Extracting and Interpreting Unknown Factors with Classifier for Foot Strike Types in Running
Chanjin Seo,
Masato Sabanai,
Yuta Goto,
Koji Tagami,
Hiroyuki Ogata,
Kazuyuki Kanosue,
Jun Ohya

Auto-TLDR; Deep Learning for Foot Strike Classification using Accelerometer Data
Similar papers
Gender Classification Using Video Sequences of Body Sway Recorded by Overhead Camera
Takuya Kamitani, Yuta Yamaguchi, Shintaro Nakatani, Masashi Nishiyama, Yoshio Iwai

Auto-TLDR; Spatio-Temporal Feature for Gender Classification of a Standing Person Using Body Stance Using Time-Series Signals
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Conditional-UNet: A Condition-Aware Deep Model for Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Wearables
Liming Zhang, Wenbin Zhang, Nathalie Japkowicz

Auto-TLDR; Coherent Human Activity Recognition from Multi-Channel Time Series Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Analytics Gait Trend Measurement for Fall Prevention and Health Monitoring
Lawrence O'Gorman, Xinyi Liu, Md Imran Sarker, Mariofanna Milanova

Auto-TLDR; Towards Health Monitoring of Gait with Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hierarchical Multimodal Attention for Deep Video Summarization
Melissa Sanabria, Frederic Precioso, Thomas Menguy

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Summarization of Professional Soccer Matches Using Event-Stream Data and Multi- Instance Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
From Human Pose to On-Body Devices for Human-Activity Recognition
Fernando Moya Rueda, Gernot Fink
Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning from Human Pose Estimation for Human Activity Recognition using Inertial Measurements from On-Body Devices
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Gait Relative Attribute Using a Signed Quadratic Contrastive Loss
Yuta Hayashi, Shehata Allam, Yasushi Makihara, Daigo Muramatsu, Yasushi Yagi

Auto-TLDR; Signal-Contrastive Loss for Gait Attributes Estimation
Location Prediction in Real Homes of Older Adults based on K-Means in Low-Resolution Depth Videos
Simon Simonsson, Flávia Dias Casagrande, Evi Zouganeli

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Learning for Location Recognition and Prediction in Smart Homes using Depth Video Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rotational Adjoint Methods for Learning-Free 3D Human Pose Estimation from IMU Data
Caterina Emilia Agelide Buizza, Yiannis Demiris
Auto-TLDR; Learning-free 3D Human Pose Estimation from Inertial Measurement Unit Data
Learning Dictionaries of Kinematic Primitives for Action Classification
Alessia Vignolo, Nicoletta Noceti, Alessandra Sciutti, Francesca Odone, Giulio Sandini

Auto-TLDR; Action Understanding using Visual Motion Primitives
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real Time Fencing Move Classification and Detection at Touch Time During a Fencing Match
Cem Ekin Sunal, Chris G. Willcocks, Boguslaw Obara

Auto-TLDR; Fencing Body Move Classification and Detection Using Deep Learning
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Toward Building a Data-Driven System ForDetecting Mounting Actions of Black Beef Cattle
Yuriko Kawano, Susumu Saito, Nakano Teppei, Ikumi Kondo, Ryota Yamazaki, Hiromi Kusaka, Minoru Sakaguchi, Tetsuji Ogawa

Auto-TLDR; Cattle Mounting Action Detection Using Crowdsourcing and Pattern Recognition
Personalized Models in Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning
Hamza Amrani, Daniela Micucci, Paolo Napoletano

Auto-TLDR; Incremental Learning for Personalized Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Detection-Based Approach to Multiview Action Classification in Infants
Carolina Pacheco, Effrosyni Mavroudi, Elena Kokkoni, Herbert Tanner, Rene Vidal

Auto-TLDR; Multiview Action Classification for Infants in a Pediatric Rehabilitation Environment
Electroencephalography Signal Processing Based on Textural Features for Monitoring the Driver’s State by a Brain-Computer Interface
Giulia Orrù, Marco Micheletto, Fabio Terranova, Gian Luca Marcialis

Auto-TLDR; One-dimensional Local Binary Pattern Algorithm for Estimating Driver Vigilance in a Brain-Computer Interface System
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Space-Time Domain Tensor Neural Networks: An Application on Human Pose Classification
Konstantinos Makantasis, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Nikolaos Doulamis, Nikolaos Bakalos

Auto-TLDR; Tensor-Based Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Pose Classifiaction using Three-Dimensional Skeleton Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anticipating Activity from Multimodal Signals
Tiziana Rotondo, Giovanni Maria Farinella, Davide Giacalone, Sebastiano Mauro Strano, Valeria Tomaselli, Sebastiano Battiato

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Multimodal Signal Embedding Space for Multi-Action Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Pose-Based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation
Zhengyuan Yang, Amanda Kay, Yuncheng Li, Wendi Cross, Jiebo Luo

Auto-TLDR; Body Language Based Emotion Recognition for Psychiatric Symptoms Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Accurate Background Subtraction Using Dynamic Object Presence Probability in Sports Scenes
Ryosuke Watanabe, Jun Chen, Tomoaki Konno, Sei Naito
Auto-TLDR; DOPP: Dynamic Object Presence Probabilistic Background Subtraction for Foreground Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Anomalies from Video-Sequences: A Novel Descriptor
Giulia Orrù, Davide Ghiani, Maura Pintor, Gian Luca Marcialis, Fabio Roli

Auto-TLDR; Trit-based Measurement of Group Dynamics for Crowd Behavior Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Extraction and Analysis of 3D Kinematic Parameters of Table Tennis Ball from a Single Camera
Jordan Calandre, Renaud Péteri, Laurent Mascarilla, Benoit Tremblais
Auto-TLDR; 3D Ball Trajectories Analysis using a Single Camera for Sport Gesture Analysis
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
InsideBias: Measuring Bias in Deep Networks and Application to Face Gender Biometrics
Ignacio Serna, Alejandro Peña Almansa, Aythami Morales, Julian Fierrez
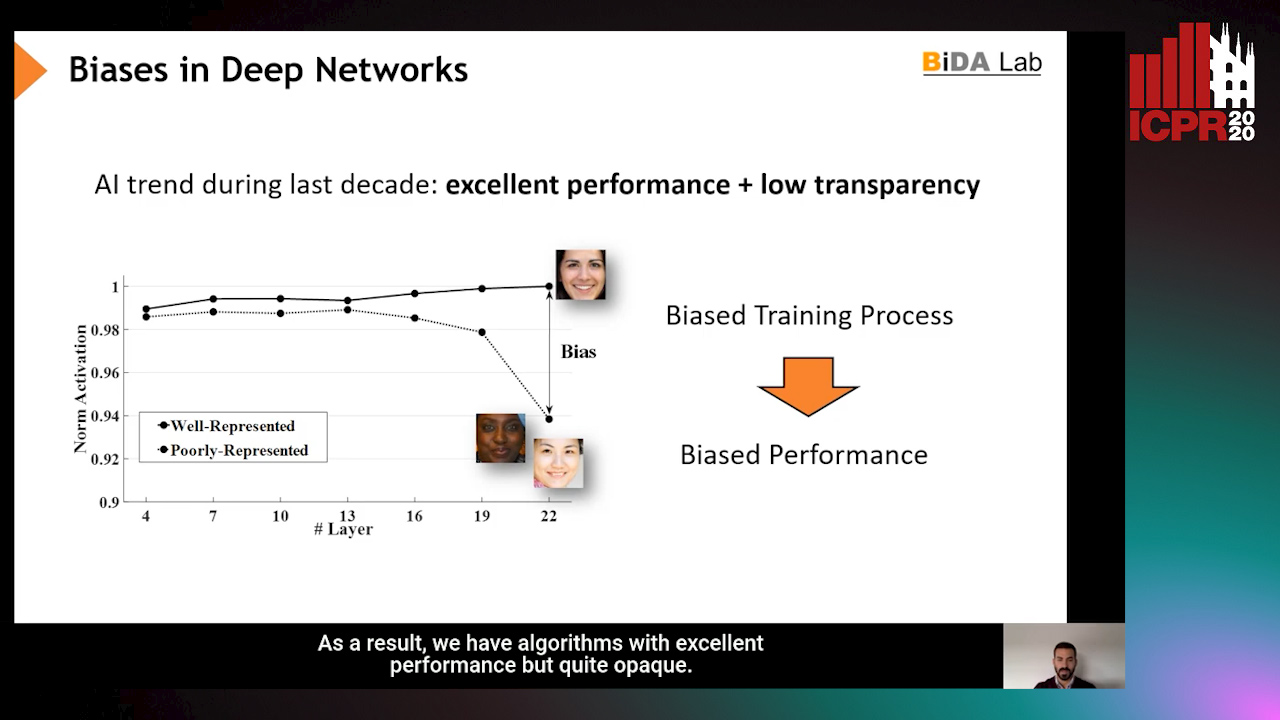
Auto-TLDR; InsideBias: Detecting Bias in Deep Neural Networks from Face Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fall Detection by Human Pose Estimation and Kinematic Theory
Vincenzo Dentamaro, Donato Impedovo, Giuseppe Pirlo

Auto-TLDR; A Decision Support System for Automatic Fall Detection on Le2i and URFD Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LFIR2Pose: Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution FIR Image Sequence
Saki Iwata, Yasutomo Kawanishi, Daisuke Deguchi, Ichiro Ide, Hiroshi Murase, Tomoyoshi Aizawa
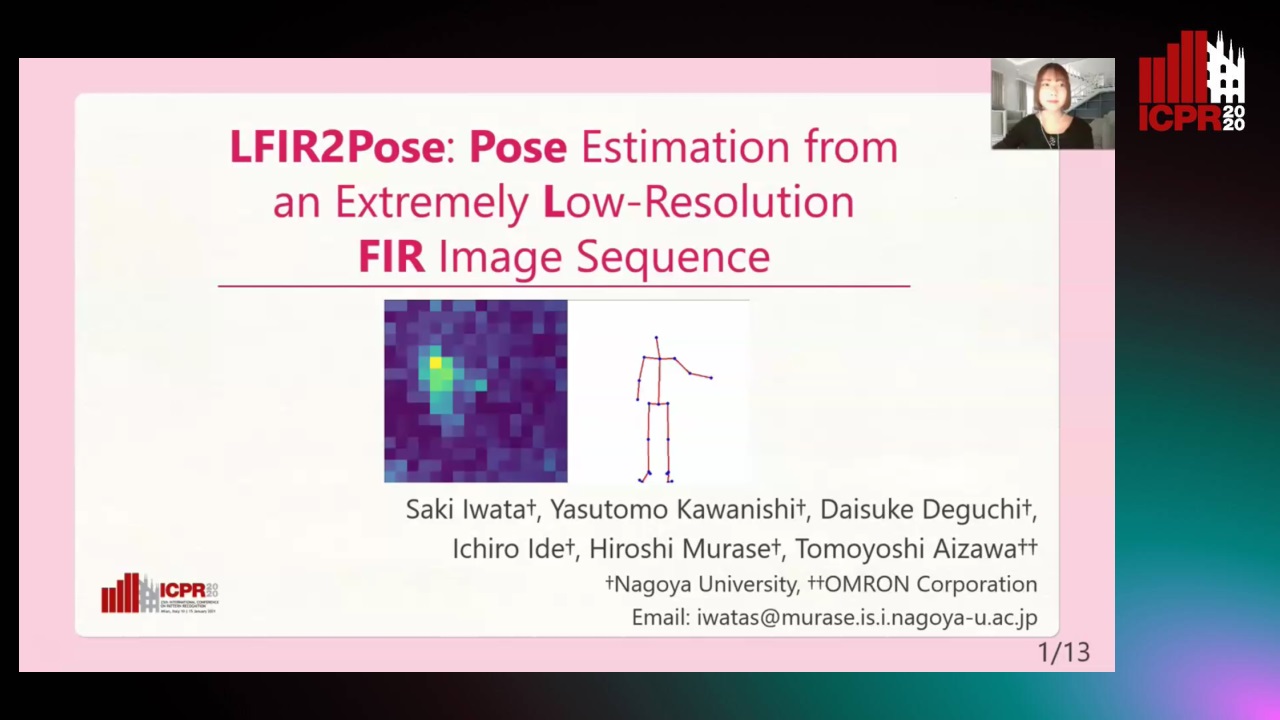
Auto-TLDR; LFIR2Pose: Human Pose Estimation from a Low-Resolution Far-InfraRed Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Surface Material Dataset for Robotics Applications (SMDRA): A Dataset with Friction Coefficient and RGB-D for Surface Segmentation
Donghun Noh, Hyunwoo Nam, Min Sung Ahn, Hosik Chae, Sangjoon Lee, Kyle Gillespie, Dennis Hong
Auto-TLDR; A Surface Material Dataset for Robotics Applications
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RMS-Net: Regression and Masking for Soccer Event Spotting
Matteo Tomei, Lorenzo Baraldi, Simone Calderara, Simone Bronzin, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; An Action Spotting Network for Soccer Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single-Modal Incremental Terrain Clustering from Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Feature Learning
Reina Ishikawa, Ryo Hachiuma, Akiyoshi Kurobe, Hideo Saito

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Variational Autoencoder for Terrain Type Clustering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Clinical Tremor Using Spatio-Temporal Adversarial AutoEncoder
Li Zhang, Vidya Koesmahargyo, Isaac Galatzer-Levy

Auto-TLDR; ST-AAE: Spatio-temporal Adversarial Autoencoder for Clinical Assessment of Hand Tremor Frequency and Severity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Anomaly Detection, Localization and Classification for Railway Inspection
Riccardo Gasparini, Andrea D'Eusanio, Guido Borghi, Stefano Pini, Giuseppe Scaglione, Simone Calderara, Eugenio Fedeli, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Anomaly Detection and Localization using thermal images in the lowlight environment
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JT-MGCN: Joint-Temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition

Auto-TLDR; Joint-temporal Motion Graph Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition
Part-Based Collaborative Spatio-Temporal Feature Learning for Cloth-Changing Gait Recognition
Lingxiang Yao, Worapan Kusakunniran, Qiang Wu, Jian Zhang, Jingsong Xu

Auto-TLDR; Part-based Spatio-Temporal Feature Learning for Gait Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Feature Representation Learning for Calving Detection of Cows Using Video Frames
Ryosuke Hyodo, Nakano Teppei, Tetsuji Ogawa

Auto-TLDR; Data-driven Feature Extraction for Calving Sign Detection Using Surveillance Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Automatic Classification of Human Granulosa Cells in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Vibrational Spectroscopy Imaging
Marina Paolanti, Emanuele Frontoni, Giorgia Gioacchini, Giorgini Elisabetta, Notarstefano Valentina, Zacà Carlotta, Carnevali Oliana, Andrea Borini, Marco Mameli

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Oocyte Quality in Assisted Reproductive Technology Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Developing Motion Code Embedding for Action Recognition in Videos
Maxat Alibayev, David Andrea Paulius, Yu Sun
Auto-TLDR; Motion Embedding via Motion Codes for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Sequence Based Cyclist Action Recognition Using Multi-Stream 3D Convolution
Stefan Zernetsch, Steven Schreck, Viktor Kress, Konrad Doll, Bernhard Sick
Auto-TLDR; 3D-ConvNet: A Multi-stream 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Cyclists in Real World Traffic Situations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Reinforcement Learning Lead to Healthy Life?: Simulation Study Based on User Activity Logs
Masami Takahashi, Masahiro Kohjima, Takeshi Kurashima, Hiroyuki Toda

Auto-TLDR; Reinforcement Learning for Healthy Daily Life
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Siamese-Structure Deep Neural Network Recognizing Changes in Facial Expression According to the Degree of Smiling
Kazuaki Kondo, Taichi Nakamura, Yuichi Nakamura, Shin'Ichi Satoh

Auto-TLDR; A Siamese-Structure Deep Neural Network for Happiness Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Activity Recognition Using First-Person-View Cameras Based on Sparse Optical Flows
Peng-Yuan Kao, Yan-Jing Lei, Chia-Hao Chang, Chu-Song Chen, Ming-Sui Lee, Yi-Ping Hung

Auto-TLDR; 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Activity Recognition with FPV Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real-Time Drone Detection and Tracking with Visible, Thermal and Acoustic Sensors
Fredrik Svanström, Cristofer Englund, Fernando Alonso-Fernandez

Auto-TLDR; Automatic multi-sensor drone detection using sensor fusion
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Complex-Object Visual Inspection: Empirical Studies on a Multiple Lighting Solution
Maya Aghaei, Matteo Bustreo, Pietro Morerio, Nicolò Carissimi, Alessio Del Bue, Vittorio Murino

Auto-TLDR; A Novel Illumination Setup for Automatic Visual Inspection of Complex Objects
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tracking Fast Moving Objects by Segmentation Network

Auto-TLDR; Fast Moving Objects Tracking by Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Precise Temporal Action Localization with Quantified Temporal Structure of Actions
Chongkai Lu, Ruimin Li, Hong Fu, Bin Fu, Yihao Wang, Wai Lun Lo, Zheru Chi

Auto-TLDR; Action progression networks for temporal action detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Two-Stream Recurrent Network for Skeleton-Based Human Interaction Recognition
Qianhui Men, Edmond S. L. Ho, Shum Hubert P. H., Howard Leung

Auto-TLDR; Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Network for Human-Human Interaction Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar