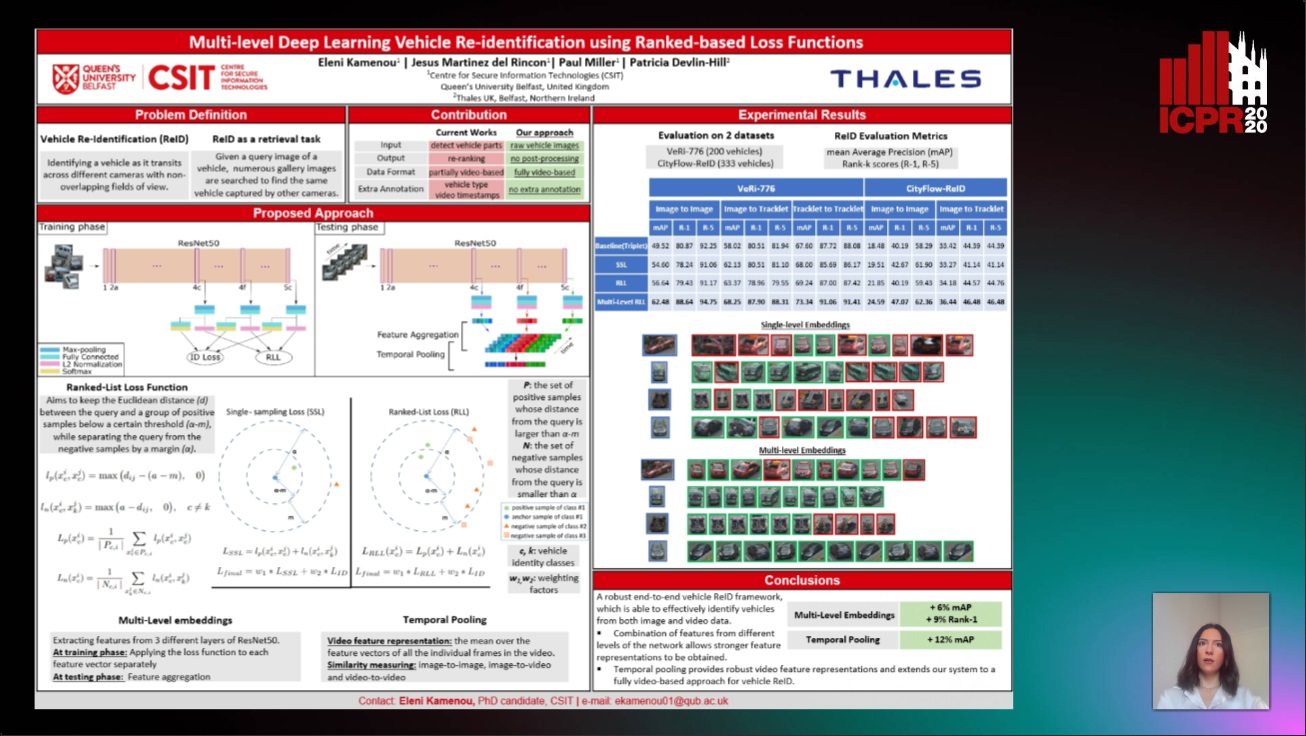
Auto-TLDR; Multi-Level Re-identification Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Sparse Deep Neural Networks Using Efficient Structured Projections on Convex Constraints for Green AI
Michel Barlaud, Frederic Guyard

Auto-TLDR; Constrained Deep Neural Network with Constrained Splitting Projection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Aggregating Object Features Based on Attention Weights for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Hongli Lin, Yongqi Song, Zixuan Zeng, Weisheng Wang

Auto-TLDR; DSAW: Unsupervised Dual-selection for Fine-Grained Image Retrieval
Adaptive Matching of Kernel Means
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Matching of Kernel Means for Knowledge Discovery and Feature Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Double Manifolds Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization for Data Representation
Jipeng Guo, Shuai Yin, Yanfeng Sun, Yongli Hu

Auto-TLDR; Double Manifolds Regularized Non-negative Matrix Factorization for Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A General Model for Learning Node and Graph Representations Jointly
Auto-TLDR; Joint Community Detection/Dynamic Routing for Graph Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Tackling Multi-Label Imbalances in Remote Sensing Imagery
Dominik Koßmann, Thorsten Wilhelm, Gernot Fink

Auto-TLDR; Class imbalance in land cover datasets using attribute encoding schemes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Machine-Learned Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation Masks
Stefano Zorzi, Ksenia Bittner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation masks using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Gait Relative Attribute Using a Signed Quadratic Contrastive Loss
Yuta Hayashi, Shehata Allam, Yasushi Makihara, Daigo Muramatsu, Yasushi Yagi

Auto-TLDR; Signal-Contrastive Loss for Gait Attributes Estimation