Automatically Gather Address Specific Dwelling Images Using Google Street View

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Address Specific Dwelling Image Collection Using Google Street View Data
Similar papers
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
End-To-End Deep Learning Methods for Automated Damage Detection in Extreme Events at Various Scales
Yongsheng Bai, Alper Yilmaz, Halil Sezen

Auto-TLDR; Robust Mask R-CNN for Crack Detection in Extreme Events
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
EAGLE: Large-Scale Vehicle Detection Dataset in Real-World Scenarios Using Aerial Imagery
Seyed Majid Azimi, Reza Bahmanyar, Corentin Henry, Kurz Franz

Auto-TLDR; EAGLE: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multi-class Vehicle Detection with Object Orientation Information in Airborne Imagery
Derivation of Geometrically and Semantically Annotated UAV Datasets at Large Scales from 3D City Models
Sidi Wu, Lukas Liebel, Marco Körner
Auto-TLDR; Large-Scale Dataset of Synthetic UAV Imagery for Geometric and Semantic Annotation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression by Learning Feature Embeddings

Auto-TLDR; FeatureNMS: Non-Maximum Suppression for Multiple Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-View Object Detection Using Epipolar Constraints within Cluttered X-Ray Security Imagery
Brian Kostadinov Shalon Isaac-Medina, Chris G. Willcocks, Toby Breckon
Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Epipolar Constraints for Multi-View Object Detection in X-ray Security Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CASNet: Common Attribute Support Network for Image Instance and Panoptic Segmentation
Xiaolong Liu, Yuqing Hou, Anbang Yao, Yurong Chen, Keqiang Li

Auto-TLDR; Common Attribute Support Network for instance segmentation and panoptic segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
A Fine-Grained Dataset and Its Efficient Semantic Segmentation for Unstructured Driving Scenarios
Kai Andreas Metzger, Peter Mortimer, Hans J "Joe" Wuensche

Auto-TLDR; TAS500: A Semantic Segmentation Dataset for Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Localization for Autonomous Driving: Mapping the Accurate Location in the City Maze
Dongfang Liu, Yiming Cui, Xiaolei Guo, Wei Ding, Baijian Yang, Yingjie Chen

Auto-TLDR; Feature Voting for Robust Visual Localization in Urban Settings
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DualBox: Generating BBox Pair with Strong Correspondence Via Occlusion Pattern Clustering and Proposal Refinement
Zheng Ge, Chuyu Hu, Xin Huang, Baiqiao Qiu, Osamu Yoshie

Auto-TLDR; R2NMS: Combining Full and Visible Body Bounding Box for Dense Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Point In: Counting Trees with Weakly Supervised Segmentation Network
Pinmo Tong, Shuhui Bu, Pengcheng Han
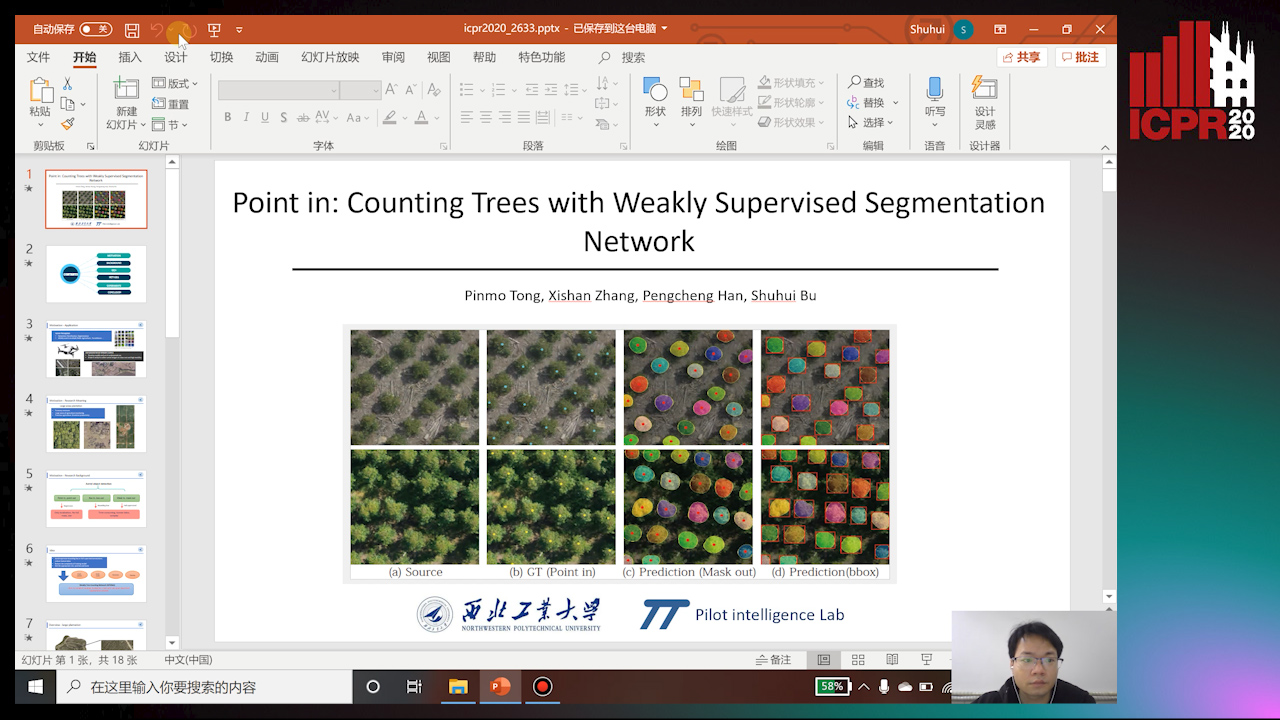
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Tree counting using Deep Segmentation Network with Localization and Mask Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Street-Map Based Validation of Semantic Segmentation in Autonomous Driving
Laura Von Rueden, Tim Wirtz, Fabian Hueger, Jan David Schneider, Nico Piatkowski, Christian Bauckhage

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation Mask Validation Using A-priori Knowledge from Street Maps
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RescueNet: Joint Building Segmentation and Damage Assessment from Satellite Imagery
Auto-TLDR; RescueNet: End-to-End Building Segmentation and Damage Classification for Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Response
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CDeC-Net: Composite Deformable Cascade Network for Table Detection in Document Images
Madhav Agarwal, Ajoy Mondal, C. V. Jawahar

Auto-TLDR; CDeC-Net: An End-to-End Trainable Deep Network for Detecting Tables in Document Images
Machine-Learned Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation Masks
Stefano Zorzi, Ksenia Bittner, Friedrich Fraundorfer

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Regularization and Polygonization of Building Segmentation masks using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
ACRM: Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix-NMS for Metallic Surface Defect Detection
Junting Fang, Xiaoyang Tan, Yuhui Wang

Auto-TLDR; Attention Cascade R-CNN with Mix Non-Maximum Suppression for Robust Metal Defect Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Vision-Based Layout Detection from Scientific Literature Using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Scientific Literature Layout Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Polarimetric Image Augmentation
Marc Blanchon, Fabrice Meriaudeau, Olivier Morel, Ralph Seulin, Desire Sidibe
Auto-TLDR; Polarimetric Augmentation for Deep Learning in Robotics Applications
A Novel Disaster Image Data-Set and Characteristics Analysis Using Attention Model
Fahim Faisal Niloy, Arif ., Abu Bakar Siddik Nayem, Anis Sarker, Ovi Paul, M Ashraful Amin, Amin Ahsan Ali, Moinul Islam Zaber, Akmmahbubur Rahman

Auto-TLDR; Attentive Attention Model for Disaster Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
IPT: A Dataset for Identity Preserved Tracking in Closed Domains
Thomas Heitzinger, Martin Kampel
Auto-TLDR; Identity Preserved Tracking Using Depth Data for Privacy and Privacy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Uncertainty Guided Recognition of Tiny Craters on the Moon
Thorsten Wilhelm, Christian Wöhler
Auto-TLDR; Accurately Detecting Tiny Craters in Remote Sensed Images Using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
An Integrated Approach of Deep Learning and Symbolic Analysis for Digital PDF Table Extraction
Mengshi Zhang, Daniel Perelman, Vu Le, Sumit Gulwani
Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning and Symbolic Reasoning for Unstructured PDF Table Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detective: An Attentive Recurrent Model for Sparse Object Detection
Amine Kechaou, Manuel Martinez, Monica Haurilet, Rainer Stiefelhagen

Auto-TLDR; Detective: An attentive object detector that identifies objects in images in a sequential manner
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Planar 3D Transfer Learning for End to End Unimodal MRI Unbalanced Data Segmentation
Martin Kolarik, Radim Burget, Carlos M. Travieso-Gonzalez, Jan Kocica

Auto-TLDR; Planar 3D Res-U-Net Network for Unbalanced 3D Image Segmentation using Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recover
Attention Based Coupled Framework for Road and Pothole Segmentation
Shaik Masihullah, Ritu Garg, Prerana Mukherjee, Anupama Ray
Auto-TLDR; Few Shot Learning for Road and Pothole Segmentation on KITTI and IDD
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
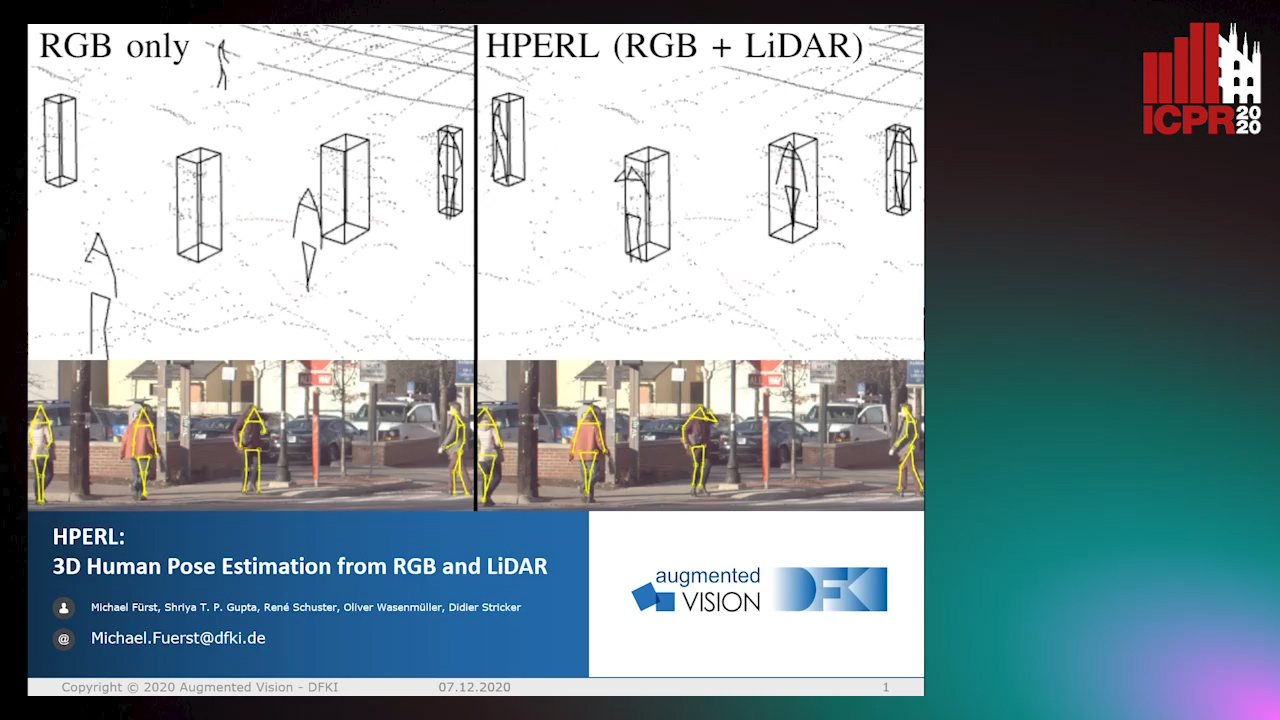
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Triplet-Path Dilated Network for Detection and Segmentation of General Pathological Images
Jiaqi Luo, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su, Limei Guo

Auto-TLDR; Triplet-path Network for One-Stage Object Detection and Segmentation in Pathological Images
The DeepScoresV2 Dataset and Benchmark for Music Object Detection
Lukas Tuggener, Yvan Putra Satyawan, Alexander Pacha, Jürgen Schmidhuber, Thilo Stadelmann

Auto-TLDR; DeepScoresV2: an extended version of the DeepScores dataset for optical music recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Abundance and Distribution of SaltMarsh Plants from Images Using Deep Learning
Jayant Parashar, Suchendra Bhandarkar, Jacob Simon, Brian Hopkinson, Steven Pennings
Auto-TLDR; CNN-based approaches to automated plant identification and localization in salt marsh images
Hierarchical Head Design for Object Detectors
Shivang Agarwal, Frederic Jurie
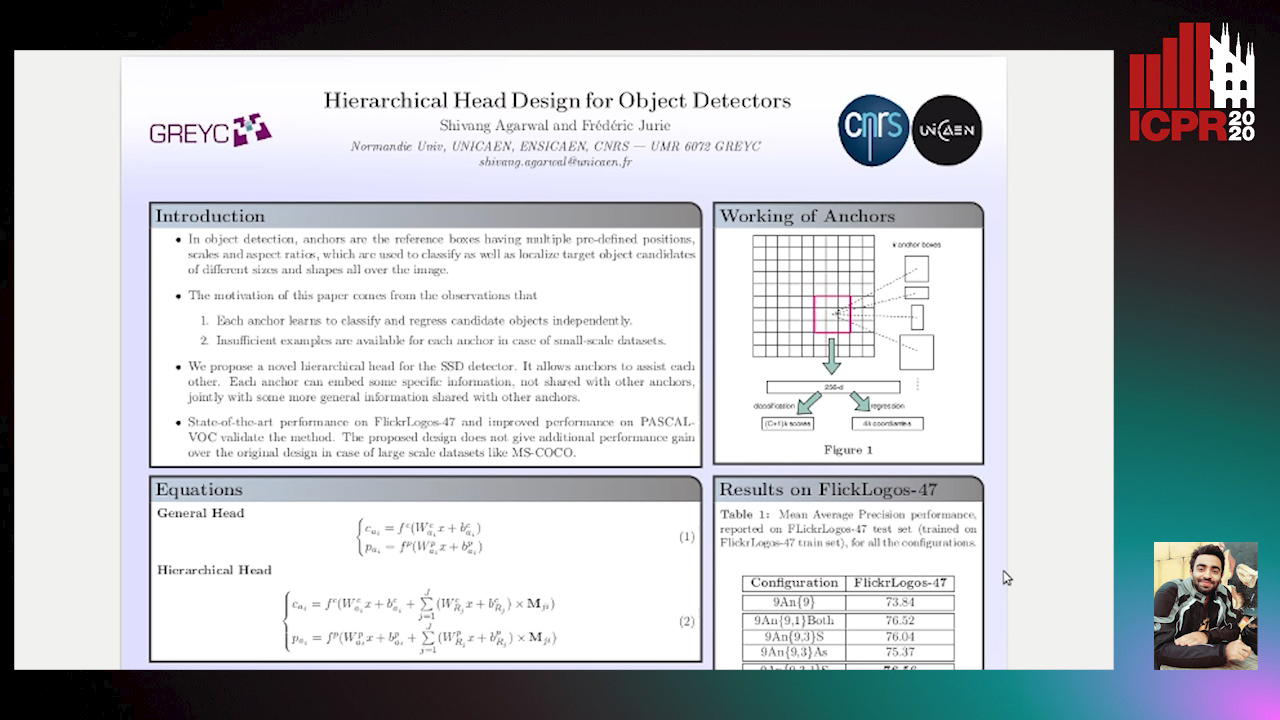
Auto-TLDR; Hierarchical Anchor for SSD Detector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
StrongPose: Bottom-up and Strong Keypoint Heat Map Based Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; StrongPose: A bottom-up box-free approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Walk the Lines: Object Contour Tracing CNN for Contour Completion of Ships

Auto-TLDR; Walk the Lines: A Convolutional Neural Network trained to follow object contours
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TGCRBNW: A Dataset for Runner Bib Number Detection (and Recognition) in the Wild
Pablo Hernández-Carrascosa, Adrian Penate-Sanchez, Javier Lorenzo, David Freire Obregón, Modesto Castrillon

Auto-TLDR; Racing Bib Number Detection and Recognition in the Wild Using Faster R-CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
3D Semantic Labeling of Photogrammetry Meshes Based on Active Learning
Mengqi Rong, Shuhan Shen, Zhanyi Hu

Auto-TLDR; 3D Semantic Expression of Urban Scenes Based on Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Dayang Yu, Rong Zhang, Shan Qin

Auto-TLDR; Cascade Saliency Attention Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Marine Species in Echograms Via Traditional, Hybrid, and Deep Learning Frameworks
Porto Marques Tunai, Alireza Rezvanifar, Melissa Cote, Alexandra Branzan Albu, Kaan Ersahin, Todd Mudge, Stephane Gauthier
Auto-TLDR; End-to-End Deep Learning for Echogram Interpretation of Marine Species in Echograms
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Complex-Object Visual Inspection: Empirical Studies on a Multiple Lighting Solution
Maya Aghaei, Matteo Bustreo, Pietro Morerio, Nicolò Carissimi, Alessio Del Bue, Vittorio Murino

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Illumination Setup for Automatic Visual Inspection of Complex Objects
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Text Recognition - Real World Data and Where to Find Them
Klára Janoušková, Lluis Gomez, Dimosthenis Karatzas, Jiri Matas

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Weakly Annotated Images for Text Extraction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Detection and Pose Estimation of Logistical Objects in 3D Sensor Data
Nikolas Müller, Jonas Stenzel, Jian-Jia Chen

Auto-TLDR; A self-supervised and fully automated deep learning approach for object pose estimation using simulated 3D data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar