Initialization Using Perlin Noise for Training Networks with a Limited Amount of Data
Nakamasa Inoue,
Eisuke Yamagata,
Hirokatsu Kataoka

Auto-TLDR; Network Initialization Using Perlin Noise for Image Classification
Similar papers
Rethinking of Deep Models Parameters with Respect to Data Distribution
Shitala Prasad, Dongyun Lin, Yiqun Li, Sheng Dong, Zaw Min Oo

Auto-TLDR; A progressive stepwise training strategy for deep neural networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
WeightAlign: Normalizing Activations by Weight Alignment
Xiangwei Shi, Yunqiang Li, Xin Liu, Jan Van Gemert

Auto-TLDR; WeightAlign: Normalization of Activations without Sample Statistics
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improved Residual Networks for Image and Video Recognition
Ionut Cosmin Duta, Li Liu, Fan Zhu, Ling Shao
Auto-TLDR; Residual Networks for Deep Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Bridging the Gap between Natural and Medical Images through Deep Colorization
Lia Morra, Luca Piano, Fabrizio Lamberti, Tatiana Tommasi

Auto-TLDR; Transfer Learning for Diagnosis on X-ray Images Using Color Adaptation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Deep Clustering: Unsupervised Partitioning of Images

Auto-TLDR; Multi-Modal Deep Clustering for Unlabeled Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GuCNet: A Guided Clustering-Based Network for Improved Classification
Ushasi Chaudhuri, Syomantak Chaudhuri, Subhasis Chaudhuri
Auto-TLDR; Semantic Classification of Challenging Dataset Using Guide Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Image Representation Learning by Transformation Regression
Xifeng Guo, Jiyuan Liu, Sihang Zhou, En Zhu, Shihao Dong

Auto-TLDR; Self-supervised Image Representation Learning using Continuous Parameter Prediction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dynamic Multi-Path Neural Network
Yingcheng Su, Yichao Wu, Ken Chen, Ding Liang, Xiaolin Hu

Auto-TLDR; Dynamic Multi-path Neural Network
Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization When Learning from Small Sample
Auto-TLDR; GLICO: Generative Latent Implicit Conditional Optimization for Small Sample Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Norm Loss: An Efficient yet Effective Regularization Method for Deep Neural Networks
Theodoros Georgiou, Sebastian Schmitt, Thomas Baeck, Wei Chen, Michael Lew

Auto-TLDR; Weight Soft-Regularization with Oblique Manifold for Convolutional Neural Network Training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving reliability of attention branch network by introducing uncertainty
Takuya Tsukahara, Tsubasa Hirakawa, Takayoshi Yamashita, Hironobu Fujiyoshi

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Attention Branch Network for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Recognizing Bengali Word Images - A Zero-Shot Learning Perspective
Sukalpa Chanda, Daniël Arjen Willem Haitink, Prashant Kumar Prasad, Jochem Baas, Umapada Pal, Lambert Schomaker
Auto-TLDR; Zero-Shot Learning for Word Recognition in Bengali Script
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data

Auto-TLDR; Low-Complex Neural Networks for Small Data Conditions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Improving Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction for Deep Neural Networks
Pak Lun Kevin Ding, Martin Sarah, Baoxin Li
Auto-TLDR; Batch Normalization with Skewness Reduction
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
MetaMix: Improved Meta-Learning with Interpolation-based Consistency Regularization
Yangbin Chen, Yun Ma, Tom Ko, Jianping Wang, Qing Li

Auto-TLDR; MetaMix: A Meta-Agnostic Meta-Learning Algorithm for Few-Shot Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enhancing Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with Inhibitory Neurons
Ihsan Ullah, Sean Reilly, Michael Madden

Auto-TLDR; Lateral Inhibition in Deep Neural Networks for Object Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CQNN: Convolutional Quadratic Neural Networks

Auto-TLDR; Quadratic Neural Network for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Stage-Wise Neural Architecture Search
Artur Jordão, Fernando Akio Yamada, Maiko Lie, William Schwartz

Auto-TLDR; Efficient Neural Architecture Search for Deep Convolutional Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Few-Shot Few-Shot Learning and the Role of Spatial Attention
Yann Lifchitz, Yannis Avrithis, Sylvaine Picard

Auto-TLDR; Few-shot Learning with Pre-trained Classifier on Large-Scale Datasets
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
How Does DCNN Make Decisions?
Yi Lin, Namin Wang, Xiaoqing Ma, Ziwei Li, Gang Bai

Auto-TLDR; Exploring Deep Convolutional Neural Network's Decision-Making Interpretability
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
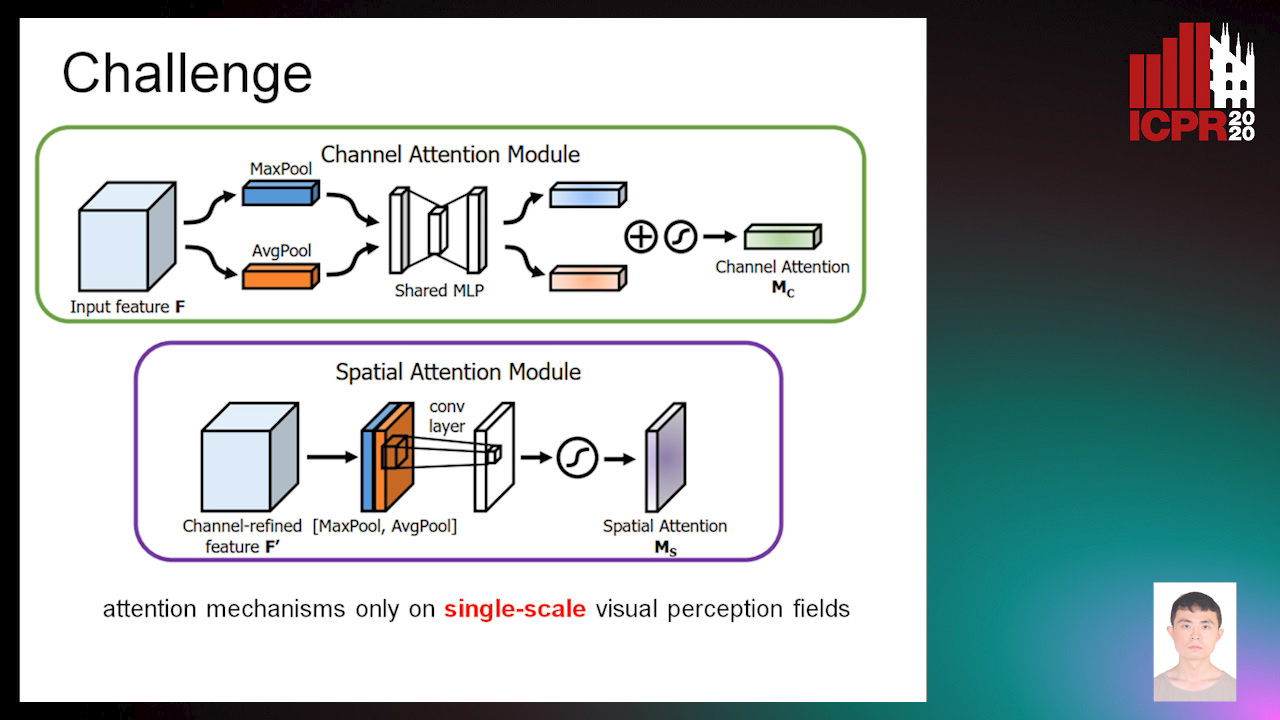
Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Residual Module for Image Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Layered Discriminative Restricted Boltzmann Machine with Untrained Probabilistic Layer

Auto-TLDR; MDRBM: A Probabilistic Four-layered Neural Network for Extreme Learning Machine
Contextual Classification Using Self-Supervised Auxiliary Models for Deep Neural Networks
Sebastian Palacio, Philipp Engler, Jörn Hees, Andreas Dengel

Auto-TLDR; Self-Supervised Autogenous Learning for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Self-Supervised Learning for Astronomical Image Classification
Ana Martinazzo, Mateus Espadoto, Nina S. T. Hirata

Auto-TLDR; Unlabeled Astronomical Images for Deep Neural Network Pre-training
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Overcoming Noisy and Irrelevant Data in Federated Learning
Tiffany Tuor, Shiqiang Wang, Bong Jun Ko, Changchang Liu, Kin K Leung

Auto-TLDR; Distributedly Selecting Relevant Data for Federated Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Hcore-Init: Neural Network Initialization Based on Graph Degeneracy
Stratis Limnios, George Dasoulas, Dimitrios Thilikos, Michalis Vazirgiannis
Auto-TLDR; K-hypercore: Graph Mining for Deep Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Trainable Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Michele Alberti, Angela Botros, Schuetz Narayan, Rolf Ingold, Marcus Liwicki, Mathias Seuret

Auto-TLDR; Trainable and Spectrally Initializable Matrix Transformations for Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Fine-Tuning DARTS for Image Classification
Muhammad Suhaib Tanveer, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung
Auto-TLDR; Fine-Tune Neural Architecture Search using Fixed Operations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attention Pyramid Module for Scene Recognition
Zhinan Qiao, Xiaohui Yuan, Chengyuan Zhuang, Abolfazl Meyarian

Auto-TLDR; Attention Pyramid Module for Multi-Scale Scene Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploiting Knowledge Embedded Soft Labels for Image Recognition
Lixian Yuan, Riquan Chen, Hefeng Wu, Tianshui Chen, Wentao Wang, Pei Chen

Auto-TLDR; A Soft Label Vector for Image Recognition
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Region-Based Non-Local Operation for Video Classification

Auto-TLDR; Regional-based Non-Local Operation for Deep Self-Attention in Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Rethinking Deep Active Learning: Using Unlabeled Data at Model Training
Oriane Siméoni, Mateusz Budnik, Yannis Avrithis, Guillaume Gravier

Auto-TLDR; Unlabeled Data for Active Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multimodal Side-Tuning for Document Classification
Stefano Zingaro, Giuseppe Lisanti, Maurizio Gabbrielli

Auto-TLDR; Side-tuning for Multimodal Document Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Can Data Placement Be Effective for Neural Networks Classification Tasks? Introducing the Orthogonal Loss
Brais Cancela, Veronica Bolon-Canedo, Amparo Alonso-Betanzos

Auto-TLDR; Spatial Placement for Neural Network Training Loss Functions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Is the Meta-Learning Idea Able to Improve the Generalization of Deep Neural Networks on the Standard Supervised Learning?

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning Based Training of Deep Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Nearest Neighbor Classification Based on Activation Space of Convolutional Neural Network
Xinbo Ju, Shuo Shao, Huan Long, Weizhe Wang

Auto-TLDR; Convolutional Neural Network with Convex Hull Based Classifier
Generalization Comparison of Deep Neural Networks Via Output Sensitivity
Mahsa Forouzesh, Farnood Salehi, Patrick Thiran
Auto-TLDR; Generalization of Deep Neural Networks using Sensitivity
Towards Robust Learning with Different Label Noise Distributions
Diego Ortego, Eric Arazo, Paul Albert, Noel E O'Connor, Kevin Mcguinness

Auto-TLDR; Distribution Robust Pseudo-Labeling with Semi-supervised Learning
Complementing Representation Deficiency in Few-Shot Image Classification: A Meta-Learning Approach
Xian Zhong, Cheng Gu, Wenxin Huang, Lin Li, Shuqin Chen, Chia-Wen Lin

Auto-TLDR; Meta-learning with Complementary Representations Network for Few-Shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Systematic Investigation on End-To-End Deep Recognition of Grocery Products in the Wild
Marco Leo, Pierluigi Carcagni, Cosimo Distante

Auto-TLDR; Automatic Recognition of Products on grocery shelf images using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Revisiting the Training of Very Deep Neural Networks without Skip Connections
Oyebade Kayode Oyedotun, Abd El Rahman Shabayek, Djamila Aouada, Bjorn Ottersten

Auto-TLDR; Optimization of Very Deep PlainNets without shortcut connections with 'vanishing and exploding units' activations'
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Augmented Bi-Path Network for Few-Shot Learning
Baoming Yan, Chen Zhou, Bo Zhao, Kan Guo, Yang Jiang, Xiaobo Li, Zhang Ming, Yizhou Wang

Auto-TLDR; Augmented Bi-path Network for Few-shot Learning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Augmentation of Small Training Data Using GANs for Enhancing the Performance of Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Generative Adversarial Network for Image Training Data Augmentation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation Via Selective Pseudo Labeling and Progressive Self-Training

Auto-TLDR; Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation with Pseudo Labels
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Graph-Based Interpolation of Feature Vectors for Accurate Few-Shot Classification
Yuqing Hu, Vincent Gripon, Stéphane Pateux

Auto-TLDR; Transductive Learning for Few-Shot Classification using Graph Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Meta Generalized Network for Few-Shot Classification
Wei Wu, Shanmin Pang, Zhiqiang Tian, Yaochen Li

Auto-TLDR; Meta Generalized Network for Few-Shot Classification
The Color Out of Space: Learning Self-Supervised Representations for Earth Observation Imagery
Stefano Vincenzi, Angelo Porrello, Pietro Buzzega, Marco Cipriano, Pietro Fronte, Roberto Cuccu, Carla Ippoliti, Annamaria Conte, Simone Calderara

Auto-TLDR; Satellite Image Representation Learning for Remote Sensing
Abstract Slides Poster Similar