On the Impact of Lossy Image and Video Compression on the Performance of Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architectures
Matt Poyser,
Toby Breckon,
Amir Atapour-Abarghouei
Auto-TLDR; The Impact of Lossy Image Compression on Deep Neural Networks for Image-based Detection and Classification
Similar papers
Object Detection in the DCT Domain: Is Luminance the Solution?
Benjamin Deguerre, Clement Chatelain, Gilles Gasso

Auto-TLDR; Jpeg Deep: Object Detection Using Compressed JPEG Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Adaptive Image Compression Using GAN Based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Ruojing Wang, Zitang Sun, Sei-Ichiro Kamata, Weili Chen
Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Image Compression using GAN based Semantic-Perceptual Residual Compensation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A NoGAN Approach for Image and Video Restoration and Compression Artifact Removal
Mameli Filippo, Marco Bertini, Leonardo Galteri, Alberto Del Bimbo

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Network for Image and Video Compression Artifact Removal and Restoration
Real-Time Monocular Depth Estimation with Extremely Light-Weight Neural Network
Mian Jhong Chiu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Hua-Tsung Chen, Jen-Hui Chuang
Auto-TLDR; Real-Time Light-Weight Depth Prediction for Obstacle Avoidance and Environment Sensing with Deep Learning-based CNN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
StrongPose: Bottom-up and Strong Keypoint Heat Map Based Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; StrongPose: A bottom-up box-free approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Fine-Grained Dataset and Its Efficient Semantic Segmentation for Unstructured Driving Scenarios
Kai Andreas Metzger, Peter Mortimer, Hans J "Joe" Wuensche

Auto-TLDR; TAS500: A Semantic Segmentation Dataset for Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
On the Use of Benford's Law to Detect GAN-Generated Images
Nicolo Bonettini, Paolo Bestagini, Simone Milani, Stefano Tubaro

Auto-TLDR; Using Benford's Law to Detect GAN-generated Images from Natural Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Real Time Fencing Move Classification and Detection at Touch Time During a Fencing Match
Cem Ekin Sunal, Chris G. Willcocks, Boguslaw Obara

Auto-TLDR; Fencing Body Move Classification and Detection Using Deep Learning
Boosting High-Level Vision with Joint Compression Artifacts Reduction and Super-Resolution
Xiaoyu Xiang, Qian Lin, Jan Allebach
Auto-TLDR; A Context-Aware Joint CAR and SR Neural Network for High-Resolution Text Recognition and Face Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MedZip: 3D Medical Images Lossless Compressor Using Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM)
Omniah Nagoor, Joss Whittle, Jingjing Deng, Benjamin Mora, Mark W. Jones

Auto-TLDR; Recurrent Neural Network for Lossless Medical Image Compression using Long Short-Term Memory
3D Attention Mechanism for Fine-Grained Classification of Table Tennis Strokes Using a Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Pierre-Etienne Martin, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Renaud Péteri, Julien Morlier

Auto-TLDR; Attentional Blocks for Action Recognition in Table Tennis Strokes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Towards Practical Compressed Video Action Recognition: A Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network
Bing Li, Longteng Kong, Dongming Zhang, Xiuguo Bao, Di Huang, Yunhong Wang

Auto-TLDR; TEMSN: Temporal Enhanced Multi-Stream Network for Compressed Video Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
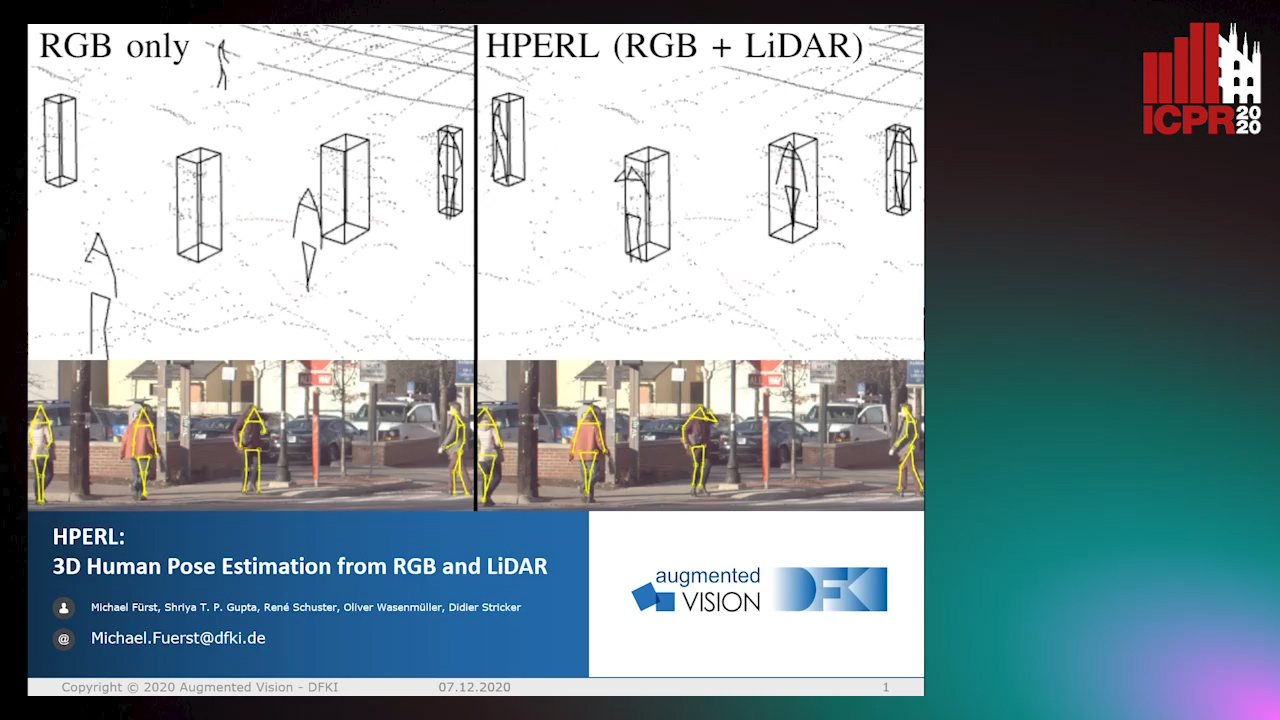
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Motion Complementary Network for Efficient Action Recognition
Ke Cheng, Yifan Zhang, Chenghua Li, Jian Cheng, Hanqing Lu

Auto-TLDR; Efficient Motion Complementary Network for Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Oriented Action Recognition for Real-Time Human-Robot Interaction
Ziyang Song, Ziyi Yin, Zejian Yuan, Chong Zhang, Wanchao Chi, Yonggen Ling, Shenghao Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-Oriented Multi-Level Network for Action Recognition in Interaction Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Modeling Long-Term Interactions to Enhance Action Recognition
Alejandro Cartas, Petia Radeva, Mariella Dimiccoli

Auto-TLDR; A Hierarchical Long Short-Term Memory Network for Action Recognition in Egocentric Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
TinyVIRAT: Low-Resolution Video Action Recognition
Ugur Demir, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; TinyVIRAT: A Progressive Generative Approach for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection on Monocular Images with Two-Dimensional Canonical Correlation Analysis

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Task Object Detection from Monocular Images Using Multimodal RGB and Depth Data
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Light3DPose: Real-Time Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation from Multiple Views
Alessio Elmi, Davide Mazzini, Pietro Tortella

Auto-TLDR; 3D Pose Estimation of Multiple People from a Few calibrated Camera Views using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Role of Cycle Consistency for Generating Better Human Action Videos from a Single Frame

Auto-TLDR; Generating Videos with Human Action Semantics using Cycle Constraints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Manipulated Facial Videos: A Time Series Solution
Zhang Zhewei, Ma Can, Gao Meilin, Ding Bowen
Auto-TLDR; Face-Alignment Based Bi-LSTM for Fake Video Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Neural Compression and Filtering for Edge-assisted Real-time Object Detection in Challenged Networks
Yoshitomo Matsubara, Marco Levorato

Auto-TLDR; Deep Neural Networks for Remote Object Detection Using Edge Computing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Estimation of Abundance and Distribution of SaltMarsh Plants from Images Using Deep Learning
Jayant Parashar, Suchendra Bhandarkar, Jacob Simon, Brian Hopkinson, Steven Pennings
Auto-TLDR; CNN-based approaches to automated plant identification and localization in salt marsh images
Weight Estimation from an RGB-D Camera in Top-View Configuration
Marco Mameli, Marina Paolanti, Nicola Conci, Filippo Tessaro, Emanuele Frontoni, Primo Zingaretti

Auto-TLDR; Top-View Weight Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Automatic Semantic Segmentation of Structural Elements related to the Spinal Cord in the Lumbar Region by Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Jhon Jairo Sáenz Gamboa, Maria De La Iglesia-Vaya, Jon Ander Gómez

Auto-TLDR; Semantic Segmentation of Lumbar Spine Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PSDNet: A Balanced Architecture of Accuracy and Parameters for Semantic Segmentation

Auto-TLDR; Pyramid Pooling Module with SE1Cblock and D2SUpsample Network (PSDNet)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Computational Data Analysis for First Quantization Estimation on JPEG Double Compressed Images
Sebastiano Battiato, Oliver Giudice, Francesco Guarnera, Giovanni Puglisi

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Discrete Cosine Transform Coefficients for Multimedia Forensics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Delivering Meaningful Representation for Monocular Depth Estimation
Doyeon Kim, Donggyu Joo, Junmo Kim

Auto-TLDR; Monocular Depth Estimation by Bridging the Context between Encoding and Decoding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
2D Deep Video Capsule Network with Temporal Shift for Action Recognition
Théo Voillemin, Hazem Wannous, Jean-Philippe Vandeborre

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Shift Module over Capsule Network for Action Recognition in Continuous Videos
Fast and Accurate Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Dilated Asymmetric Convolutions
Leonel Rosas-Arias, Gibran Benitez-Garcia, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Keiji Yanai
Auto-TLDR; FASSD-Net: Dilated Asymmetric Pyramidal Fusion for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Partially Supervised Multi-Task Network for Single-View Dietary Assessment
Ya Lu, Thomai Stathopoulou, Stavroula Mougiakakou
Auto-TLDR; Food Volume Estimation from a Single Food Image via Geometric Understanding and Semantic Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Future Urban Scenes Generation through Vehicles Synthesis
Alessandro Simoni, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Simone Calderara, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Predicting the Future of an Urban Scene with a Novel View Synthesis Paradigm
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Late Fusion of Bayesian and Convolutional Models for Action Recognition
Camille Maurice, Francisco Madrigal, Frederic Lerasle

Auto-TLDR; Fusion of Deep Neural Network and Bayesian-based Approach for Temporal Action Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Single View Learning in Action Recognition
Gaurvi Goyal, Nicoletta Noceti, Francesca Odone

Auto-TLDR; Cross-View Action Recognition Using Domain Adaptation for Knowledge Transfer
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Better Prior Knowledge Improves Human-Pose-Based Extrinsic Camera Calibration
Olivier Moliner, Sangxia Huang, Kalle Åström

Auto-TLDR; Improving Human-pose-based Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-Camera Systems
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Gabriella: An Online System for Real-Time Activity Detection in Untrimmed Security Videos
Mamshad Nayeem Rizve, Ugur Demir, Praveen Praveen Tirupattur, Aayush Jung Rana, Kevin Duarte, Ishan Rajendrakumar Dave, Yogesh Rawat, Mubarak Shah

Auto-TLDR; Gabriella: A Real-Time Online System for Activity Detection in Surveillance Videos
Motion U-Net: Multi-Cue Encoder-Decoder Network for Motion Segmentation
Gani Rahmon, Filiz Bunyak, Kannappan Palaniappan
Auto-TLDR; Motion U-Net: A Deep Learning Framework for Robust Moving Object Detection under Challenging Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Driven Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Swagat Kumar, Marry O'Brien, Ardhendu Behera

Auto-TLDR; Attention-based Body Pose Encoding for Human Activity Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Early Wildfire Smoke Detection in Videos
Taanya Gupta, Hengyue Liu, Bir Bhanu

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Spatio-Temporal Video Object Segmentation for Automatic Detection of Smoke in Videos during Forest Fire
Multi-Scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Jing Liu, Xiaona Zhang, Zhaoxin Li, Tianlu Mao
Auto-TLDR; Multi-scale Residual Pyramid Attention Network for Monocular Depth Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tilting at Windmills: Data Augmentation for Deeppose Estimation Does Not Help with Occlusions
Rafal Pytel, Osman Semih Kayhan, Jan Van Gemert

Auto-TLDR; Targeted Keypoint and Body Part Occlusion Attacks for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
RWF-2000: An Open Large Scale Video Database for Violence Detection
Ming Cheng, Kunjing Cai, Ming Li

Auto-TLDR; Flow Gated Network for Violence Detection in Surveillance Cameras
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Robotic Grasping on Monocular Images Via Multi-Task Learning and Positional Loss
William Prew, Toby Breckon, Magnus Bordewich, Ulrik Beierholm
Auto-TLDR; Improving grasping performance from monocularcolour images in an end-to-end CNN architecture with multi-task learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Ordinal Depth Classification Using Region-Based Self-Attention
Minh Hieu Phan, Son Lam Phung, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum

Auto-TLDR; Region-based Self-Attention for Multi-scale Depth Estimation from a Single 2D Image
Abstract Slides Poster Similar