Enhanced User Interest and Expertise Modeling for Expert Recommendation
Tongze He,
Caili Guo,
Yunfei Chu

Auto-TLDR; A Unified Framework for Expert Recommendation in Community Question Answering
Similar papers
Integrating Historical States and Co-Attention Mechanism for Visual Dialog
Tianling Jiang, Yi Ji, Chunping Liu
Auto-TLDR; Integrating Historical States and Co-attention for Visual Dialog
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Dual Path Multi-Modal High-Order Features for Textual Content Based Visual Question Answering
Yanan Li, Yuetan Lin, Hongrui Zhao, Donghui Wang

Auto-TLDR; TextVQA: An End-to-End Visual Question Answering Model for Text-Based VQA
Multi-Stage Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Aakansha Mishra, Ashish Anand, Prithwijit Guha

Auto-TLDR; Alternative Bi-directional Attention for Visual Question Answering
Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Networks
Tao Sun, Yongjun Xu, Fei Wang, Lin Wu, 塘文 钱, Zezhi Shao

Auto-TLDR; TULAR: Trajectory-User Link with Attention Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Temporal Collaborative Filtering with Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
Esther Rodrigo-Bonet, Minh Duc Nguyen, Nikos Deligiannis

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Collaborative Filtering with Graph-Neural-Network-based Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Yaoyuan Liang, Xin Wang, Xuguang Duan, Wenwu Zhu

Auto-TLDR; Multi-modal Contextual Graph Neural Network for Text Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Probabilistic Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering with Bayesian Inference
Jiansheng Fang, Xiaoqing Zhang, Yan Hu, Yanwu Xu, Ming Yang, Jiang Liu

Auto-TLDR; Bayesian Latent Factor Model for Collaborative Filtering
An Intransitivity Model for Matchup and Pairwise Comparison
Yan Gu, Jiuding Duan, Hisashi Kashima

Auto-TLDR; Blade-Chest: A Low-Rank Matrix Approach for Probabilistic Ranking of Players
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PIN: A Novel Parallel Interactive Network for Spoken Language Understanding
Peilin Zhou, Zhiqi Huang, Fenglin Liu, Yuexian Zou

Auto-TLDR; Parallel Interactive Network for Spoken Language Understanding
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Ratio of Edge-User Estimation in Mobile Networks
Jiehui Deng, Sheng Wan, Xiang Wang, Enmei Tu, Xiaolin Huang, Jie Yang, Chen Gong

Auto-TLDR; EAGAT: Edge-Aware Graph Attention Network for Automatic REU Estimation in Mobile Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Constructing Geographic and Long-term Temporal Graph for Traffic Forecasting
Yiwen Sun, Yulu Wang, Kun Fu, Zheng Wang, Changshui Zhang, Jieping Ye

Auto-TLDR; GLT-GCRNN: Geographic and Long-term Temporal Graph Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network for Traffic Forecasting
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Graph Convolutional Network for Relationship-Driven Stock Movement Prediction
Jiexia Ye, Juanjuan Zhao, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; Multi-GCGRU: A Deep Learning Framework for Stock Price Prediction with Cross Effect
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A Novel Attention-Based Aggregation Function to Combine Vision and Language
Matteo Stefanini, Marcella Cornia, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

Auto-TLDR; Fully-Attentive Reduction for Vision and Language
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
GCNs-Based Context-Aware Short Text Similarity Model

Auto-TLDR; Context-Aware Graph Convolutional Network for Text Similarity
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PrivAttNet: Predicting Privacy Risks in Images Using Visual Attention
Chen Zhang, Thivya Kandappu, Vigneshwaran Subbaraju
Auto-TLDR; PrivAttNet: A Visual Attention Based Approach for Privacy Sensitivity in Images
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Label Incorporated Graph Neural Networks for Text Classification
Yuan Xin, Linli Xu, Junliang Guo, Jiquan Li, Xin Sheng, Yuanyuan Zhou
Auto-TLDR; Graph Neural Networks for Semi-supervised Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Webly Supervised Image-Text Embedding with Noisy Tag Refinement
Niluthpol Mithun, Ravdeep Pasricha, Evangelos Papalexakis, Amit Roy-Chowdhury
Auto-TLDR; Robust Joint Embedding for Image-Text Retrieval Using Web Images
MA-LSTM: A Multi-Attention Based LSTM for Complex Pattern Extraction
Jingjie Guo, Kelang Tian, Kejiang Ye, Cheng-Zhong Xu
Auto-TLDR; MA-LSTM: Multiple Attention based recurrent neural network for forget gate
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Moto: Enhancing Embedding with Multiple Joint Factors for Chinese Text Classification
Xunzhu Tang, Rujie Zhu, Tiezhu Sun

Auto-TLDR; Moto: Enhancing Embedding with Multiple J\textbf{o}int Fac\textBF{to}rs
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Cross-Supervised Joint-Event-Extraction with Heterogeneous Information Networks
Yue Wang, Zhuo Xu, Yao Wan, Lu Bai, Lixin Cui, Qian Zhao, Edwin Hancock, Philip Yu

Auto-TLDR; Joint-Event-extraction from Unstructured corpora using Structural Information Network
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Episode Boundary Detection with Joint Episode-Topic Model
Shunyao Wang, Ye Tian, Ruidong Wang, Yang Du, Han Yan, Ruilin Yang, Jian Ma
Auto-TLDR; Unsupervised Video Episode Boundary Detection for Bullet Screen Comment Video
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Multi-Scale Relational Reasoning with Regional Attention for Visual Question Answering

Auto-TLDR; Question-Guided Relational Reasoning for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Assessing the Severity of Health States Based on Social Media Posts
Shweta Yadav, Joy Prakash Sain, Amit Sheth, Asif Ekbal, Sriparna Saha, Pushpak Bhattacharyya

Auto-TLDR; A Multiview Learning Framework for Assessment of Health State in Online Health Communities
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Attentive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Jesus Perez-Martin, Benjamin Bustos, Jorge Pérez

Auto-TLDR; Adaptive Visual Semantic Specialized Network for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representations for fNIRS-based Intimacy Detection via an Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
Chao Li, Qian Zhang, Ziping Zhao

Auto-TLDR; Intimate Relationship Prediction by Attention-enhanced Cascade Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Style Extraction from Chart Images for Chart Restyling
Danqing Huang, Jinpeng Wang, Guoxin Wang, Chin-Yew Lin

Auto-TLDR; Exploiting Visual Properties from Reference Chart Images for Chart Restyling
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Learning Neural Textual Representations for Citation Recommendation
Thanh Binh Kieu, Inigo Jauregi Unanue, Son Bao Pham, Xuan-Hieu Phan, M. Piccardi

Auto-TLDR; Sentence-BERT cascaded with Siamese and triplet networks for citation recommendation
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Zero-Shot Text Classification with Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network
Tengfei Liu, Yongli Hu, Junbin Gao, Yanfeng Sun, Baocai Yin

Auto-TLDR; Semantically Extended Graph Convolutional Network for Zero-shot Text Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Road Network Metric Learning for Estimated Time of Arrival
Yiwen Sun, Kun Fu, Zheng Wang, Changshui Zhang, Jieping Ye

Auto-TLDR; Road Network Metric Learning for Estimated Time of Arrival (RNML-ETA)
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Transformer Networks for Trajectory Forecasting
Francesco Giuliari, Hasan Irtiza, Marco Cristani, Fabio Galasso

Auto-TLDR; TransformerNetworks for Trajectory Prediction of People Interactions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Region and Relations Based Multi Attention Network for Graph Classification
Manasvi Aggarwal, M. Narasimha Murty
Auto-TLDR; R2POOL: A Graph Pooling Layer for Non-euclidean Structures
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Visual Oriented Encoder: Integrating Multimodal and Multi-Scale Contexts for Video Captioning

Auto-TLDR; Visual Oriented Encoder for Video Captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Global Feature Aggregation for Accident Anticipation
Mishal Fatima, Umar Karim Khan, Chong Min Kyung

Auto-TLDR; Feature Aggregation for Predicting Accidents in Video Sequences
Context Visual Information-Based Deliberation Network for Video Captioning
Min Lu, Xueyong Li, Caihua Liu
Auto-TLDR; Context visual information-based deliberation network for video captioning
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Tackling Contradiction Detection in German Using Machine Translation and End-To-End Recurrent Neural Networks
Maren Pielka, Rafet Sifa, Lars Patrick Hillebrand, David Biesner, Rajkumar Ramamurthy, Anna Ladi, Christian Bauckhage

Auto-TLDR; Contradiction Detection in Natural Language Inference using Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
A CNN-RNN Framework for Image Annotation from Visual Cues and Social Network Metadata
Tobia Tesan, Pasquale Coscia, Lamberto Ballan

Auto-TLDR; Context-Based Image Annotation with Multiple Semantic Embeddings and Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Equation Attention Relationship Network (EARN) : A Geometric Deep Metric Framework for Learning Similar Math Expression Embedding
Saleem Ahmed, Kenny Davila, Srirangaraj Setlur, Venu Govindaraju

Auto-TLDR; Representational Learning for Similarity Based Retrieval of Mathematical Expressions
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
PICK: Processing Key Information Extraction from Documents Using Improved Graph Learning-Convolutional Networks
Wenwen Yu, Ning Lu, Xianbiao Qi, Ping Gong, Rong Xiao

Auto-TLDR; PICK: A Graph Learning Framework for Key Information Extraction from Documents
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
SAT-Net: Self-Attention and Temporal Fusion for Facial Action Unit Detection
Zhihua Li, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Yin

Auto-TLDR; Temporal Fusion and Self-Attention Network for Facial Action Unit Detection
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
More Correlations Better Performance: Fully Associative Networks for Multi-Label Image Classification

Auto-TLDR; Fully Associative Network for Fully Exploiting Correlation Information in Multi-Label Classification
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Enriching Video Captions with Contextual Text
Philipp Rimle, Pelin Dogan, Markus Gross
Auto-TLDR; Contextualized Video Captioning Using Contextual Text
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Answer-Checking in Context: A Multi-Modal Fully Attention Network for Visual Question Answering
Hantao Huang, Tao Han, Wei Han, Deep Yap Deep Yap, Cheng-Ming Chiang
Auto-TLDR; Fully Attention Based Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
AG-GAN: An Attentive Group-Aware GAN for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Yue Song, Niccolò Bisagno, Syed Zohaib Hassan, Nicola Conci
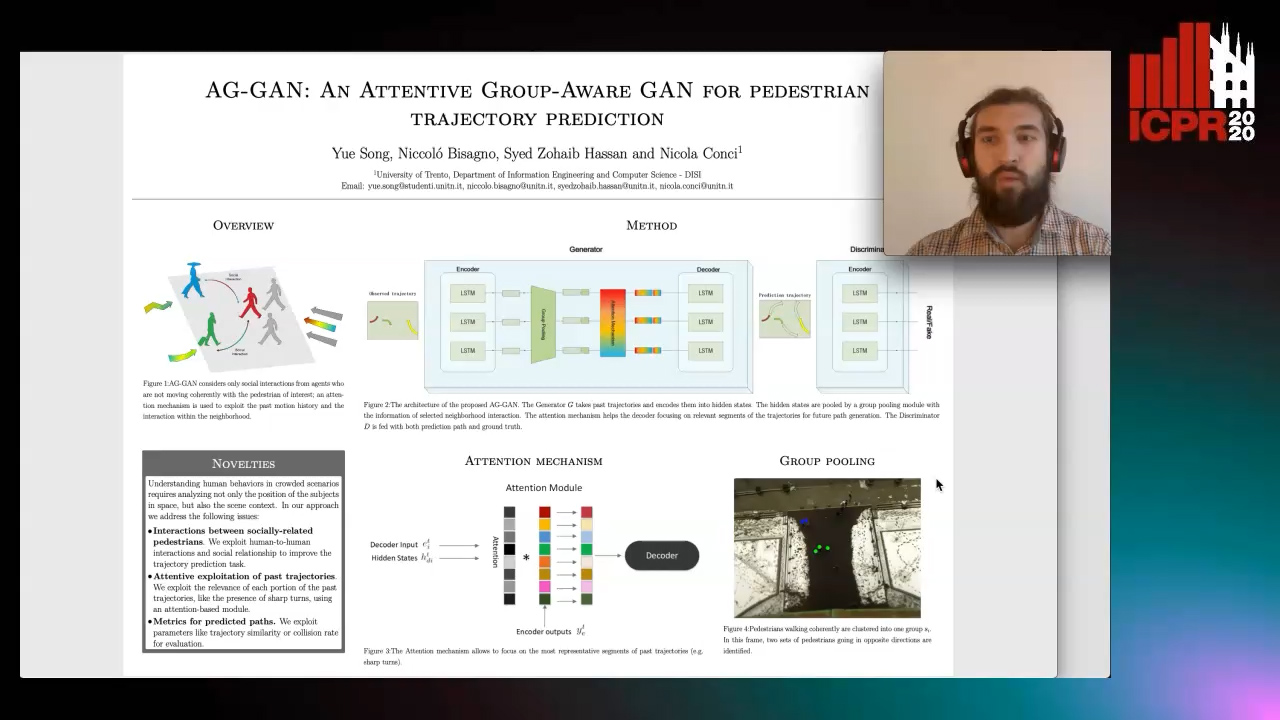
Auto-TLDR; An attentive group-aware GAN for motion prediction in crowded scenarios
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
CKG: Dynamic Representation Based on Context and Knowledge Graph
Xunzhu Tang, Tiezhu Sun, Rujie Zhu

Auto-TLDR; CKG: Dynamic Representation Based on Knowledge Graph for Language Sentences
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Moshiur R Farazi, Salman Hameed Khan, Nick Barnes

Auto-TLDR; Question-Agnostic Attention for Visual Question Answering
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Deep Convolutional Embedding for Digitized Painting Clustering
Giovanna Castellano, Gennaro Vessio

Auto-TLDR; A Deep Convolutional Embedding Model for Clustering Artworks
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Video Summarization with a Dual Attention Capsule Network
Hao Fu, Hongxing Wang, Jianyu Yang

Auto-TLDR; Dual Self-Attention Capsule Network for Video Summarization
Abstract Slides Poster Similar
Interpretable Structured Learning with Sparse Gated Sequence Encoder for Protein-Protein Interaction Prediction
Kishan K C, Feng Cui, Anne Haake, Rui Li

Auto-TLDR; Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions Using Sequence Representations
Abstract Slides Poster Similar