Simple Multi-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation
Trung Tran Quang,
Van Giang Nguyen,
Daeyoung Kim

Auto-TLDR; Multi-resolution Heatmap Learning for Human Pose Estimation
Similar papers
StrongPose: Bottom-up and Strong Keypoint Heat Map Based Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; StrongPose: A bottom-up box-free approach for human pose estimation and action recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
P2 Net: Augmented Parallel-Pyramid Net for Attention Guided Pose Estimation
Luanxuan Hou, Jie Cao, Yuan Zhao, Haifeng Shen, Jian Tang, Ran He

Auto-TLDR; Parallel-Pyramid Net with Partial Attention for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient High-Resolution High-Level-Semantic Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation

Auto-TLDR; Spatial enhanced separated temporal spatial convolutional neural network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient Grouping for Keypoint Detection
Alexey Sidnev, Ekaterina Krasikova, Maxim Kazakov
Auto-TLDR; Automatic Keypoint Grouping for DeepFashion2 Dataset
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tilting at Windmills: Data Augmentation for Deeppose Estimation Does Not Help with Occlusions
Rafal Pytel, Osman Semih Kayhan, Jan Van Gemert

Auto-TLDR; Targeted Keypoint and Body Part Occlusion Attacks for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Light3DPose: Real-Time Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation from Multiple Views
Alessio Elmi, Davide Mazzini, Pietro Tortella

Auto-TLDR; 3D Pose Estimation of Multiple People from a Few calibrated Camera Views using Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
HPERL: 3D Human Pose Estimastion from RGB and LiDAR
Michael Fürst, Shriya T.P. Gupta, René Schuster, Oliver Wasenmüler, Didier Stricker
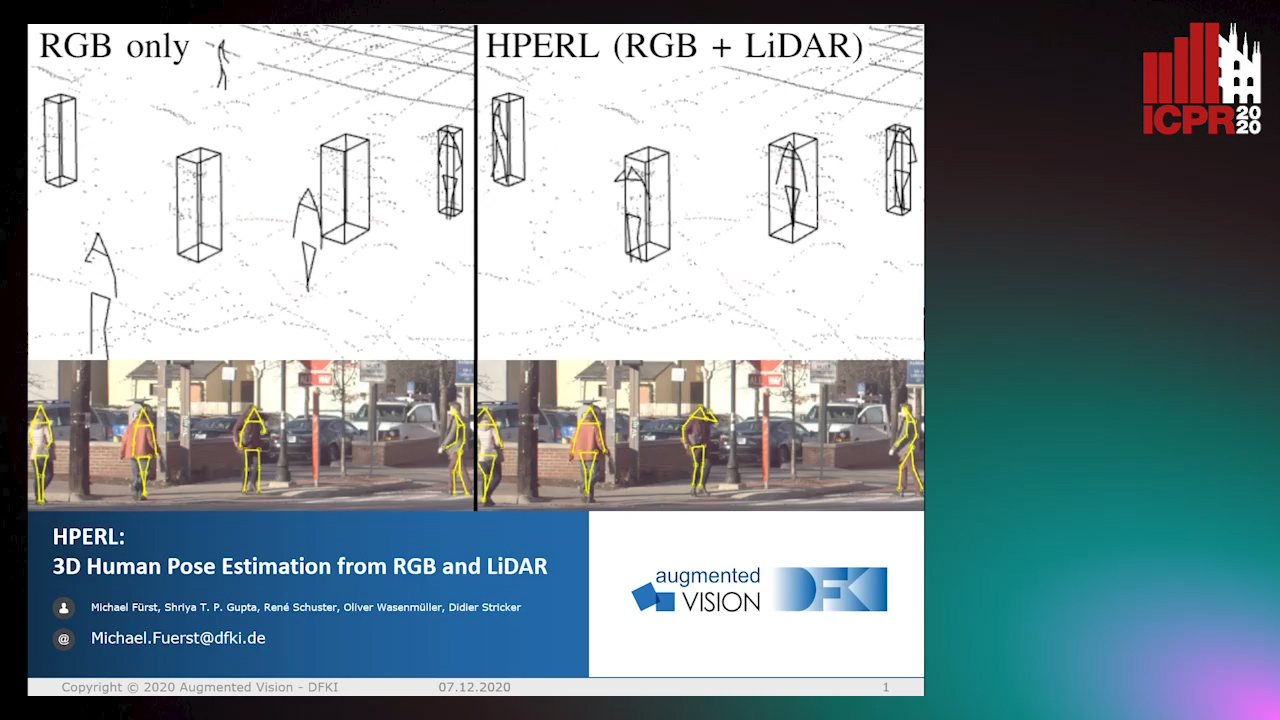
Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation Using RGB and LiDAR Using Weakly-Supervised Approach
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Small Object Detection by Generative and Discriminative Learning
Yi Gu, Jie Li, Chentao Wu, Weijia Jia, Jianping Chen

Auto-TLDR; Generative and Discriminative Learning for Small Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; BMFPN: Bidirectional Matrix Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SyNet: An Ensemble Network for Object Detection in UAV Images
Auto-TLDR; SyNet: Combining Multi-Stage and Single-Stage Object Detection for Aerial Images
Exploring Severe Occlusion: Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation with Gated Convolution
Renshu Gu, Gaoang Wang, Jenq-Neng Hwang

Auto-TLDR; 3D Human Pose Estimation for Multi-Human Videos with Occlusion
RefiNet: 3D Human Pose Refinement with Depth Maps
Andrea D'Eusanio, Stefano Pini, Guido Borghi, Roberto Vezzani, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; RefiNet: A Multi-stage Framework for 3D Human Pose Estimation
SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection

Auto-TLDR; SFPN: Semantic Feature Pyramid Network to Address Information Dilution Issue in FPN
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PEAN: 3D Hand Pose Estimation Adversarial Network
Linhui Sun, Yifan Zhang, Jing Lu, Jian Cheng, Hanqing Lu

Auto-TLDR; PEAN: 3D Hand Pose Estimation with Adversarial Learning Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Orthographic Projection Linear Regression for Single Image 3D Human Pose Estimation
Yahui Zhang, Shaodi You, Theo Gevers

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Neural Network for 3D Human Pose Estimation from a Single 2D Image in the Wild
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation
Leonardo Rossi, Akbar Karimi, Andrea Prati

Auto-TLDR; Generic RoI Extractor for Two-Stage Neural Network for Instance Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CenterRepp: Predict Central Representative Point Set's Distribution for Detection
Yulin He, Limeng Zhang, Wei Chen, Xin Luo, Chen Li, Xiaogang Jia

Auto-TLDR; CRPDet: CenterRepp Detector for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hybrid Cascade Point Search Network for High Precision Bar Chart Component Detection
Junyu Luo, Jinpeng Wang, Chin-Yew Lin
Auto-TLDR; Object Detection of Chart Components in Chart Images Using Point-based and Region-Based Object Detection Framework
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning a Dynamic High-Resolution Network for Multi-Scale Pedestrian Detection
Mengyuan Ding, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang

Auto-TLDR; Learningable Dynamic HRNet for Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Efficient-Receptive Field Block with Group Spatial Attention Mechanism for Object Detection
Jiacheng Zhang, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; E-RFB: Efficient-Receptive Field Block for Deep Neural Network for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Detecting Objects with High Object Region Percentage
Fen Fang, Qianli Xu, Liyuan Li, Ying Gu, Joo-Hwee Lim
Auto-TLDR; Faster R-CNN for High-ORP Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Object Detection Model Based on Scene-Level Region Proposal Self-Attention
Yu Quan, Zhixin Li, Canlong Zhang, Huifang Ma

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Semantic Informations for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Forground-Guided Vehicle Perception Framework
Kun Tian, Tong Zhou, Shiming Xiang, Chunhong Pan

Auto-TLDR; A foreground segmentation branch for vehicle detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Unsupervised 3D Human Pose Estimation in Multi-view-multi-pose Video
Cheng Sun, Diego Thomas, Hiroshi Kawasaki

Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised 3D Human Pose Estimation from 2D Videos Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Superpixel-Based Refinement for Object Proposal Generation
Christian Wilms, Simone Frintrop

Auto-TLDR; Superpixel-based Refinement of AttentionMask for Object Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Construction Worker Hardhat-Wearing Detection Based on an Improved BiFPN
Chenyang Zhang, Zhiqiang Tian, Jingyi Song, Yaoyue Zheng, Bo Xu

Auto-TLDR; A One-Stage Object Detection Method for Hardhat-Wearing in Construction Site
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Human-Centric Parsing Network for Human-Object Interaction Detection
Guanyu Chen, Chong Chen, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su

Auto-TLDR; Human-Centric Parsing Network for Human-Object Interactions Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Face Super-Resolution Network with Incremental Enhancement of Facial Parsing Information
Shuang Liu, Chengyi Xiong, Zhirong Gao

Auto-TLDR; Learning-based Face Super-Resolution with Incremental Boosting Facial Parsing Information
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Multi-Task Neural Network for Action Recognition with 3D Key-Points
Rongxiao Tang, Wang Luyang, Zhenhua Guo

Auto-TLDR; Multi-task Neural Network for Action Recognition and 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CASNet: Common Attribute Support Network for Image Instance and Panoptic Segmentation
Xiaolong Liu, Yuqing Hou, Anbang Yao, Yurong Chen, Keqiang Li

Auto-TLDR; Common Attribute Support Network for instance segmentation and panoptic segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jinwang Wang, Wen Yang, Haowen Guo, Ruixiang Zhang, Gui-Song Xia

Auto-TLDR; Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images Using Multiple Center Points Based Learning Network
ScarfNet: Multi-Scale Features with Deeply Fused and Redistributed Semantics for Enhanced Object Detection
Jin Hyeok Yoo, Dongsuk Kum, Jun Won Choi
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Fusion of Multi-scale Feature Maps for Object Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Grid-Based Representation for Human Action Recognition
Soufiane Lamghari, Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau, Nicolas Saunier

Auto-TLDR; GRAR: Grid-based Representation for Action Recognition in Videos
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention-Oriented Action Recognition for Real-Time Human-Robot Interaction
Ziyang Song, Ziyi Yin, Zejian Yuan, Chong Zhang, Wanchao Chi, Yonggen Ling, Shenghao Zhang

Auto-TLDR; Attention-Oriented Multi-Level Network for Action Recognition in Interaction Scenes
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
End-To-End Hierarchical Relation Extraction for Generic Form Understanding
Tuan Anh Nguyen Dang, Duc-Thanh Hoang, Quang Bach Tran, Chih-Wei Pan, Thanh-Dat Nguyen

Auto-TLDR; Joint Entity Labeling and Link Prediction for Form Understanding in Noisy Scanned Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GSTO: Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Multi-Scale Feature Learning in Semantic Segmentation
Zhuoying Wang, Yongtao Wang, Zhi Tang, Yangyan Li, Ying Chen, Haibin Ling, Weisi Lin

Auto-TLDR; Gated Scale-Transfer Operation for Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Shape Consistent 2D Keypoint Estimation under Domain Shift
Levi Vasconcelos, Massimiliano Mancini, Davide Boscaini, Barbara Caputo, Elisa Ricci

Auto-TLDR; Deep Adaptation for Keypoint Prediction under Domain Shift
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Weakly Supervised Body Part Segmentation with Pose Based Part Priors
Zhengyuan Yang, Yuncheng Li, Linjie Yang, Ning Zhang, Jiebo Luo
Auto-TLDR; Weakly Supervised Body Part Segmentation Using Weak Labels
What and How? Jointly Forecasting Human Action and Pose
Yanjun Zhu, Yanxia Zhang, Qiong Liu, Andreas Girgensohn

Auto-TLDR; Forecasting Human Actions and Motion Trajectories with Joint Action Classification and Pose Regression
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MagnifierNet: Learning Efficient Small-Scale Pedestrian Detector towards Multiple Dense Regions
Qi Cheng, Mingqin Chen, Yingjie Wu, Fei Chen, Shiping Lin

Auto-TLDR; MagnifierNet: A Simple but Effective Small-Scale Pedestrian Detection Towards Multiple Dense Regions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FastSal: A Computationally Efficient Network for Visual Saliency Prediction

Auto-TLDR; MobileNetV2: A Convolutional Neural Network for Saliency Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
FourierNet: Compact Mask Representation for Instance Segmentation Using Differentiable Shape Decoders
Hamd Ul Moqeet Riaz, Nuri Benbarka, Andreas Zell

Auto-TLDR; FourierNet: A Single shot, anchor-free, fully convolutional instance segmentation method that predicts a shape vector
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
JUMPS: Joints Upsampling Method for Pose Sequences
Lucas Mourot, Francois Le Clerc, Cédric Thébault, Pierre Hellier

Auto-TLDR; JUMPS: Increasing the Number of Joints in 2D Pose Estimation and Recovering Occluded or Missing Joints
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
LFIR2Pose: Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution FIR Image Sequence
Saki Iwata, Yasutomo Kawanishi, Daisuke Deguchi, Ichiro Ide, Hiroshi Murase, Tomoyoshi Aizawa
Auto-TLDR; LFIR2Pose: Human Pose Estimation from a Low-Resolution Far-InfraRed Image Sequence
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
DualBox: Generating BBox Pair with Strong Correspondence Via Occlusion Pattern Clustering and Proposal Refinement
Zheng Ge, Chuyu Hu, Xin Huang, Baiqiao Qiu, Osamu Yoshie

Auto-TLDR; R2NMS: Combining Full and Visible Body Bounding Box for Dense Pedestrian Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Auto-TLDR; A Mutual-Supervised Feature Modulation Network for Occluded Pedestrian Detection
Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Moshiur R Farazi, Salman Hameed Khan, Nick Barnes

Auto-TLDR; Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
The Color Out of Space: Learning Self-Supervised Representations for Earth Observation Imagery
Stefano Vincenzi, Angelo Porrello, Pietro Buzzega, Marco Cipriano, Pietro Fronte, Roberto Cuccu, Carla Ippoliti, Annamaria Conte, Simone Calderara

Auto-TLDR; Satellite Image Representation Learning for Remote Sensing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar